Following privileged access management best practices helps security professionals balance security and productivity.
Security administrators use PAM solutions to regulate privileged users, accounts, and sessions according to the company’s privileged access management policy.
The goal is to prevent breaches and protect sensitive data and resources. Equally important, a well-built PAM policy should not disrupt the company’s workflow.
PAM best practices are easy to follow and integrate into daily activity if you have the right tools at hand. I’ll explain what and why you should aim for and how to get there.
Key takeaways
- apply the principle of least privilege and the principle of just-in-time access for securing privileged access
- enforce a zero-trust approach when enabling access to sensitive data
- go for an automated, unified privileged access management solution to save time and increase efficiency
Top 10 Privileged Access Management Best Practices
Following these best practices will help you implement an effective Privileged Access Management strategy.
Assess Infrastructure with PAM in Mind
First you need to inventory privileged accounts and their whereabouts.
Who needs privileged access permissions in your infrastructure? There are three types of users for privileged accounts:
- human users
- applications that need access permissions to databases or to communicate with other software or devices
- devices
Map them all out and see how they are interconnected.
Legacy infrastructure and role-changing inside the company can evolve in a security risk. Ideally, you should know at any moment who – human, software or device – needs access to what and for how long.
As soon as a user leaves the company or changes position, you should disable their privileged account.
Stay protected with our PAM suite, designed to secure privileged sessions, streamline credential management, and ensure compliance.
Track and Monitor Privileged Sessions with Heimdal
Therefore, using an automated asset discovery and access assessment tool to track devices is essential. This will grant you:
- full visibility over assets and privileges
- a faster way to revoke privileges in case of noncompliance, incidents or internal changes
- a faster way to enable privileges when needed
Security admins should separate administrative accounts from standard accounts.
Additionally, they should keep auditing capabilities within admin accounts separated from system functions like read, edit, write, execute etc.
Apply the Principle of Least Privilege
The Principle of Least Privilege (POLP) is a best practice in any Identity and Access Management (IAM) strategy.
Enforcing POLP means allowing each privileged user just enough access to complete their tasks and nothing more.
The benefits of implementing least privilege are:
- Smaller attack surface
- Enhanced security and better data classification
- Increased system stability
- Better compliance & audit readiness
Apply the Zero Trust Security Model
This model comes in contrast with traditional beliefs that all users inside an organization are trustworthy. But not only outsiders can be a threat.
The zero-trust security model denies resource access until it inspects and authenticates users and devices.
Deploy Attribute-Based Access Control
Attribute-based access control (ABAC) helps establish policies regarding sensitive data, network infrastructure, and IT resources. In addition to roles and assets, ABAC also includes actions and environment.
Actions like read, write, copy and delete define what the privileged user is authorized to do with the resource.
Environment refers to the broader context of where and when an authorized user can leverage a specific resource, including the device itself and any supporting protocols.
Monitor and Alert
You should monitor and record privileged sessions. An unauthorized user trying to access assets or execute actions beyond their privilege levels should trigger an alert.
Periodic monitoring of routine actions provides valuable insight into behavioral and chronological changes.
Privileged session management (PSM) is a tool feature that allows admins to control, monitor and record privileged sessions. It helps them detect and block suspicious activities faster and with less effort.
Monitoring activities involves capturing keystrokes and live screens so that users are accountable for any security incidents or breaches that may occur.
Change Default Usernames and Passwords
As obvious as it may sound, using default usernames and passwords is a security risk. Yet, people keep choosing commodity over safety, if possible.
Enforce password security by setting and applying clear rules across the infrastructure.
Here are a few rules when it comes to password policies in general:
- use strong, complex passwords
- implement multi-factor authentication
- don’t allow using the same credentials for multiple accounts
- train your employees to choose passwords based on the most recent NIST guidelines.
Set and keep privileged account credentials as safe as possible. Hackers are aware of the value of privileged passwords, so they’ll use phishing, social engineering and brute force attacks to gain access.
Breaching a privileged account enables attackers to lateral movement and privilege escalation.
Manage Shared Accounts
PAM tools are critical when it comes to managing shared accounts. Otherwise, shared privileged accounts lack access control and responsibility tracking.
Prepare for Fast Data Recovery and Mitigation
In case of unusual activity, a privileged session should shut down automatically. This prevents further infiltration in case of an attack.
PAM tools make the difference when it comes to fastening your organization recovery in case of a privilege-abuse based incident.
Enforce Just-in-Time access
Enforcing the principle of least privilege is one of the strongest PAM safety measures. Bolster security by also applying just-in-time access for administrative tasks.
This means that once a task that needs elevated permissions is done, the user should no longer have access to that specific asset.
It’s like only keeping the vault’s door open when you need to bring in or take out the money. For the rest of the time, the door remains closed for everybody, regardless of their privilege level.
Morten Kjaersgaard, founder of Heimdal, explains how the just-in-time access principle works:

- ,
Educate Employees to understand PAM benefits
A safe IT environment benefits both the company and the users. Train your colleagues to become your partners in protecting the integrity of the network.
Explain the risks of
- using weak and repetitive passwords
- not signing off when finishing a session
- sharing credentials to suspicious third parties
Common challenges of implementing PAM best practices
Applying PAM best practices is sometimes easier said than done, here’s why:
Implementation issues
Revoking or limiting access permissions can impact productivity. To avoid disrupting workflows, IT teams need to plan and test the access patterns for:
- Privileged users
- Applications
- Devices
An overly restrictive PAM policy can block the activity and frustrate employees. Faulty implementation of pam management can impact a coworker or even a business partner.
Tracking and monitoring privileged accounts
Employees come and go; they change roles and departments. As the user’s access needs changes, you should monitor and adjust privileges for user accounts.
Failing to revoke privileges once they are no longer necessary generates privilege creep. That makes the whole system vulnerable in case of an infection.
But tracking permissions for user accounts in the dynamic environment of a large company is time and resource consuming.
Automated privileged access management solutions, like Heimdal’s, increase visibility across the infrastructure.
It would only take a few settings and clicks to automatically revoke Brad’s access to Accounting’s database once he moved to HR, for example.
If Brad clicks on a phishing link and compromises his user account, there will be less damage. The potential attacker will only gain access to HR data, instead of HR and Accounting.
Stay protected with our PAM suite, designed to secure privileged sessions, streamline credential management, and ensure compliance throughout the IT ecosystem.
Boost your security with PASM.
User resistance
Balancing security and productivity is another challenge of applying PAM best practices.
Users complain that not having direct and continuous access to assets and resources hinders their productivity.
A slow, manual access management process might do that indeed. This triggers two potential risky situations:
- Top management will prioritize productivity over safety to meet financial goals.
- Users will try to evade compliance with the access management system.
Both scenarios can lead to system breaching and considerable money and reputation loss for the enterprise.
Best privileged access management software is equipped with the feature of just-in-time access.
This kind of tool grants users rights for a specific amount of time. It’s the safe, fast and effective way of dealing with user permissions.
PAM benefits for companies
Implementing a robust privileged access management strategy helps stop an infection from spreading across the whole network.
But there are also other benefits of PAM:
- It eliminates the risk of privilege abuse
- Better rights monitoring and control as well as local rights removal
- It ensures compliance
- If implemented right, it facilitates productivity
How Can Heimdal® Help?
Heimdal’s Privileged Access Management suite has three modules that cover all PAM processes, from credential management to safe remote access and streamline access:
- Privileged Account and Session Management (PASM)
- Privilege Elevation and Delegation Management (PEDM)
- Application Control
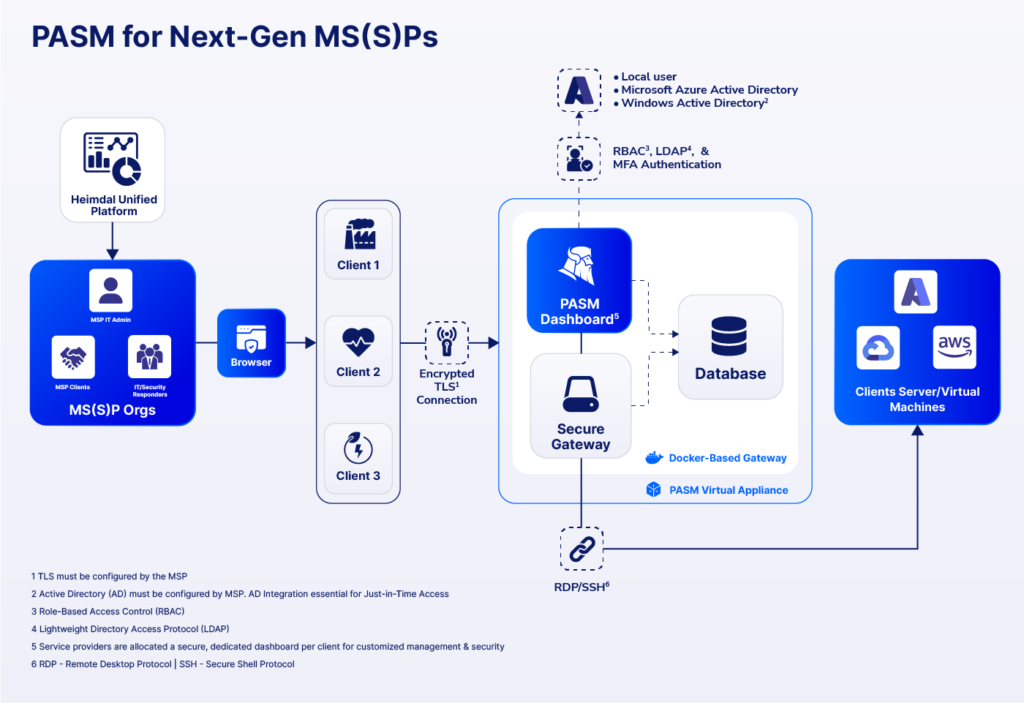
Some of the advantages of using this PAM solution are:
- when you use it with Heimdal’s Next-Gen Antivirus, it turns into the only software that automatically de-escalates user rights, in case it detects a threat compromised the device.
- complete control over the user’s elevated session. You can approve or deny session elevation from the dashboard or from your mobile. The integrated approach eases management for both administrative and user-level privileges
- the zero – trust execution protection is included in the Privileges & App Control – Privileged Access Management view. Here you can see the processes (non-signed executable files) that the zero-trust execution protection engine intercepted, with data on:
- hostname
- username
- process name
- md5 hash
- timestamp
- status

- advanced data analytics that help investigate incidents and create audit and compliance reports. It only takes a few clicks to display the hostname, average escalation duration, users or files escalated, files or processes ran during escalation, etc.
- application execution approval/denial, or live session customization
Click here for pricing and a free trial.
System admins waste 30% of their time manually managing user rights or installations.
Heimdal Privileged Access Management
Wrapping Up
Managing and monitoring the use of privileged rights makes Privileged Access Management a key part of the company’s defense. Read more about this must-have cybersecurity tool in the Privileged Access Management guide.
Following the best practices above will ensure a smooth management of privileged accounts and privileged sessions.










 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management  Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security








