Contents:
An endpoint security strategy sets the ground for better endpoint protection against threats. The key element of implementing it is using a strong endpoint detection and response solution.
Following clear endpoint security policies and using the right tools will enable you to prevent system breaches and offer better incident response.
Key takeaways
- Antivirus software can’t protect you from advanced persistent threats;
- Lack of visibility is one of the most common cybersecurity challenges;
- Using a unified endpoint protection platform raises the chances of keeping a safe remote work environment;
- Hackers often target endpoint users to gain access to a company’s network.
What Is an Endpoint Security Strategy?
An endpoint security strategy is a plan built to keep all devices safe from cyber-attacks.
An endpoint is any computing device that connects to a network. A company’s endpoint inventory can include desktops, laptops, smartphones, printers, POS devices, cameras, etc.
Endpoint security ensures that:
- All desktop computers and mobile devices are safe and clean;
- The connection between those devices and the corporate network is safe.
A robust strategy offers a framework for:
- Protecting endpoints from potential threats, like phishing attempts;
- Identifying threats once they’ve managed to compromise an endpoint;
- Monitoring activity on your systems;
- Applying endpoint security best practices.
Endpoint Security Strategy Benefits
Creating an endpoint security strategy offers a series of benefits:
- Clear objectives to reach for;
- Operations predictability, which increases coherence;
- Clear action paths, which sets the foundation for better incident response.
Endpoint Security Challenges
Organizations have different security needs and industry regulations. However, they also face common endpoint security challenges:
Lack of Visibility
Large, complex infrastructures have hundreds or thousands of endpoints running on different Operating Systems. This makes it difficult for security teams to detect and respond to threats in a timely manner.
Having a clear, responsive map of what and where is going on in your infrastructure means:
- Faster threat detection;
- Attack pattern identification;
- Faster understanding of potential impact on other assets;
- Better response to advert or contain the incident.
Unified platforms, like Heimdal’s Endpoint Detection and Response solution, increase visibility by bringing all endpoint security operations under the same umbrella.
Limited Resources
Endpoint security can be resource-intensive, especially if there are a lot of assets to protect. Organizations may not have the staff or budget to dedicate to endpoint security. This can make it difficult for IT teams to create and follow an endpoint security strategy.
Complexity of the environment
Owning a variety of devices, running on different operating systems, are a challenge for endpoint security. For example, it can make patch management more difficult.
Instead of following, prioritizing, testing and applying patches for one OS you’ll need to juggle with Windows, plus Linux, plus macOS. Using automated patch management can help keep all the balls in the air. Best endpoint security software usually includes such tools.
BYOD
The bring your own device (BYOD) policy peaked during and after the Covid-19 pandemics. It brought both advantages and disadvantages, mainly cybersecurity-related.
BYOD devices often do not have the same level of security as corporate-owned devices. Yet, they are often used to access sensitive data or impersonate legitimate users. Applying privilege access management, endpoint and network security best practices saves the day when it comes to making remote work environments safe.
Sophistication of Threats
Endpoint users are the most common entry point for cyberattacks, says Verizon’s annual Data Breach Investigation Report.
Cybercriminals target endpoint users to exploit known vulnerabilities or use advanced tactics to bypass defenses. Phishing campaigns and social engineering are some of the most common initial access techniques.
BYOD WHITEPAPER
Key Components of an Endpoint Security Strategy
Regardless the organization’s size, the key components of an endpoint security strategy include:
Security Controls
Choose security controls according to your activity and industry compliance regulation. There are a variety of security controls you can implement:
- Antivirus/anti-malware software;
- Firewalls;
- Patch management;
- Intrusion detection / intrusion prevention systems;
- Endpoint detection and response (EDR) software.
Antivirus software is the most famous security tool on the list. But they are no longer enough to prevent advanced threats. Go for a layered security approach to make sure malicious actors will find all the gates to your infrastructure closed.
Visibility and Monitoring
Organizations need visibility into what is happening on their endpoints, so they detect and respond to threats fast enough. Asset management tools help IT teams have a better view over their infrastructure, including legacy devices.
Real-time monitoring tools and unified platforms enhance visibility.
Threat Intelligence
Gathering intelligence on the latest threats helps organizations proactively defend against cyberattacks. Threat intelligence documenting includes:
- Subscribing to threat intelligence feeds;
- Conducting regular vulnerability scans;
- Using a unified security platform with threat intelligence capabilities.
Employee Training
Educating employees regarding risks, cybersecurity best practices and company policies is part of most compliance regulations.
Training employees to identify a phishing email, or a social engineering attempt can deny initial access to attackers.
Also, employees should have clear steps to follow in case they suspect their endpoint has been compromised. Like knowing who to report a potential attack to and what information do they need to provide.

How to Build an Effective Endpoint Security Strategy
As Morten Kjaersgaard, Heimdal’s CEO, says:
[…] you cannot afford not to have a strong cyber security strategy. Today, a major breach episode is more a question of “when” and “how serious” than of “if” in any company, with constant breaches, code leaks, and credential disclosures being reported practically daily – only in 2021, “the average number of cyberattacks and data breaches increased by 15.1% from the previous year.
In terms of developing a robust endpoint security strategy, here’s what you need to consider:
Identify Your Business Assets
The first step in any security strategy is to identify your most valuable assets. There are various types of sensitive data that your endpoint security strategy should aim to protect:
- Financial data;
- Intellectual property;
- Customers’ and employees’ personal data;
- Operational data;
Assets protection also includes safeguarding the way your company’s endpoints are used. Hackers might not be after your private data, but they could try to compromise your devices and enroll them in botnets.
Understand Your Threat Profile
Once you’ve identified your business assets, it’s important to understand the threat profile for each asset. This will help you decide which security solutions are best suited for protecting each asset. You need:
- end-to-end encryption and DNS filtering to prevent data breaches
- nextGen Antiviruses and endpoint detection and response based on behavior analysis, to prevent ransomware encrypting your data
- patch management software to close vulnerabilities quicker than a hacker could find and exploit it
- privileged access management to automate safe access to internal data, to prevent breaches and lateral movement.
Develop a Layered Security Approach
A layered security approach is always the best option when it comes to endpoint security. By implementing multiple layers of security, you reduce the risk of an attack penetrating your network. It’s like using more than a door lock to protect your house. To keep thieves away from your property you might use, besides a key, a fence, a surveillance camera, and an alarm system.
In our case, common layers of endpoint security can include:
- firewalls
- intrusion detection/prevention systems
- DNS filtering
- NextGenAntivirus/antimalware solutions
Test and Validate Your Strategy
Regularly testing and validating your endpoint security strategy is essential to ensure it is still efficient against new and evolving threats. A solid penetration testing plan should include both internal and external scenarios. When preparing to run such a test, don’t forget to also update your assets inventory.
Keep Your Expenses in Check and Use Unified Platforms
Aim to simplify your endpoint security solution selection. A unified cybersecurity platform will reduce the number of endpoint security tools you deploy. Thus, you avoid integration issues and limit resource consumption.
Choosing a unified security suite to manage all of your endpoint security issues will also increase visibility.
How Can Heimdal® Help?
Heimdal’s security professionals anticipated the importance of a consolidated security suite before the cybersecurity market started to discuss about it.
Therefore, our core products:
- DNS Security
- Patch and Asset Management
- Next-Gen Antivirus
- Ransomware Encryption Protection
- Privilege Access Management
- Application Control
are designed not only to work as stand-alone solutions, but also integrate seamlessly in a unified platform. Depending on your company’s needs, you can choose an EDR, XDR or MXDR platform to secure endpoints.
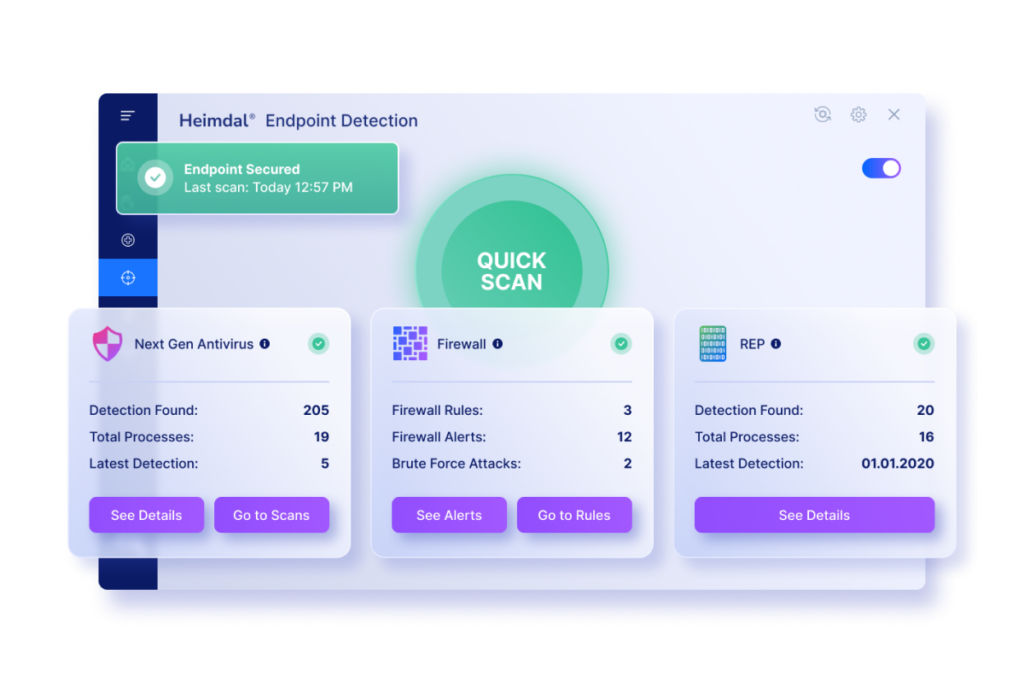
Heimdal’s EDR Software
Our EDR ecosystem is based on cutting-edge technology that enables continuous prevention through DNS-based attack protection and patching, as well as immediate response to advanced cyber threats of all types. You will find and seal all exploits without relying on individual threat-hunting solutions or analysts.
Heimdal’s XDR Software
With the help of our XDR service, you can go beyond endpoint protection and bring all infrastructure under the same umbrella:
- endpoints
- networks
- cloud
This service will also provide you with detailed incident reporting, actionable remediation items, disaster recovery plans, and advanced detection approaches.

- End-to-end consolidated cybersecurity;
- Complete visibility across your entire IT infrastructure;
- Faster and more accurate threat detection and response;
- Efficient one-click automated and assisted actioning
Final Thoughts
When it comes to endpoint security, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. The starting point of a comprehensive strategy is assesing the specific needs of your organization.
Developing an endpoint security strategy requires careful planning and consideration of known and unknown threats. Taking the time to build it will pay off in the long run by helping to keep your company’s systems safe from attack.
Follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube to keep up to date with everything we post!










 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management  Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security








