Cyber threat hunting is a proactive search for malicious activity in your system.
Threat hunting is a must-have part of the defense strategy. It focuses on threat detection and responding rapidly to unknown, unresolved threats.
Security analysts purposely look for malicious activities at an endpoint or network level. Threat hunters analyze security data for hidden malware or suspicious activity patterns.
Rather than waiting for an attack to strike, a threat hunter actively searches for events that could affect the system.
Key takeaways
- proactive threat hunting helps keep a safe environment, by detecting advanced persistent threats
- there are three types of threat hunting: structured, unstructured, and situation-driven
- skilled personnel are one of the four key elements of cyber threat hunting
- IT teams can use Heimdal’s Threat-hunting & Action Center to cover the lack of an upskilled workforce or gain time to focus on other activities
Why Is Threat Hunting Important?
Malicious actors frequently remain and act unnoticed for months in case of a network breach. This gives them enough time to:
- search and collect data
- perform a lateral movement
Joseph Ochieng’s Cyber Threat Hunting study says cybercriminals spend about 192 days inside a system before they are spotted.
Threat hunting is a critical element of the security strategy as it makes incident response faster.
Since no system is 100% secure, companies should use threat hunting techniques to bolster defense.
Basic cyber hygiene, well-configured firewalls, DNS filtering, and other security tools can prevent cyberattacks. Thus, they prevent money and other resources loss.
Yet sometimes threat actors succeeded in evading threat detection tools and penetrating the system.
After responding to an incident, you’ll want potential advanced persistent threats out of your network. So, stay alert and start threat hunting!
Leave it to us. Stay protected with our Threat-Hunting & Action Center.
Who Does the Threat-Hunting in Your Team?
The Cyber Threat Hunting Process in 5 Steps
Cyber threat hunting is a multi-stage, cyclic process. Since the hunt itself is proactive, the hunter doesn’t know what exactly to look for.
The process begins with defining the purpose of the threat hunt.
Data collection and analysis follows. Then it’s time for remediation, response, and learning.
This proactive approach shouldn’t become a burden for the existing IT team.
Automated security tools, like Heimdal’s Threat-hunting & Action center, can support both MSSPs and Security Operations Centers to find potential threats faster.
Our Threat-hunting and Action Center will supercharge SecOps and leapfrog the effectiveness of any cybersecurity operations. Heimdal is continuing its commitment to drive groundbreaking changes to the industry.
We are certain that this new tool will evolve threat hunting by mitigating risks faster with less effort, as well as drive a change in productivity for enterprise, as well as MSP and MSSPs.
Morten Kjaersgaard, Heimdal’s Chairman & Founder
No matter how you decide to deal with it, here’s what happens during each of the 5 steps in the threat hunting process:
Defining the Cyber Threat Hunt Goal
For the first step of the threat hunt, define the main reasons why you are doing it. Set clear objectives after you found the answers to these questions:
- What kind of assets in your infrastructure are most valuable and might need extra care?
- Which ones could lead to further, more impactful damage, if they were compromised?
- What flaws or vulnerabilities could a threat actor find and exploit?
Since there is a wide variety of potential cyber threats and security data to retrieve, conducting a hunt without previously setting the objectives is likely to fail.
A series of small, directed hunts is always better than a large undirected threat hunting program.
Data Collection
The quality of the data collection stage will have a direct impact on the threat hunting quality.
Incomplete data leads to a half-good threat hunt and a false sense of security.
To gain valuable insights and records of the activities in your enterprise’s IT environment, use a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solution.
Additionally, as a threat hunter, you should subscribe to feeds on the latest cyber threats.
Sites and platforms like CISA’s news and events page, PhishTank, or the SANS Technology Institute are good threat intelligence sources.
Description of tactics, techniques and procedures (TTPs) on MITRE are also a must know for cyber threat hunters.
Quality data collection doesn’t mean high volumes. Adjust the collection process to the goals of your threat hunting.
More data doesn’t guarantee a better outcome, for the following reasons:
- Volume – a collection of more data means the team will spend more time processing it. Depending on the hunt’s circumstances, a larger amount of data may only result in more redundant work.
- Classifying – some techniques work best with smaller data sets than larger data sets, such as grouping and stack counting.
To answer the core question when threat hunting, it’s essential to focus on the information required.
Also, cyber threat hunting should be a continuous process not a once in 5 years event.
So is data collection. Past hunts should be the base and motivation for future ones.

Data Analysis
This stage can be really challenging since you are dealing with a large amount of data.
Encryption and encoding are often used by data logs to remain undisclosed even after collection.
Threat hunters should eliminate logs that split attack payload into small packets to fully check every ounce of information, asset, or data.
There are two results you can expect once the analysis is complete:
- Correct hypothesis – indicating there is no evidence of an attack agent’s presence within the system.
- Incorrect hypothesis – if the stated hypothesis is confirmed, the hunter should check the nature, extent, and effect of the attack on the system as soon as possible. What’s more, the threat hunter is required to draft an effective attack response.
Response
After analyzing the data, the threat hunter must generate the best response to the threat.
So, it’s time to define both short-term and long-term solutions to counter the attack.
The goal here is to terminate the ongoing attack as quickly as possible. Your security team should also:
- protect the affected host
- prevent system damages
- eliminate the possibility of a future attack
Lessons Learned
As a threat hunter, you’ll want to be able to avoid a similar attack in the future.
Document what happened during the cyber threat hunting stages.
You’ll be able to use this information to prevent similar events in the future.
This step’s main goal is to improve the security process by taking every element into account.
The human factor is a significant threat and can be a vulnerability, as you can read in this year’s Data Breach Investigation Report.
For example, failing to patch systems in a timely manner can lead to security breaches.
Firing the person involved would not eliminate the threat or resolve the solution.
Instead, a better response would be implementing automated patching throughout the organization.
Detect & mitigate threats in real-time, with no additional pressure or effort for your security team.
Find out more about Heimdal's Threat-Hunting & Action Center.
Threat Hunting Types
- Structured hunting
The starting points for this type of threat hunt can be:
- indicators of attack (IoAs)
- tactics, techniques and procedures (TTPs) of a malicious actor
For structured cyber threat hunting use the MITRE Adversary Tactics Techniques and Common Knowledge (ATT&CK) framework.
- Unstructured hunting
In this case, the indicators of compromise (IoC) work as a trigger for the threat hunting process. IoCs are forensic data that help researchers find malicious activity on networks and devices. Data breaches, malware, and trojans can be among the revealed threats.
- Situation-driven
Specific business-related risks, trends, and vulnerabilities analysis that are unique to a company’s system can also be the starting point of a threat hunt.
Key Elements of Cyber Threat Hunting
The main job of a cyber threat hunter is to monitor day-to-day activities and traffic across the network.
During the proactive cyber threat hunting process, you will investigate anomalies in search of undiscovered malicious activities.
Threat hunting presents four key elements:
- Methodology. For a successful cyber threat hunting process, organizations must engage in a proactive, ongoing, and ever-evolving approach. An ad-hoc, improvised perspective will be counterproductive and only produce minimal results.
- Technology. Most organizations already have comprehensive endpoint security solutions with automated detection in place. Threat hunting works in addition to these and adds advanced technologies to find anomalies, unusual patterns, and other traces of attackers that shouldn’t be in systems and files.
- Skilled personnel. Threat hunters are cybersecurity experts who not only know how to use the security technology mentioned. They also combine a persistent aspiration to go on the offensive with instinctive problem-solving capabilities to uncover and mitigate hidden threats.
- Threat intelligence. Having access to evidence-based global intelligence increases and facilitates the hunt for already existing indicators of compromise (IOCs). Information such as attack classifications for malware and threat group identification, as well as advanced threat indicators, can help identify IOCs.
A revolutionary platform that provides security teams with an advanced risk-centric view of their entire IT landscape.
Heimdal® Threat Hunting & Action Center
Cyber Threat Hunting with Heimdal®
The Heimdal Threat-hunting and Action Center provides security teams with an advanced threat and risk-centric view of their entire IT landscape.
It also offers granular telemetry across endpoints and networks. Increased visibility enables Sysadmins to take swift and efficient decisions.
The platform is powered by an advanced XTP engine and fully integrated with Heimdal’s award-winning suite.
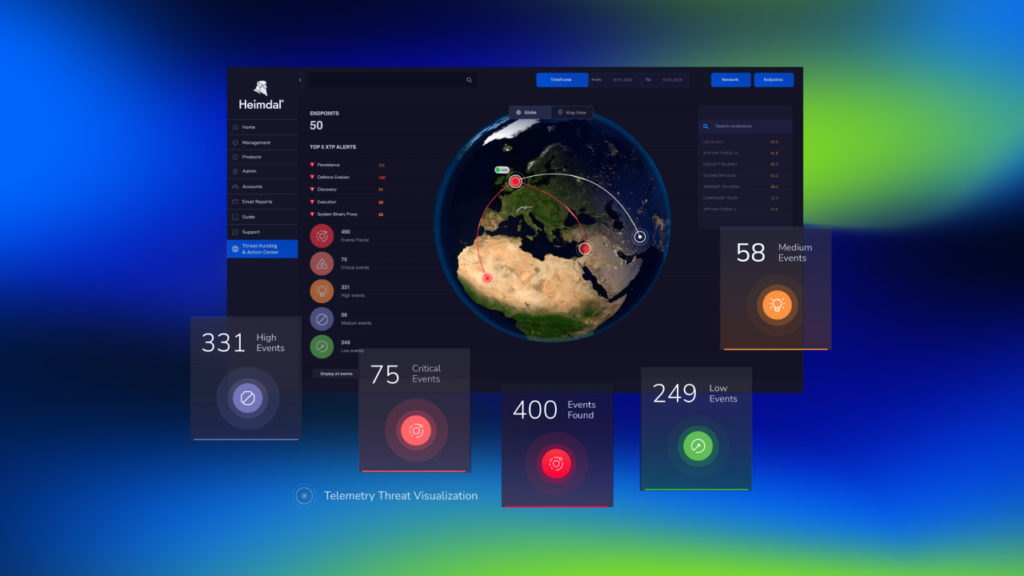
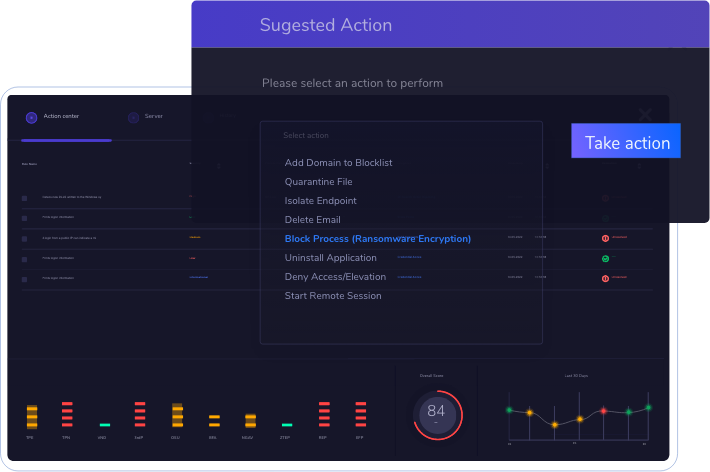
Its built-in hunting and action capabilities are easy to use and manage due to the unified interface we’ve created.
Cornerstone elements from Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) and Security Orchestration, Automation and Response (SOAR) are brought together due to a visionary approach to threat hunting.
Briefly, the Heimdal Threat-hunting and Action Center enables your SecOps team to visualize, hunt, and act using the same dashboard.
The product offers total visibility, threat intelligence put in context, and actionable tools, all in a unified and integrated platform.
Wrapping It Up
For cyber threat hunting, security experts leverage the latest behavioral monitoring tools and threat intelligence to detect suspicious patterns of behavior.
Using top threat detection solutions helps reduce average detection and response times to just minutes instead of weeks.
By using Heimdal Threat-hunting and Action Center, you can stop faster information-stealing hackers and their tracks.
If you want to know more about the cyber threat hunting process, the specialists at Heimdal Security always have your back.
Our team is here to create a cybersecurity culture to the benefit of anyone who wants to learn more about it.
If you liked this article, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and Youtube, for more cybersecurity news and topics.


 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management
 Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security










