Contents:
The latest Data Breach Investigation Report says 30% of last year’s system intrusions involved a third-party element. It wasn’t always an unpatched vulnerability at the root of those cases, yet the numbers are high enough to make any CISO pay more attention to third-party patch management.
Third-party patch management is a key security tool in your cyber defense strategy. It covers widely used apps like Adobe Reader, Chrome, Zoom, Salesforce, etc. — software that’s often overlooked in system updates but frequently targeted by hackers. If these apps aren’t regularly patched, they can become easy entry points for cyberattacks.
This article dives into the nuances of patching third-party applications and discusses its critical role, benefits, and inherent risks.
What Is Third-Party Patching?
Third-party patch management deploys updates for software other than those of the device itself or the OS. It addresses bugs, security vulnerabilities, and adds new functionalities. This process is critical for maintaining the health and security of various software applications installed on devices.
An example of a third-party app that needs patching is Adobe Illustrator, Facebook, Spotify, etc.
Why Patching Third-Party Apps Is Important?
Patching third-party apps is vital for both cybersecurity and functionality. Third-party apps are used by millions of employees and are often targeted by threat actors due to potential vulnerabilities.
A staggering 75% of cyberattacks exploit such vulnerabilities. Regular patching of third-party apps is therefore not just beneficial but essential to maintain a robust cybersecurity posture.
Takeaways
- Third-party apps are common targets for cyberattacks.
- Significant percentage of attacks exploit these app vulnerabilities.
- Regular patching crucial for cyber defense.
- Essential for maintaining robust cybersecurity posture.
Possible Risks Associated with Third-Party Patching
While third-party patching is beneficial, it’s not without risks. Compatibility issues can arise, leading to system downtime. Patches from third-party vendors may lack the rigorous testing of major software vendors, potentially introducing new vulnerabilities.
Additionally, there’s a risk of downloading malware disguised as legitimate patches, a tactic often used by hackers.
Takeaways
- Compatibility issues leading to system downtime.
- Potential for introducing new vulnerabilities.
- Risk of downloading malware through fake patches.
- Necessitates careful vetting and testing of patches.
Automated Third-Party Patch Management and Its Benefits
Automating third-party patch management streamlines the update process. It ensures timely patch application, crucial for security.
Automated solutions handle the volume of patches efficiently, reducing the risk of human error. Other benefits include compliance with industry standards, better resource allocation, and continuous productivity.
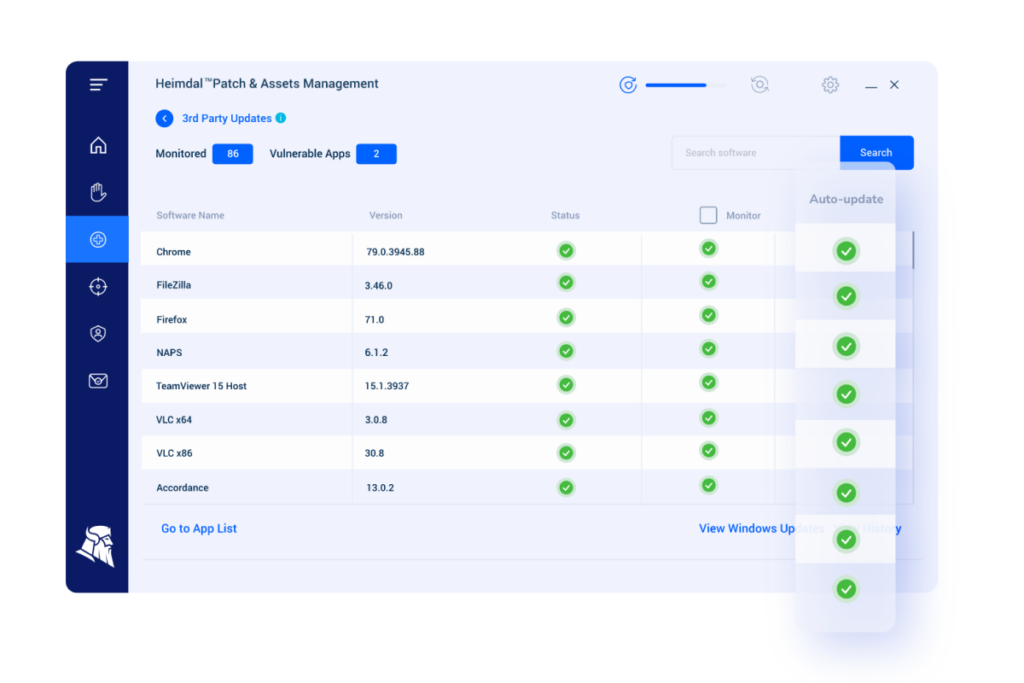
A comprehensive solution, like the Heimdal® Patch & Asset Management, provides tested and secure patches, along with additional features like software inventory and vulnerability management.
Choosing Heimdal®’s Patch Management for Your Business
When selecting a patch management solution for your business, Heimdal®’s Patch & Asset Management stands out as a robust choice. Here’s why:
- Automated Patch Deployment: Heimdal®’s solution automates the process of deploying patches, reducing the manual workload and ensuring timely updates. This feature is crucial for businesses looking to maintain security without overburdening their IT staff.
- Broad Software Coverage: A key strength is its extensive software coverage. This ensures that not only popular applications but also niche or business-specific software receive timely updates, enhancing overall security.
- Customizable Patching Policies: The ability to customize patching policies to fit specific business needs is a significant advantage. Businesses can prioritize patches based on severity, compatibility, or operational requirements, allowing for a more targeted approach to security.
- Security and Compliance: emphasizes security and compliance, ensuring that businesses meet regulatory standards by keeping their software up-to-date. This is particularly important for companies in regulated industries.
- Reduced Vulnerabilities and Risks: By keeping software consistently updated our solution minimizes vulnerabilities, reducing the risk of cyber attacks and data breaches, a vital aspect for protecting business data and maintaining customer trust.
- Reporting and Analytics: Advanced reporting and analytics capabilities, offering insights into the patching process and helping businesses understand their security posture.
- Ease of Use and Support: User-friendly interfaces combined with professional support make the adoption and utilization of the patch management system smoother, ensuring businesses can leverage the full potential of the tool without extensive technical expertise.
Takeaways
- Streamlines and secures patch application.
- Efficient handling of patch volumes.
- Ensures compliance and resource optimization.
- Reduces downtime and enhances security.
Conclusion
Third-party patch management is integral to a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy.
With escalating vulnerabilities in third-party applications, it’s imperative to include them in security plans.
Effective third-party patching reduces cyberattack risks and ensures regulatory compliance.
By adopting efficient third-party patch management, organizations safeguard against external threats and maintain smooth network operations.
Additional points to consider about third-party patch management
- Third-party management is vital to comprehensive cybersecurity.
- Addresses rising third-party application vulnerabilities.
- Reduces risk of cyberattacks.
- Ensures compliance and smooth network operations.
Third-Party Patch Management FAQ
Welcome to our Third-Party Patch Management FAQ section. Here, we address common Q&As about managing third-party updates.
What Are the Best Practices for Implementing Third-Party Patch Management?
- Prioritize patches based on risk assessment.
- Automate the patch management process.
- Regularly review and update patch management policies.
- Ensure comprehensive testing before widespread deployment.
How Can IT Administrators Effectively Monitor Patch Compliance?
- Utilize patch management tools with reporting features.
- Conduct regular audits of patch deployment.
- Set up alerts for non-compliance issues.
- Regularly review compliance reports and take corrective actions.
What Strategies Should Be Employed to Manage Patches for Remote Workers?
- Implement VPNs or secure network connections for patch deployment.
- Use cloud-based patch management solutions.
- Regularly communicate with remote workers about necessary updates.
- Ensure remote devices meet security standards for patch updates.
How to Handle Patches for Legacy Systems or Incompatible Software?
- Assess the risk of not patching versus potential system incompatibilities.
- Explore alternative security measures like virtual patching.
- Work closely with vendors for tailored patch solutions.
- Consider upgrading or replacing legacy systems that pose significant risks.
What Are the Challenges in Third-Party Patch Management and How to Overcome Them?
- Managing diverse patch release schedules: Use automated tools to track and deploy updates.
- Ensuring compatibility with existing systems: Conduct thorough testing in a controlled environment.
- Staying informed about new vulnerabilities: Subscribe to security bulletins and threat intelligence feeds.
- Balancing patch urgency with operational stability: Develop a prioritized patching strategy based on risk assessment.
Can Patch Management Be Fully Automated, and What Are the Limitations?
- Full automation is achievable but should be balanced with manual oversight.
- Limitations include potential over-reliance on automation and missing context-specific nuances.
- Regular review of automated processes is recommended to ensure effectiveness.
- Automation should be complemented with human expertise, especially for complex patches.
How Can IT Administrators Stay Informed About New Patches?
- Subscribe to vendor security bulletins and RSS feeds.
- Join relevant cybersecurity forums and networks.
- Utilize centralized patch management tools that offer update notifications.
- Attend webinars and training sessions on emerging cybersecurity trends.
What Role Does Patch Testing Play in Third-Party Patch Management?
- Patch testing is crucial to prevent compatibility issues and system instability.
- IT administrators should set up test environments that mirror live systems.
- Testing results should be thoroughly documented and reviewed before deployment.
- Continuous testing helps in adapting to new patches and changing IT landscapes.
If you liked this article, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and Youtube, for more cybersecurity news and topics.


 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management
 Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security