Contents:
Endpoints are one of the hackers’ favorite gates to attack organizations’ networks. So you can figure out why we’ve created this endpoint security best practices article, to teach you how to stay safe from cyberattacks.
Did you know that threat actors need only one connected device to infiltrate a company’s network and to install malware, start phishing attacks, and steal data.
If you put all your eggs in the antivirus basket and expect to be safe, stop dreaming, you will need more to solidify your endpoint protection.
Antiviruses are a great corporate endpoint security part of the solution, but they only cover already known threats that have already penetrated the network.
To keep up and take the best decisions for your enterprise’s, customers’, and team’s data protection, make sure you are aware of what modern endpoint security solutions have to offer.
Here’s a video from our YouTube channel explaining endpoint security, its benefits, and critical components.
Threat actors can target endpoints with known, unknown, and zero-day threats, no matter if the machines are on or offline, on or off-premise.
Let’s move on and reveal the 10 endpoint security best practices we’ve promised.
Top 10 Endpoint Security Best Practices

1. Patch & Secure All Devices
Make sure that all the devices that connect to your network are professionally secured. Laptops, mobile devices, printers, smart watches, servers, you name it.
If they are allowed to connect to the enterprise’s network, track them all. Update the endpoints’ inventory every time a new device joins the network.
Beware never to miss a software update or the latest patch and upscale your patch management policy. Use an automated patching solution.
Keep track of all devices that connect to your network. Update your inventory frequently. Make sure endpoints have the latest software updates and patches.
2. Strengthen Passwords
Can’t think of any situation in which the ‘the stronger, the better’ principle wouldn’t apply. And this includes endpoint security and endpoint security solutions as well.
So, use it on your endpoints to: ask users to generate complex passwords.
Using a multi-factor authentication solution is also a good idea to help secure your endpoints.
3. Apply the Principle of Least Privilege (POLP)
Enforcing a principle of least privilege (POLP) policy helps you stop the potential infection before it gets to the whole system.
It also allows you to limit the damage and data loss, as well as track and identify where and how did the breach happen.
Evaluate and decide strictly which users really need to have admin privileges. Avoid letting unauthorized users install executable code onto the endpoints to save yourself a lot of headaches.
4. Encrypt Endpoints
Use encryption to add an extra layer of protection to your data. Encrypt the device’s disk or memory to keep the information on it safe even if the endpoint is stolen or lost.
Reading the data on it will be either impossible or inaccessible.
5. Enforce USB Port Access Policy
Printers, cameras, external drives as well as endpoints that have USB ports are a simple way of spreading malware or exfiltrating company data.
Access to USB ports should be included in the least privilege policy in order to avoid an attack.
Hackers are still keen on this old-school trick, and the consequences of this method of infecting endpoints were seen in the Turla attack on Ukraine.
6. Only Use VPN Access for Remote Endpoints
As more and more companies turn to a remote or hybrid way of working, enforcing a VPN access policy is a must. Unfortunately, DNS spoofing, DNS tunneling, Man-in-the-Middle and other external attacks could still target your devices.
So, to keep in line with endpoint security best practices, you should consider limiting VPN usage by only permitting it at the app layer.
And, of course, as stated above, when we talked about passwords, multi-factor authentication will help keep your data safe.
7. Enforce a Safe BYOD Policy
BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) is the practice where employees can use their own personal devices to connect to the organization’s network and access the resources needed for them to do their job.
Also due to remote or hybrid ways of working, BYOD has gained popularity in the past years. This brings a need to review your internal security protocol.
The safest way to deal with BYOD is to enforce a guest access account policy and strengthen your defense by adding the fourth endpoint security practice we recommended earlier.
Encryption will protect the user in case he or she loses the device.
8. White/Blacklisting Apps
Keep it clean and minimalistic. If the user doesn’t necessarily need a certain app, it is better not to authorize its installation.
This will limit the risk of becoming a victim of zero-day vulnerabilities and other threats.
Whenever granting access to any app, restrict its communication possibilities with irrelevant segments.
9. Go with the Zero Trust Security Model
Zero Trust is a security strategy based on the principle of ‘never trust, always check’. That goes for every user, endpoint, app, workload, etc.
Access should only be granted after thoroughly checking one`s identity and device. Apply the principle of least privilege with every occasion.
The main tools that you need to build a zero-trust policy are network segmentation, that isolates and prevents infection spreading, workloads security, data usage controls, and multi-factor authentication as we’ve already stated.
10. Keep Employees Security-Wise
As in many cases, education is the key and is a great prevention measure in cybersecurity as well.
Education will help a user spot a spoofed message and avoid a phishing, smishing, vishing, or CEO fraud attack. If users acknowledge what are the risks when they click on a seemingly harmless link and download some benign-looking program, they will think twice before doing it.
This will save them a lot of stress, in the long term. Also, it will save the company a lot of money it would’ve had to pay to ransomware threat groups, for example.
Most Common Endpoint Security Risks
All devices connected to a network: laptops, mobile devices, printers, etc. can and will be at some point, if not properly secured, hit by endpoint attacks.
The list of potential threats is quite extensive.
- Hidden threats in emails;
- Misleading information in data packets;
- New, unknown vulnerabilities.
For now, we’ll only mention the most common ones:
1. Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware is a type of malware which prevents organizations from accessing endpoints and data stored on them.
Ransomware attacks are on the rise, as cyber researchers and the daily cybersecurity news show every day. After they manage to breach the system, threat actors encrypt databases and other critical files.
Then they show up and demand to be paid for returning the stolen data. This kind of attack is either very expensive for the victim or a further threat to the breached enterprise’s safety.
Its reputation is also at stake if customers’ personal data are among the stolen data. The forums abound in announcements of threat actors selling private data they’ve managed to steal.
2. Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks are also very frequent because they are easy to launch and have a fair success rate. Threat actors use them to get access to login data, deploy malware, spy on the user’s activity, or gain an access point to a corporation’s network.
Lots of big brands already experienced being hit with this kind of attack. Not later than in August last year, 130 organizations, such as T-Mobile, MetroPCS, Verizon Wireless, Slack, Twitter, CoinBase, Microsoft, Epic Games, etc. were compromised in an Oktapus phishing campaign.
3. Device Loss
Losing a device is another factor that can cause data breaches. If an employee loses or has his device stolen, the consequences can be devastating.
4. Malware and Fileless Infections
Malware and fileless infections are besides ransomware, two more dangers your organization’s endpoints could face. Data stealers, rootkits, worms, trojans, and adware are among the hackers’ favorite tools.
5. Unproper Patch Management
Unproperly managing patches will permit malicious actors to exploit unpatched vulnerabilities in the systems and swiftly steal your data.
Having a solid patch management policy is one of your best bets when it comes to keeping your systems locked and safe from unknown entry points that can be leveraged by threat actors to wreck havoc.
Ideally you would want to opt for an automated patch management solution to be safer, save time, and not overload your IT team.
Even if we all know and understand that endpoint security is no longer optional, it would be wise for us to acknowledge that endpoint security is on the opposite side of the scale from operational flexibility – be discerning when it comes to selecting and configuring your endpoint security platform as you don’t want your users to become an angry mob…
Andrei Hinodache, Cybersecurity Community Leader
Endpoint Security and More: Heimdal® XDR
So thus far we have spoken about what’s best to do when it comes to endpoint security, and what to look out for, but choosing the right endpoint security solution is just as important.
You must know by now that an antivirus won’t fully solve your problem, so what you need is an advanced, modern endpoint security solution, and we got you covered.
At Heimdal® we offer you our Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) software, which will empower you to counter event the most sophisticated malware attack swiftly and seamlessly. But if you truly want more from your cybersecurity posture, our platform is the widest on the market.

Heimdal® Extended Detection and Response (XDR) is the only platform you will need to achieve unparalleled protection. Designed to protect your organization from all angles, our XDR platform will equip you with top-of-the-line solutions in:
- Endpoint Security;
- Network Security;
- Vulnerability Management;
- Privileged Access Management;
- Email & Collaboration Security;
- Threat Hunting;
- Unified Endpoint Management;
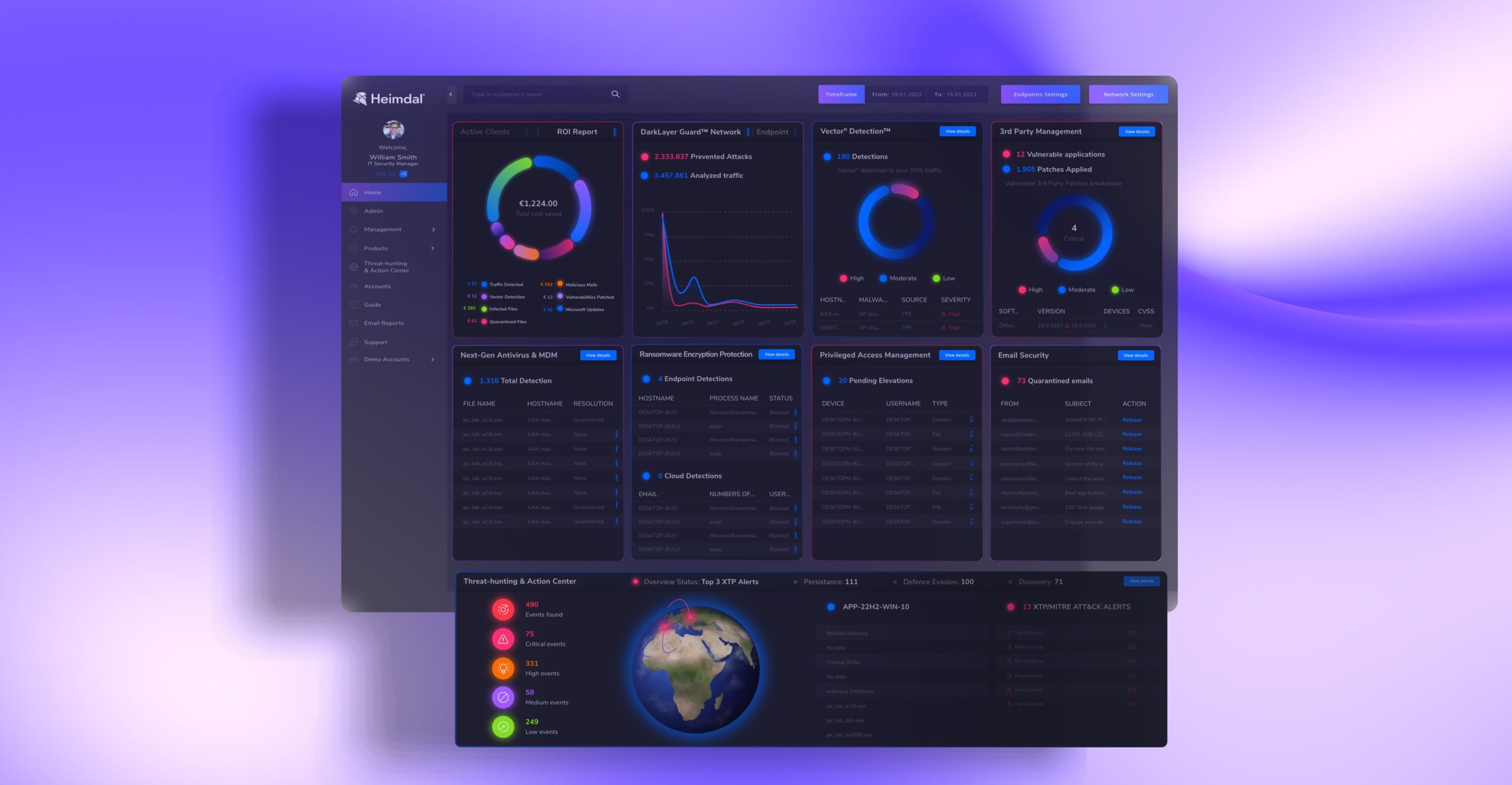
When we said we can offer an advanced endpoint security solution and more, we really mean it. You can check out the full extent of our XDR platform right here, or you can book a demo and one of our experts will guide you.










 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management  Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security











