Contents:
The cyber security industry is growing as you’re reading this. More specialists join the ranks, more malware is being launched every day than ever before. In 2015, 230,000 new malware sample were recorded daily. Naturally, more resources are being deployed to counter cyber attacks. That’s why I thought it would be helpful to sum up 10 cyber security facts that define the current information security landscape.
Don’t think that hackers are only targeting corporations, banks or wealthy celebrities. They go for individual users like you and me also.
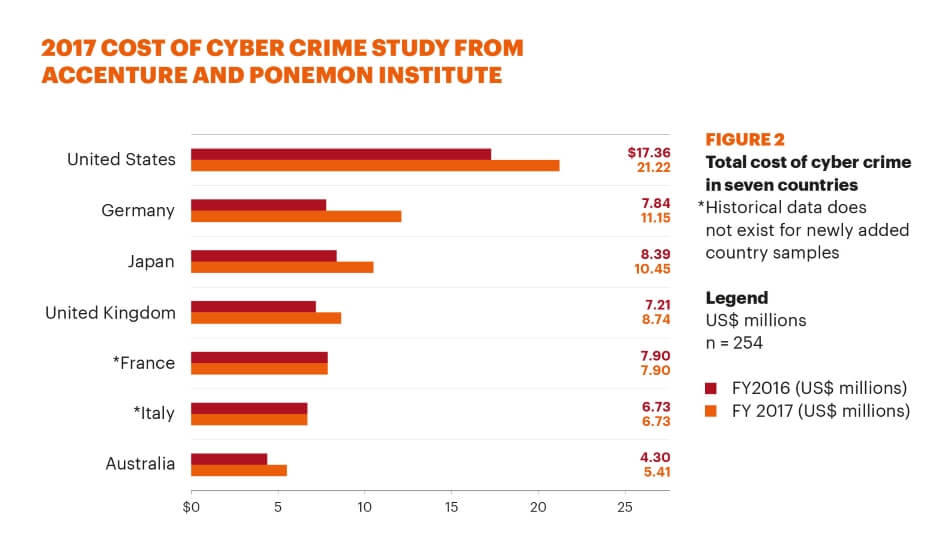
Source: 2017 Cost of Cyber Crime Study: Global by Accenture and Ponemon
As long as you’re connected to the Internet, you can become a victim of cyber attacks.
So that’s why we wanted to walk you through some of the most shocking cyber security facts that you maybe wish you’d known until the present moment.
These will give you a much more accurate idea of how dangerous it really is to go online without proper protection.
1.The most wanted cyber criminals in the world
In 2016, there were 19 individuals on FBI’s Most Wanted List for cyber criminals you. Each of them was responsible responsible for consumer losses ranging from $350,000 to more than $100 million. In 2018, that same list has 41 cybercriminals from around the world.

For example, on the list of FBI’s most wanted cyber criminals are the JABBERZEUS subjects, a group of individuals involved in a wide-ranging racketeering enterprise and scheme that installed, without authorization, malicious software known as Zeus on victims’ computers.
This type of financial malware was used to capture bank account numbers, passwords, personal identification numbers, and other confidential information necessary to log into online banking accounts.
[Tweet “Who are the most wanted cybercriminals in the world? Find out + 9 other cyber security facts.”]Starting in September of 2011, the FBI began investigating a modified version of the Zeus Trojan, known as GameOver Zeus (GOZ), which we covered in depth. Thousands of corporations were infected with GameOver Zeus and as many as 1.2 million computers were infected prior to the take down of Zeus. It is believed GameOver Zeus is responsible for financial losses of more than $100 million.
How it affects you and what can you do to get protected:
- Zero Day attacks can be powerful and very dangerous.
- If you keep up to date with major news in the cyber security industry, it might help you identify attacks and know what to do about them.
- Keep your software updated and take all necessary precautions to keep your financial and confidential information safe.
2. The most expensive computer virus of all times
Ever wondered how much damage a computer virus can do? Let us give you a compelling example through this next cyber security fact. MyDoom is considered to be the most expensive virus in the world and in cyber security history, having caused an estimated financial damage of $38.5 billion!
MyDoom was first spotted in January 2004 and it became the fastest-spreading email worm ever, exceeding all previous records. The virus’s origins are believed to be in Russia, but its author was never discovered.
[Tweet “The most expensive computer virus of all times cause damage worth $38.5 billion!”]Mydoom was mainly transmitted by email, disguised as spam email. A user might inadvertently open the attachment in the email and the worm would re-send itself to every address it could find. The original version contained a payload that did two things: it opened a backdoor into the user’s computer, allowing remote control of it, while also conducting a DDoS attack (Direct Denial Of Service) against SCO group’s website.

How it affects you and what can you do to get protected:
- Viruses such as MyDoom can be extremely dangerous, because if a cybercriminal gains control over your computer, there’s no telling if and how you may regain control over your device.
- Severe malware usually morphs and has a very low detection score, so antivirus solutions can’t detect it.
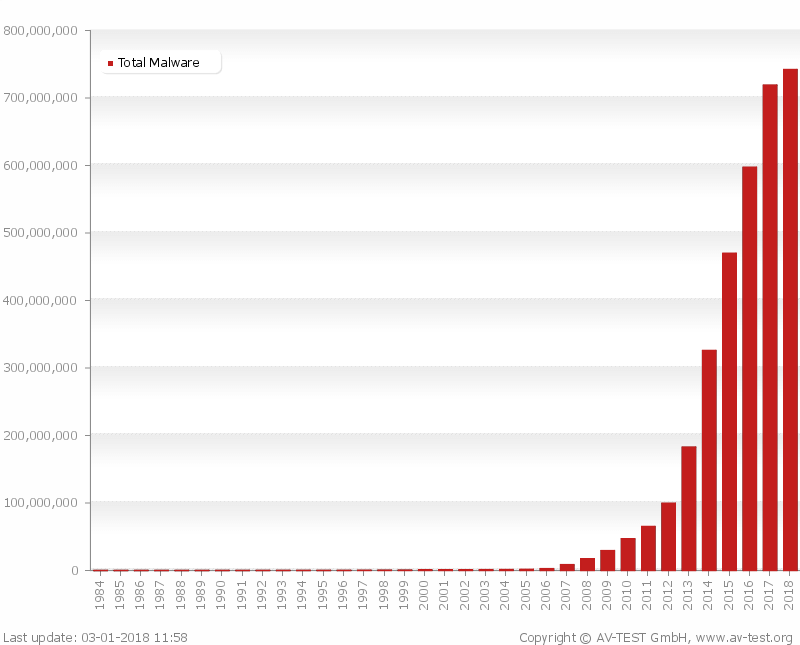
- You need a proactive solution that can work as a supplement for your AV, scanning your Internet traffic and warning you when potential threats appear, while also blocking access to hacker-controlled servers and keeping your data from leaking. We explained this in-depth here and, to put it in perspective, here is the volume of malware on a yearly basis.
3. Social media – a hackers’ favorite target
Currently, according to in-depth statistics, there are more than 3 billion active social network users worldwide.
[Tweet “Find out which kind of attacks hackers use most often in social media + 9 other infosec facts!”]This is precisely why cyber attackers love social media as well!
Users that spend a lot of time on social networks are very likely to click links posted by trusted friends, which hackers use to their advantage. After the entire Facebook and Cambridge Analytica data breach, the threat of using social media to sway elections and the pervasiveness of political of bots should make you pause.
Here are some of the most popular types of cyberattacks directed at social media platforms:
- Like-jacking: occurs when criminals post fake Facebook “like” buttons to webpages. Users who click the button don’t “like” the page, but instead download malware.
- Link-jacking: this is a practice used to redirect one website’s links to another which hackers use to redirect users from trusted websites to malware-infected websites that hide drive-by downloads or other types of infections.
- Phishing: the attempt to acquire sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details (and sometimes, indirectly, money) by disguising itself as a trustworthy entity in a Facebook message, Tweet or other social media message
- Social spam: is unwanted spam content appearing on social networks and any website with user-generated content (comments, chat, etc.). It can appear in many forms, including bulk messages, profanity, insults, hate speech, malicious links, fraudulent reviews, fake friends, and personally identifiable information.

Why are cyber attacks on social media so frequent?
Because social media users usually trust their circles of online friends. The result: more than 600.000 Facebook accounts are compromised every single day! Also, 1 in 10 social media users said they’ve been a victim of a cyber attack and the numbers are on the rise. Now, this is a cybersecurity statistic that we don’t want you to become part of.
How it affects you and what can you do to get protected:
- Don’t click any strange links.
- Educate yourself about how cyber attacks look and work on social media platforms and learn how to protect your Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter and Instagram accounts.
- Install a cybersecurity solution that can protect you against malware and dangerous web locations.
4. 99% of computers are vulnerable to exploit kits
Cybersecurity fact: Oracle Java, Adobe Reader or Adobe Flash is present on 99% of computers. That means that 99% of computer users are vulnerable to exploit kits (software vulnerabilities).
Why? Because the vulnerabilities that these types of software often present are extremely critical: all it takes is one click on an infected advertising banner to give a hacker full access to your computer.

Adobe Flash has a huge number of vulnerabilities, so cybercriminals target it in the majority of their attacks. By using these security holes in Flash, attackers can infect your computer with ransomware, such as various CryptoLocker variants or Teslacrypt and CTB-Locker.
[Tweet “99% of computers are vulnerable to cyber-attacks. Find out why and how to get protection.”]The rise of exploit kits-as-a-service and the increasing use of automation has led to more sophisticated and aggressive attacks. Without adequately protecting your browsers and your entire system, you’ll leave yourself vulnerable to a huge range of cyber threats.
How it affects you and what can you do to get protected:
- Keep your software updated at all times (the experts say so, not just us). The best way to do it, install a solution that updates the software automatically and silently.
- Keep your operating system up to date.
- Install an AV solution and a supplement that can do what AV fails to do: protect your system proactively from cyber threats by scanning incoming and outgoing Internet traffic.
5. Security warning: inside jobs
Maybe you’ll be surprised to find out that a shocking 59% of employees steal proprietary corporate data when they quit or are fired. But there are more types of insider threats to get protection against:
- Malicious insiders are the least frequent but have the potential to cause significant damage due to their level of access. Administrators with privileged identities are especially risky. According to the Ponemon Institute, “data breaches that result from malicious attacks are most costly.”
- Exploited insiders may be “tricked” by external parties into providing data or passwords they shouldn’t.
- Careless insiders
- Careless insiders may simply press the wrong key and accidentally delete or modify critical information. A badly configured Amazon S3 leaked the data of over 150.000 Americans.

These types of security risks is being acknowledged by companies everywhere, and strategies are put together to mitigate them:
“Almost half of European organizations believe that insider threats are now more difficult to detect, with senior IT managers being very worried about the things their own users can do with corporate data”
said Andrew Kellett, principal analyst at Ovum.
[Tweet “Did you know that 59% of employees steal proprietary corporate data when they quit or are fired?”]How it affects you and what can you do to get protected:
- If a soon-to-be-ex-colleague decides to do some damage before he/she leaves the company, make sure your work goes unaffected.
- Be careful how you manage your passwords: use a password management application, use strong passwords and change them regularly.
- Protect your shared documents and keep updated backups of all the information you’re working on.
6. Social engineering – cyber criminals’ favorite way to manipulate victims
People are the weakest link when it comes to cybersecurity, which is why psychological manipulation of cyber attack victims is so common.
According to the definition, social engineering, in the context of information security, refers to the psychological manipulation of people into performing actions or divulging confidential information. This is a type of confidence trick for the purpose of information gathering, fraud, or system access, and the first type of attack of this kind known in history is the Trojan horse itself (not the computer virus, but the Greek mythical event).
[Tweet “Do you know that social engineering is one of the most dangerous cybercriminal tactics?”]For example, in this attack, an international cybercrime ring based out of Eastern Europe managed to steal $1 billion in 2 years from 100 different banks in nearly 30 countries using spear-phishing emails targeting bank employees. The spear-phishing technique is, by far, the most successful on the internet today, accounting for 91% of attacks!

How it affects you and what can you do to get protected:
- Always check the recipient of an email and the source of a message.
- Don’t click any strange links and know what a phishing attack looks like.
- Don’t install software from untrusted sources.
- Don’t trust people blindly and don’t give away confidential information to strangers.
7. Your government is making you more vulnerable
Cybersecurity fact: governments around the world are creating malware and using it as digital weapons or in espionage programs. In the past 5 years, more than a handful of government malware have been discovered (such as Stuxnet), but their origins have yet to receive full attribution. The worst of those was the leaked NSA exploit EternalBlue which lead to the spread of WannaCry, the worst ransomware attack in history. If you also look at how North Korea forces programmers into indentured servitude and has them creating ransomware, things are looking pretty grim.
Besides civilians and private organizations becoming collateral damage, there are also other severe consequences.

In an article on Dark Reading, some key points are made as to how governments are making all of us more vulnerable to cyber attacks:
- Government malware accelerates the evolution of criminal malware – cybercriminals do a lot of reverse engineering on government malware, and use its tactics and technical approach to create new, more advanced malware of their own.
- Governments have fortified zero-day vulnerability black markets – Zero Day vulnerabilities auctions have become common, but governments are buying the intelligence related to these vulnerabilities and weaponizing them, instead of disclosing them responsibly, as is the norm in the cybersecurity industry.
- Governments try to restrict/backdoor/break encryption – in the name of transparency and protection against cybercriminals and terrorists, governments all over the world are trying to limit every individual’s right to encrypt confidential information. This is why “cyber policies” can do more damage than good.
Source: McAfee Labs Threats Report, August 2015
[Tweet “Find out how governments are exposing us to increasingly stronger cyber attacks.”]How it affects you and what can you do to get protected:
- Increase your individual protection by installing an AV solution and a complementary solution that can strengthen your defenses.
- Educate yourself about cybersecurity and keep an eye on the news in the industry.
- Use a VPN solution and encryption technology to protect your confidential information.
8. There is a real-time map that shows cyber attacks in action
Ever wondered how cyber attacks look on a global scale? Check out this real-time map put together by Norse.

You might notice that the U.S. is one of the favorite targets for cyber criminals. For example, Chinese attackers alone caused more than $100 million worth of damage to U.S. Department of Defense networks according to leaked documents from Edward Snowden. Back in 2012, the same department used to suffer more than 10 million cyberattacks per day, and, given the evolution of cyber criminals, we can assume that these figures have climbed dramatically since then. For example, the U.S. Navy, which receives 110.000 cyber attacks every hour.
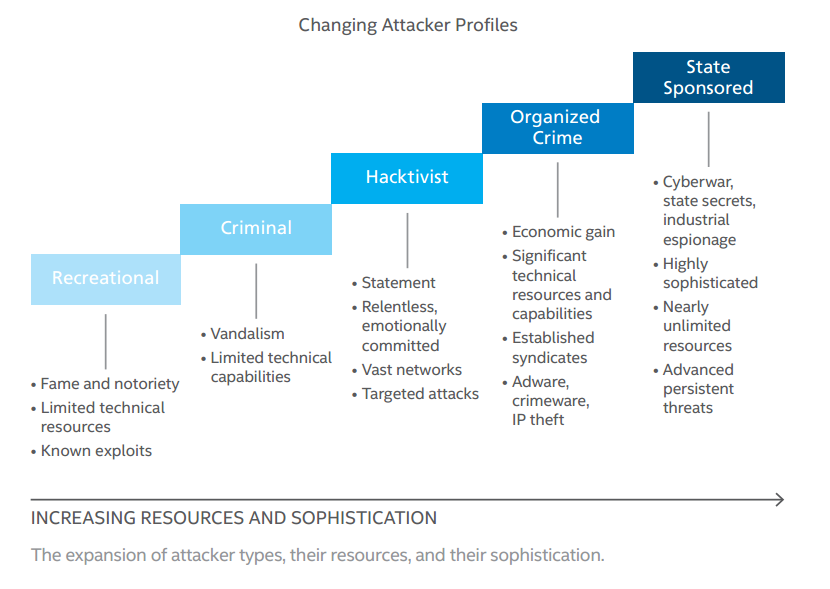
9. Hacktivism is the main motivation that drives cyber attacks
Hacktivism accounts for half of the cyber attacks launched in the world. The term represents a subversive use of computers and computer networks to promote a political agenda. With roots in hacker culture and hacker ethics, its ends are often related to the free speech, human rights, or freedom of information.

Although it may seem like the term has a positive spin, it really depends on who is using the term. Hacktivism can be a politically motivated technology hack, a constructive form of anarchic civil disobedience, or an undefined anti-systemic gesture. It can signal anticapitalist or political protest; it can denote anti-spam activists, security experts, or open source advocate.
[Tweet “Hacktivism is one of the major causes for cybercrime + 9 other essential #cybersecurity facts.”]Hacktivists use code, website mirroring, geo-bombing and anonymous blogging to achieve their objectives, the oldest events of this type dating back to 1989. Anonymous may be the most widely known hacktivist group in the world, but there are many others that carry on cyber attacks of this kind.
How it affects you and what can you do to get protected:
- Be careful about the websites you visit and always make sure they use the SSL security protocol.
- Keep your passwords long, complicated, updated often and managed through a dedicated app (NEVER store them in your browser).
- Keep your system and software updated and also keep an eye out for trouble.
10. 68% of funds lost as a result of a cyber attack were declared unrecoverable
Cybercrime is not only costly, but poses other problems as well for organizations worldwide.
It’s becoming increasingly difficult to detect cyber attacks and resolve the security issues created by them: the average time to detect a malicious or criminal attack by a global study sample of organizations was 170 days (according to a research conducted by the Ponemon Institute). Moreover, no industry is safe: all business sectors are affected to a higher or lower degree.

The same research conducted by the Ponemon Institute found the average annualized cost of cybercrime incurred by a benchmark sample of U.S. organizations was $12.7 million, representing a 96% increase since the study was initiated 5 years ago.
As a result, organizations experienced a 176% increase in the number of cyberattacks, with an average of 138 successful attacks per week, compared to 50 attacks per week when the study was initially conducted in 2010.
[Tweet “More than half of funds stolen through cybercrime will never be recovered. #infosec”]And what’s more worrisome is that 68% of all these funds that were lost as a result of a cyber attack were never recovered and will probably never be.
How it affects you and what can you do to get protected:
- Keep your financial information protected by using a password manager application to enter your passwords in your online banking website.
- Be aware of phishing attempts and never give your confidential information over email or other means of electronic communication.
- Get additional protection through threat prevention software that can detect cyber threats and block them before they infect your system and leak financial data.
No threat is too small, no protection is too strong
However big or small, cybersecurity threats should be treated with caution. You may not be a millionaire (yet) or a C-level manager, but that doesn’t mean that you’re protected against a potential hacker attack. Don’t spare any precautions you can take and try to develop your own protection system with the tools and information you find online, such as this list of cybersecurity facts.
We recently published a guide to help you choose the best antivirus solution for you and there are plenty more security guides you can use to secure your social media accounts, your email, your operating system and more. Use them and navigate the web with a lot more peace of mind.
See the full infographic below:
Share This Infographic On Your Site

INSTALL IT, FORGET IT AND BE PROTECTED
Download Heimdal™ FREE*This article was initially published by Andra Zaharia in May 2016 and updated with current information in March 2018 by Ana Dascalescu.










 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management  Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security