Contents:
There are a lot of different hacking techniques to be aware of.
At the time of publication, the MITRE ATT&CK framework identified some 236 hacking techniques across 14 different categories. Luckily, you don’t need to understand all these tactics to stay safe. Many are close variations of the same basic approach. The best cybersecurity tools will be able to detect a whole swathe of these issues without you needing to know the details.
But while you don’t need to know about all 236 techniques, there are some that you really do need to understand. These attacks are much more dangerous and pervasive than most other techniques a hacker can employ.
In this blog, we’re going to take a deep dive into three of these attacks and discuss how you can take an effective, layered approach to staying safe.
Read on to find out how to defend against:
- Phishing
- Ransomware
- Supply chain attacks
Phishing: Closing down the most common entry point
There’s a good chance you’re wondering why phishing is on this list. It certainly is a dangerous attack vector. But does it really warrant a place alongside ransomware and supply chain attacks as one of the most dangerous security challenges?
On its own, perhaps not. Phishing is, after all, incredibly common. If a hacker infiltrates a non-privileged account, there isn’t much damage they can do outright.
Nonetheless, phishing is one of the most common ways for a hacker to gain initial access into your environment. Often, they’ll target non-privileged accounts to evade detection. Once they have a foothold, they can attempt to move laterally, perform reconnaissance, or start covering their tracks.
Phishing sets the ground for something much more dangerous:
- supply chain attacks
- data theft
- ransomware, etc.
Investing in a robust phishing defense is therefore extremely valuable.
So how do you get phishing defense right? Here’s what you need to know:
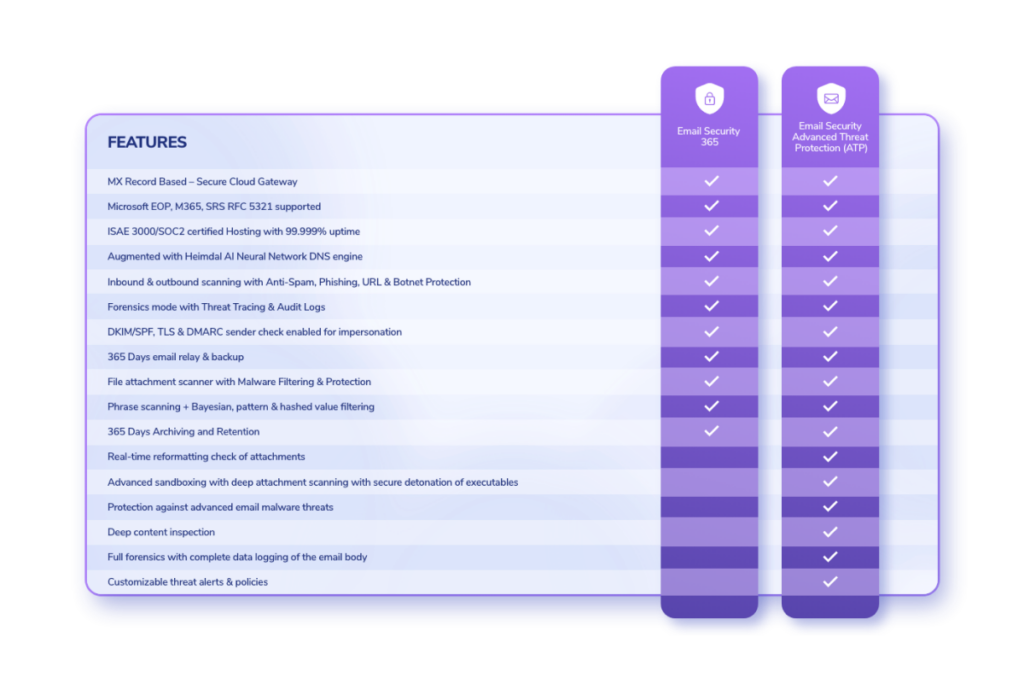
Email security
Email security tools use anomaly analysis and machine learning to detect and filter suspicious messages. Then, they send the suspicious emails to an isolated environment for IT teams to safely investigate, without the risk of data loss or malware injection. This is a crucial first line of defense because it reduces the chance of an employee interacting with a phishing email.
Read more: What Is Email Security?

Employee training
Phishing directly targets end users, so training them to look out for the warning signs is also hugely important. Since no email security tool will be 100% effective, education helps create a layered defense strategy.
Read more: Why You Need IT and Cybersecurity Training: Hidden Dangers
Least privilege
With elevated admin rights, a hacker can execute a whole range of damaging attacks and activities. Therefore, it’s important to remove unnecessary admin rights in your organization as much as possible. This will reduce the chance of a successful phishing attempt infiltrating a privileged account. Applying the principle of least privilege will also give the hacker fewer options for lateral movement and privilege escalation.
Read more: What Is the Principle of Least Privilege (POLP)?
Secure internet traffic
Hackers can also redirect users to phishing pages by DNS spoofing and other types of DNS attacks. A forged domain and website that mimic the legitimate one increase the chances that the phishing attack is effective. Investing in strong DNS security tools prevent or at least mitigate phishing attempts..
Read more: What Is DNS Security and How Does It Work [A Comprehensive Guide]
Forensic telemetry
Gaining access to a non-privileged user account is a common first point of entry for hackers. From there, they’ll use a range of tactics to perform lateral movement and gain additional privileges. But behavior like this is quite anomalous and is often picked up by behavioral monitoring tools like SIEMs and XDRs.
Email security made easy
Your employees’ inbox is the primary entry point for some of the most dangerous threats imaginable. With the right tools, you can detect, manage, end, and report on email-based threats from a single centralized dashboard. Find out more.
Ransomware: How to prevent the nightmare scenario
Ransomware doesn’t start as a ransomware attack – that’s just the final stage. It starts as a remote code execution, a zero-day exploit, or phishing – and these in the end develop into ransomware attacks. So if you can start by resolving these issues first, your hacker will have a very hard time developing their attack to the level of ransomware.
Andrei Hinodache, Cybersecurity Architect & Technical Product Marketing Manager
When it comes to security, ransomware is one of the absolute worst-case scenarios. If a hacker succeeds in encrypting your data, you’ll be left with very few good options.
If you don’t get your data back, the business disruption could be far-reaching and potentially terminal. Often, the only way to unencrypt your files is to pay an expensive, potentially crippling ransom. Yet, paying that ransom won’t guarantee the safe return of your data and might even be illegal, depending on the laws in your area. Also, it will support further malicious activities, as hackers see this as a successful business.
As always, prevention is better – and cheaper – than healing. While there are a few tools to defend against ransomware attacks as they’re happening, you should really be aiming to stop them from ever being a possibility.
Effective ransomware protection includes stopping the hacker from entering your environment.
Here is what that involves:
Patch vulnerabilities
Before they can install ransomware, a hacker will first have to gain initial access to your system. Then they need to escalate their privileges to admin level. To do this, they’ll often exploit unpatched vulnerabilities. You should therefore ensure you have a process to identify and prioritize unpatched vulnerabilities in your IT environment. The most comfortable solution to this is to use an EDR or XDR tool that includes vulnerability management.
Read more: What Is Vulnerability Assessment?
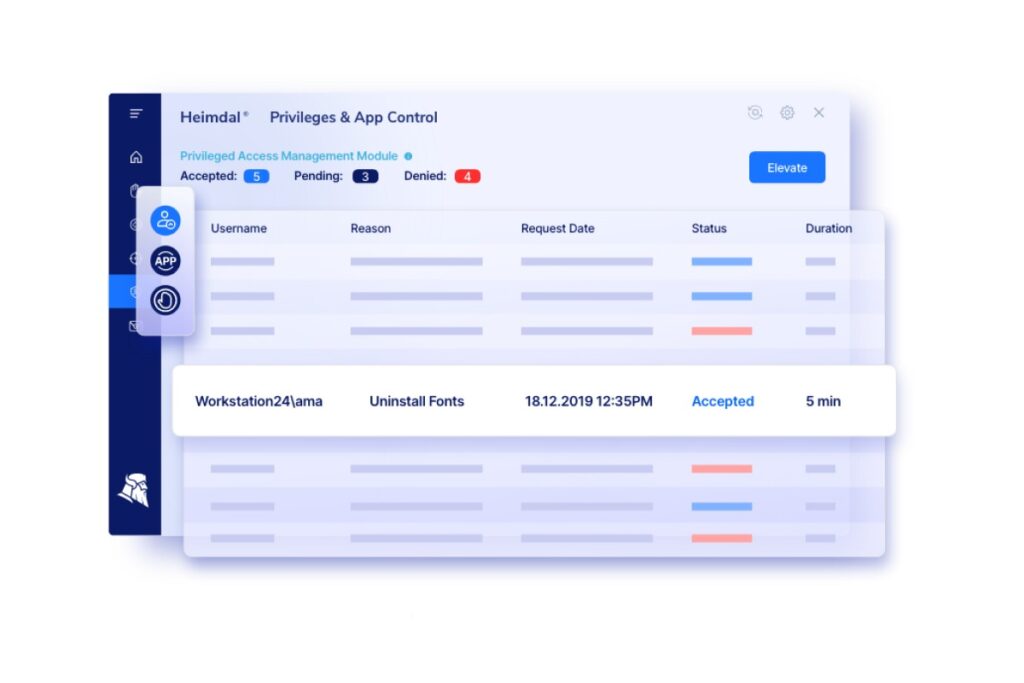
Apply the principle of least privilege
To access, encrypt, and exfiltrate data, the hacker will almost certainly need elevated privileges. It’s therefore important to reduce your admin accounts to an absolute minimum. Users should only have enough privileges to complete their tasks.
Besides applying the principle of least privilege, you should also enable just-in-time access. Thus, you can ensure privileged access is given for a limited period, on a case-by-case basis, rather than certain individuals having ‘always on’ rights. These access security measures will give hackers a much harder time if they try to install ransomware even if they do access admin accounts.
Read more: Just-in-Time Access (JIT Access): The Most Sophisticated PAM Feature on the Market
Enforce multi-factor authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) might seem like a pretty rudimentary tool on the surface. Yet it can play a huge role in preventing ransomware attacks. MFA creates an extra barrier of defense to stop hackers from logging into accounts, even if they’ve obtained passwords through phishing or other tactics. It’s very difficult for a hacker to effectively log into an admin account if the real admin needs to also type in a code on their smartphone to prove their identity.
Read more: What Is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)?
Powerful XDR/SIEM tools
If a hacker wants to install ransomware, they’ll have to do their homework first. This will involve lateral movement, reconnaissance, disabling security tools, and covering their tracks if they can. All of this behavior is highly anomalous, since end users don’t generally have the skills or need to do any of this. By analyzing the behavior of all users, XDRs and SIEMs can therefore identify suspicious activity through anomaly analysis. This helps to identify and lock down the infected account before the hacker can install the ransomware and escalate the attack.
Read more: EDR vs. SIEM: Key Differences, Features, Functionality Gaps, and More
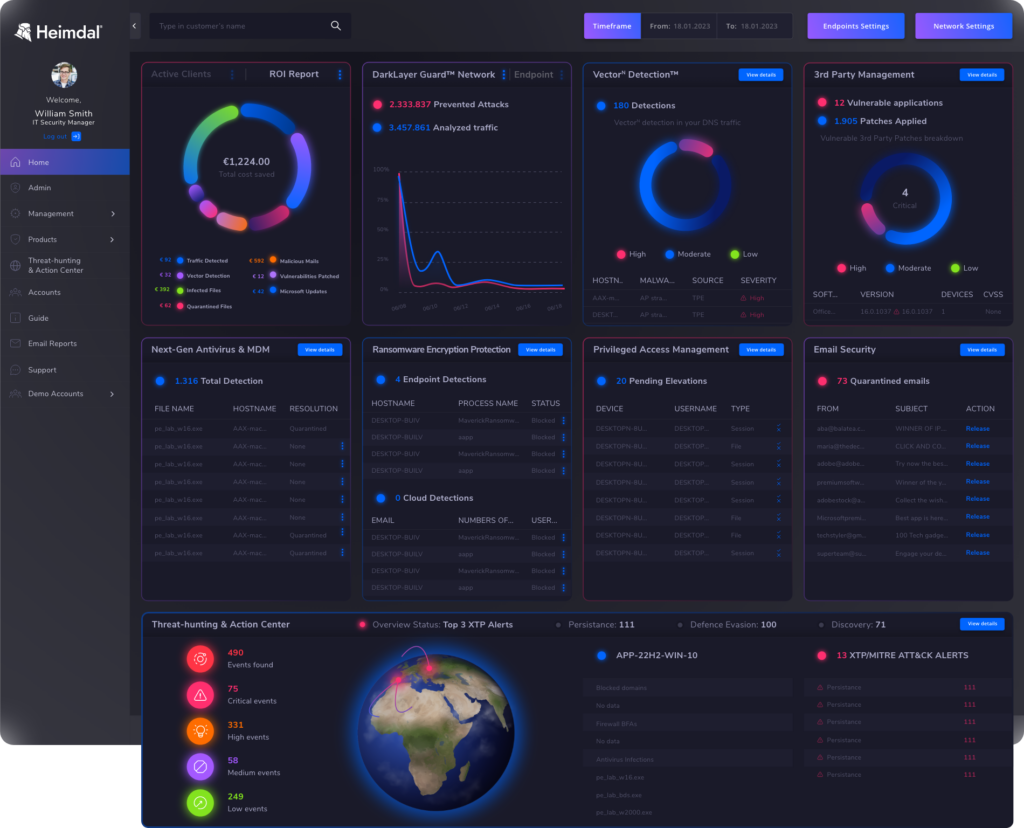
Fast and effective incident response
In order to quickly lock down a ransomware attempt, you need to first identify it. This can be easier said than done. Again, the right approach here is to rely on threat detection tools like XDRs and SIEMs. These tools can monitor behavioral signals and quickly categorize suspicious behavior according to the MITRE framework. This is crucial, because every second spent understanding the hackers’ activity and diagnosing the right response gives them precious time to further escalate their attack.
Read more: How to Create a Cybersecurity Incident Response Plan
Ransomware encryption protection (REP)
If all else fails, encryption protection is a valuable final line of defense when hackers attempt to install ransomware. REP tools are designed to detect and repel attempts to encrypt data, by using anomaly analysis.
Read more: The History of Ransomware: From Simple Scams to Geopolitical Threats
Stop ransomware in its tracks
If the worst happens, you’ll want a program like Heimdal’s Ransomware Encryption Protection fighting your corner. Our revolutionary product takes a 100% signature-free approach to protecting your IT environment. Check out the full product page to find out more.
Supply chain attacks: How to defend against a Trojan horse
One of the biggest issues we see around supply chain security is when companies trust too many providers in the first place. Often, you’ll get a new software tool or application for various business needs and then forget to check whether it can, for example, be integrated with an identity and access management solution… Does it support encryption? Does it support MFA? How do they manage security on their side?
If you do a little bit of extra work before installing a new tool, you can significantly reduce the risk of supply chain issues.
Thomas Engli Baasnes, Cybersecurity Director, Verdane
Since the infamous SolarWinds attack, supply chain vulnerabilities have been at the top of everybody’s priority list. They are some of the most persistent and dangerous attacks a company can encounter.
As cybersecurity has evolved, much of the hackers’ traditional toolkit has become harder to successfully pull off – largely as a result of the many security tools we’ve discussed in this list. That means they’ve had to find more insidious tactics.
In a supply chain attack, the hacker will target one or multiple organizations via a third-party tool or service they’re using. This works like a Trojan horse: piggybacking on software the business relies on to function. It allows the hacker to pass undetected through security protections that would otherwise filter them out.
The risk is huge, because all organizations now rely on third-party software. Generally, they have little visibility over the vulnerabilities that software may already have.
In truth, there is very little you can do to proactively prevent supply chain-related issues. You can use reactive tools to identify and lock down when hackers are trying to exploit 3rd party software vulnerabilities. Also, there are some steps you can take to reduce the chance of introducing infected software into your environment. Here’s what you need to know:
Due diligence
The best way to avoid supply chain vulnerabilities is to not buy the infected software in the first place. Reduce the number of products and licenses wherever possible. You should also do due diligence on any potential software vendors to ensure they have high security standards of their own.
Read more: Supply Chain Risk Management (SCRM) Explained
Software visibility
Having a clear overview of all software makes it easier to respond if a supply-chain vulnerability is exploited. Full visibility helps identify faster which software is causing the issue and lock it down. It also reduces the chance of vulnerabilities created by ‘shadow IT’ tools. Shadow IT refers to devices and software that the employees are using unofficially. To prevent harmful effects of shadow IT use endpoint management, app management, and other similar tools that offer complete visibility to asset inventory and management.
Read more: Application Allowlisting: Definition, Challenges & Best Practices
MITRE translation
When an attack is about to take place, a fast response is the difference between success and failure for the hacker. For that, you first need to understand what the hacker is trying to achieve and how they’re aiming to do so. This is what makes the MITRE attack framework so important. By using it as the basis of your threat response, you can build fast and effective automated policies that can quickly identify what a hacker is up to and deploy the right response.
Read more: Automated Incident Response: What You Need to Know
Powerful telemetry
By using products like XDRs, SIEMs, next-gen antiviruses, etc. – it’ll be much easier to detect and mitigate supply chain attacks. If a particular app starts displaying unconventional behavior and working out of scope, machine learning and anomaly analysis can identify the activity and trigger an alert. For this to work, the tool needs to analyze and monitor all user behavior, at all times – which is why telemetry information from across your IT environment is so important.
Read more: Security Information and Event Management (SIEM). What It Is and How It Works
Effective reactive defense for real time attacks
When supply chain attacks come out of nowhere, time is of the essence. Your cybersecurity tools need to work in tandem to understand what your hacker is doing and quickly prevent it.
Heimdal’s threat hunting action center combines real time telemetry signals from right across your IT environment to identify dangerous activity as it’s happening. From there, you can build automated policies to quickly lock down or isolate the infected account.
Find out more about threat hunting with Heimdal.
One platform to defend against them all
As you’ll have noticed, there are a lot of different security tools discussed in this blog. From DNS monitoring to privileged access management, threat hunting, SIEMs, and more… the list just goes on.
This is because the best defense is a layered one. No single cybersecurity tool can guarantee your safety, just like building a fence or a door won’t prevent thieves from breaking into your home.
But having so many different tools creates security challenges of its own. As we’ve seen, hackers have various tools at their disposal, and they often use many as part of the same attack. If each of these is being picked up by a different tool, there’s a strong chance you’ll miss the overall picture of what they’re trying to achieve. Buying the best security tools in the world will be of no use if they’re not cooperating to defeat the main threat.
So what’s the solution?
The simple answer is to combine as many security tools and protections as possible into a single unified dashboard. This gives you visibility and control over the whole scope of potential security issues. It will be much quicker to diagnose, understand, and prevent them.
If this sounds like the kind of approach you need, then good news: You’re in the right place. With Heimdal, you get access to the single widest cybersecurity platform on the market, complete with virtually all of the tools and protections we’ve discussed in this blog.
And helpfully, this is also the best way to defend against the other 233 attack techniques we didn’t discuss.
So where do you start? Find out more.
FAQs
What are the most dangerous cyberattack techniques?
There is no single most dangerous cyberattack technique. Techniques change depending on the IT environment and the specific targeted assets. Nonetheless, three of the most common and dangerous attacks you’ll need to focus on are phishing, ransomware, and supply chain attacks.
How many MITRE ATT&CK techniques are there?
At the time of writing, there are 236 MITRE ATT&CK techniques across fourteen different categories, as well as several sub-techniques. This number keeps growing as researchers discover new techniques.
How do you defend against phishing?
Like all cyber-attacks, the best defense against phishing is a layered one. This should include several different protections:
- email security
- employee training
- implementing the principle of least privilege
- DNS security
- real time threat detection, etc.










 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management  Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security










