A Patch Management Policy is a set of steps and procedures aimed to managing and mitigating vulnerabilities in your environment through a regular and well-documented patching process.
In this article, we’re going to cover the importance of patch management policies, components, benefits, and more.
Enjoy and don’t forget to download your patch management policy template!
Key Points
- Patch Management Policies Explained.
- The Importance of a Patch Management Policy.
- The Components of a Patch Management Policy.
- The Benefits of Implementing a Patch Management Policy.
- Patch Management Policy Templates.
See Heimdal's Patch & Asset Management in Action:
Schedule a Live Demo Now
Patch Management Policies Explained
Basically, a patch management policy lists the guidelines and requirements for the proper management of vulnerabilities and involves various phases such as testing, deploying, and documenting the security patches applied to your organization’s endpoints.
A vulnerability appears when a released software’s code is flawed, which means that malicious actors may exploit it.
Every time a vulnerability is discovered, it may publicly be disclosed or not.
What’s more, when a vulnerability is revealed an exploit code may also follow.
Oftentimes, exploit kits are published and sold in underground markets, or published as POCs by security researchers who attempt to demonstrate how security flaws may be leveraged.
A zero-day exploit can occur when the proof-of-concept code is revealed prior to a vulnerability being patched, which means that zero-day flaws arise after security vulnerabilities are discovered before the vendor gets the chance to fix them.
Publishing POC code for zero-day exploits has always been problematic as it leaves networks vulnerable, potentially leading to successful exploits.
The Importance of a Patch Management Policy
Implementing an effective patch management policy can help your organization minimize exposure to cyberattacks.
Besides, an effective policy will also minimize the business downtime caused by improper patching practices.
Let’s see how the implementation of a good patch management policy can help improve your business.
Effective risk management
A patch management policy eases organizations by ensuring them that risks are properly managed and the organization is at bay from cyberattacks.
Avoiding conflicts
The process of patch management is an intricate task, that can hinder processes and lead to crashes between departments over patching time.
An effective policy can ease the job of your employees.
On time and on point
Sometimes, problems can appear regarding compliance requirements.
Failing to keep your systems up to date can lead to fines, audits, or even the denial of insurance claims if your company suffers from a breach.
With a good patch management policy implemented, your company will benefit from well-documented and tested patches that update regularly.
The more effective, the happier the customers
Ff your company is selling technology, providing timely patches to manage vulnerabilities or improve performances should be a priority.
In 2 out of 3 cases, cyberattacks could have been avoided if certain patches were implemented faster, so addressing breaches and bugs efficiently will boost the satisfaction of your customers.
Good reputation
You don’t want your company to be recognized for slowly delivering updates and rarely improving products, but rather be recognized as a constant innovator and a reliable and safe service.
The Components of a Patch Management Policy
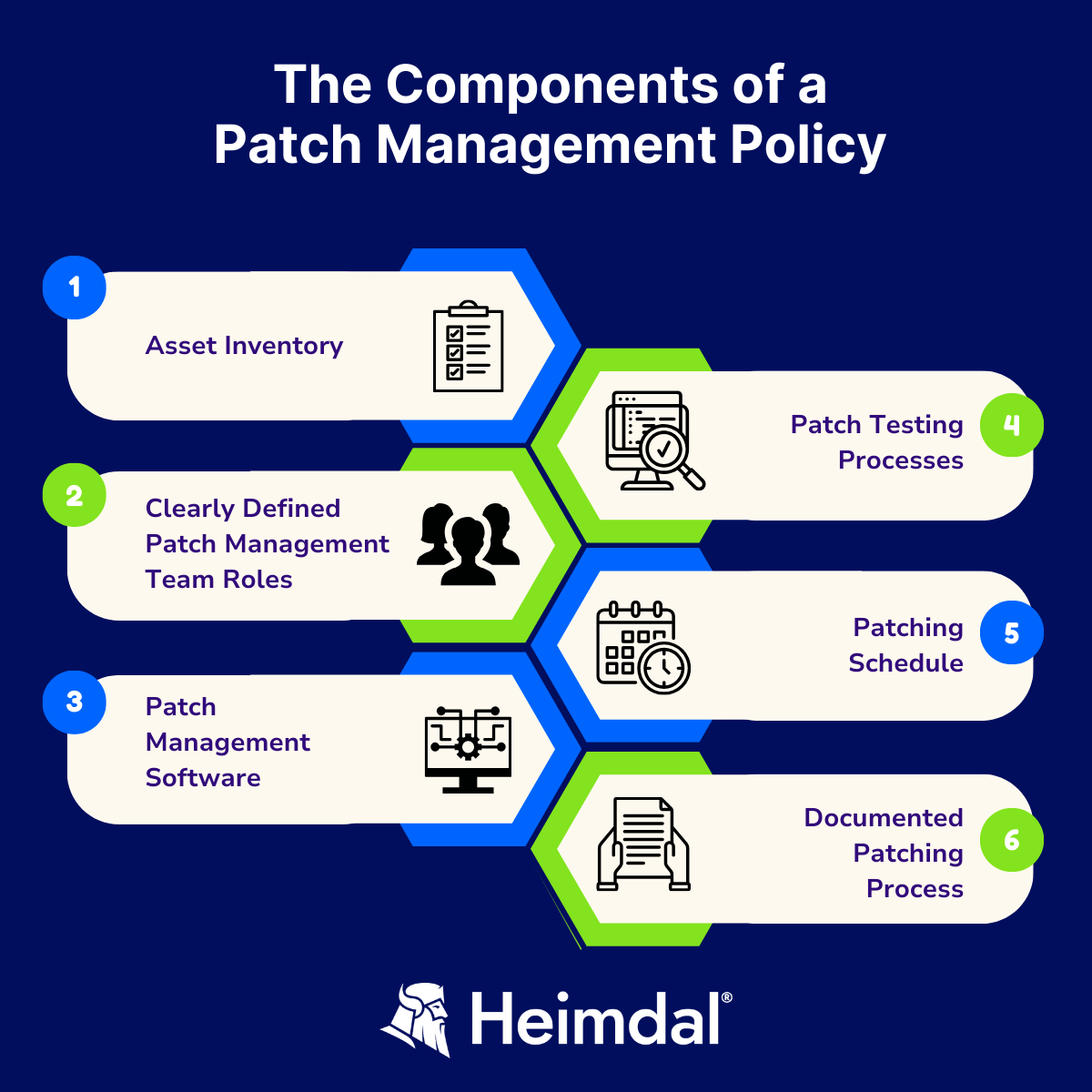
An effective patch management policy and procedure should be conducted based on several different stages.
Here are the main steps that any efficient patch management SOP (Standard Operating Procedure) should include:
Asset inventory
Having an asset inventory in place will allow you to track your hardware and software assets that need to be patched.
This way, you will discover all installed software on your devices, as well as identify all the machines owned by your organization.
Therefore, you will be certain all potential security gaps are successfully closed.
What’s more, asset inventory and tracking should be accompanied by categorization and reporting, so you have detailed info about your hardware and software available after a scan and thus gain full visibility in your environment.
Assigning patch management roles in your team
The key to an efficient patch management process is putting the right people in charge, who will be able to properly handle patch management-related aspects.
Everyone on the team should have clearly defined roles and responsibilities in the patching process.
All parties involved must know exactly who owns which patch management process.
Additionally, the main aspect that you should keep in mind is to never let your users take care of the patching themselves.
Choose the right patch management software
When deciding upon what patch management software is adequate for your organization, one vital aspect you should keep in mind is automation.
An automated patch management software will save you a significant amount of time and money, and empower your sysadmins to shift their focus from cumbersome, manual tasks to other activities.
For instance, the Heimdal® Patch & Asset Management software will enable your sysadmins to easily create an effective patch management policy to automatically install patches on your endpoints, according to a well-defined schedule.
Establishing this process will keep your endpoints up to date without the admin’s involvement.
A patch management policy can be created by defining the type of patches you want to apply – be they security patches, operating systems patches, or third-party patches.
Should you choose the manual deployment of patches, the Heimdal® Patch & Asset Management dashboard will display a list of updates that are already installed, the updates that are in the process of installing, the updates that are available to be installed, as well as the total number of updates (installed, pending, and available) per endpoint.
Test your patches
First, you should create a test environment that is a replica of the environment surrounding production, with systems that include servers covering all of your mission-critical programs.
In case you have a small organization that does not allow the testing phase to take place, in this case, you must deploy the patches to the least critical servers that could be easily recovered in case of system failure.
This means that you should establish in advance which servers and endpoints are non-critical and then conduct patch testing on them.
If there are no issues, you can continue to roll out your patches to your entire environment.
Just keep in mind that even though vendors who release patches do test them, they may not necessarily match your environment, so you should cover this aspect on your side as well.
Create a patching schedule
By developing and implementing a patch management schedule, you will be assured that all of your software is up-to-date and secured from future risks, as well as be able to monitor and decide when the updates are installed.
This way, your IT staff will be able to keep your systems clean and safe and ensure that the patches are applied regularly, in a timely manner.
Document your patching process
It’s highly important to keep a summary and overview of your patching status.
Thanks to these reports, you will have a complete picture of the patching status of each user and see if any of your endpoints are missing a specific patch.
What’s more, reports are essential for you to become fully compliant and be able to demonstrate in great detail exactly what takes place in your environment, and it gives you the chance to tweak your patch management policy.
For further information, you can check the video my colleague made regarding patch management policy.
The Benefits of Implementing a Patch Management Policy
Here are some benefits associated with working with a great patch management policy.
Reducing attack surface
Vulnerabilities may be hiding in a lot of apps without us knowing about them.
Compliance with regulations
As I explained earlier, there is a level of conformity with regulations each company must comply with.
The implementation of a patch management policy will help you accomplish the required level of conformity easily.
Better functionality
Patching can boost features as well as software problems because software patches frequently bring improved functionality.
Improved productivity
Patches can correct a variety of faults and bugs, improving system stability.
As a result of not having to deal with system faults or downtime every two days, your staff won’t waste time due to downtime and will instead be more productive for your business operations.
Spotting old software
This solution will assist you in locating the software that has not gotten updates in a considerable amount of time, allowing you to promptly replace it if your software vendor is out of business or experiencing another issue.
Automation
As explained previously, patch management is not a simple task, but it can become with the right resources and tools.
Implementing a patch management policy will remove the need for manual patching processes, leaving your IT team with more time on their hands.
Furthermore, an automatic patch management solution can improve the quality of their work even more, as it will search for missing updates regularly.
What it will also do is decrease your company’s risks related to zero-day vulnerabilities.
If you want to upgrade your patching game, you can check out my article on best patch management practices you should follow.
Automate your patch management routine.
Heimdal® Patch & Asset Management Software
Patch Management Policy Templates
This template outlines the fundamental policies governing patch management.
It includes policy statements, roles, responsibilities, and compliance standards.
This template is vital for establishing a clear framework for patch management activities.
Key Components
- Policy statements;
- Roles and responsibilities;
- Patching guidelines;
- Compliance standards.
-
Download Patch Management Policy Template (PDF)
-
Download Patch Management Policy Template (WORD)
-
Download Patch Management Policy Template (GOOGLE DOCS)
Conclusion
Since the vulnerability-discovery-to-exploitation time is becoming shorter, this puts a strain on IT managers to swiftly patch systems and keep up with the latest updates.
But defining a functional patch management policy will save you time and money and highly decrease security issues.
What’s more, as automatic patch management systems install patches periodically, they will eliminate the manual components of patch management.
Also, it will ensure the software flaws are detected as soon as they are discovered, and that they can be quickly patched via software update.
Obviously, patch management alone will not address all vulnerability-related problems, but it will act as a fundamental protection mechanism in your overall vulnerability management program.
If you liked this article, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and Youtube for more cybersecurity news and topics.


 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management
 Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security










