Contents:
The process of vulnerability management requires going through multiple steps to properly secure your systems. Together, these steps represent the vulnerability management lifecycle.
Key Takeaways:
- What Vulnerability Management Lifecycle Is;
- Key Steps in the Lifecycle;
- Automating Vulnerability Management;
- What Is Vulnerability Management.
What Is Vulnerability Management Lifecycle?
The vulnerability management lifecycle is the key process for finding and remediating security weaknesses before they are exploited. Policy definition, assessment, shielding, mitigation and monitoring are required.
Vulnerabilities can be described as being holes found in an IT system, that leave the system open to cyberattacks. Some people believe that their systems are flawless because they haven’t been affected by cyberattacks so far, which may be true in some instances, but in a lot of cases, companies do not realize that their systems may be flawed until it’s too late to act.
This is why vulnerability management practices have a crucial role in your company’s security and data privacy.
Vulnerability Management Lifecycle: Steps and Stages
The vulnerability management lifecycle can be divided into five steps, each one with its specific role in identifying, preventing, mitigating, and classifying vulnerabilities existent in your IT infrastructure.
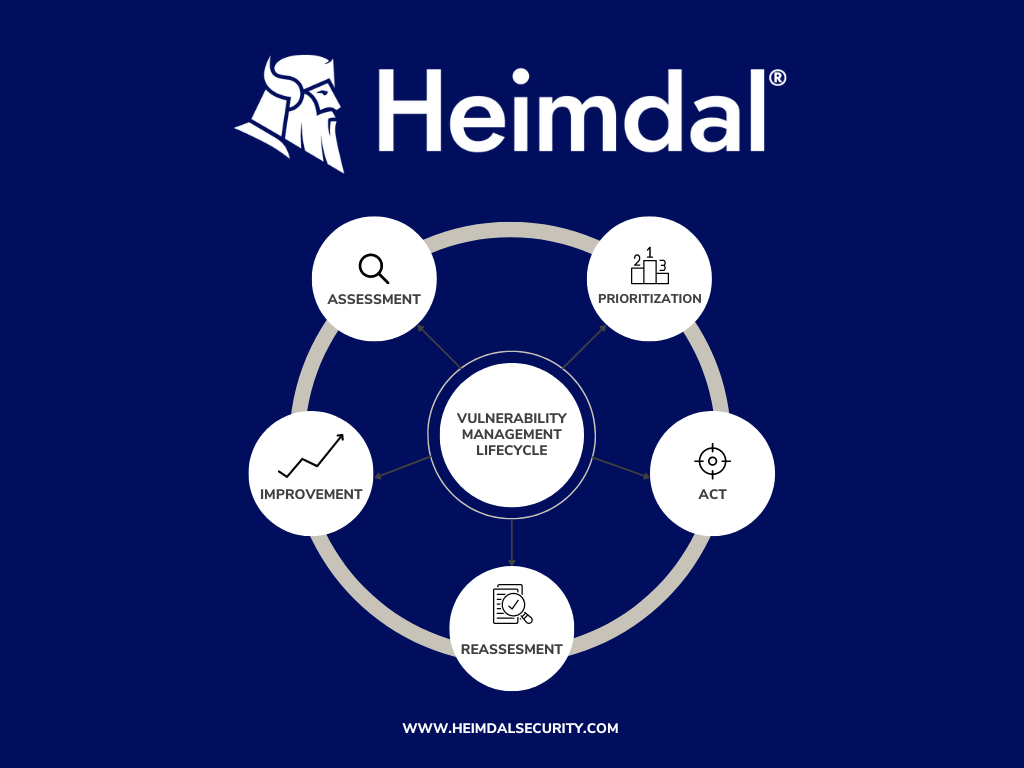
The five steps are sequential, so when the final step of the lifecycle ends, the process restarts.
Step 1: Assessment
Experts pick which parts of the system to check. They look for weaknesses and decide which needs patching, additional research, or remediation.
There are two methods for completing a vulnerability assessment: using an “agent”, which requires installing a sensor on individual assets to detect vulnerabilities or using a network-based solution, which requires all endpoints to be connected to the same network.
Step 2: Prioritization
After finding weaknesses, they rank them by importance.
With the vulnerabilities now ranked based on their importance, it is time to assess the threat to exposure of each asset. Based on the level of exposure, you can prioritize the remediation of the assets, from the most to the least exposed.
Step 3: Action
With the information gathered in the first steps, it is time to start the process of remediating the vulnerabilities. There are more ways in which you can patch vulnerabilities, based on the level of exposure:
- Low Exposure: you can accept the risks of the assets to your system;
- Mid Exposure: you can mitigate the vulnerability to stop the attacker from taking advantage of the exposure through security policies;
- High Exposure: it is recommended to remediate the vulnerability through patches.
Step 4: Reassessment
After dealing with the vulnerabilities, a reassessment is necessary. This process will tell you whether the actions you took to nullify the vulnerability have been efficient or not.
Step 5: Improvement
After following all the previous steps, you may find flaws that need to be fixed. However, manual steps take time. Heimdal® Patch & Asset Management automates this with a continuous vulnerability management program.

But before concluding this article, it’s essential to circle back to the foundation of Vulnerability Management.
What Is Vulnerability Management?
Vulnerability management is the process of identifying, preventing, mitigating, and classifying vulnerabilities in an IT system, based on the level of threat they possess.
Vulnerabilities have to be remediated as soon as they are discovered, or otherwise, threat actors may take advantage of them to enter your system and steal data. It is an important piece and acts as a cornerstone for a top-notch security strategy.
The vulnerability management lifecycle is designed to make it possible for enterprises to detect vulnerabilities in their computer system security, rank assets, evaluate, report, and rectify the flaws, and then confirm that they have been fixed.
Conclusion
Your business’s protection against cyberattacks largely depends on how you handle system vulnerabilities. Effective vulnerability management is crucial for your company’s security.

Heimdal® Patch & Asset Management
- Create policies that meet your exact needs;
- Full compliance and CVE/CVSS audit trail;
- Gain extensive vulnerability intelligence;
- And much more than we can fit in here...
If you liked this article, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, YouTube, and Instagram for more cybersecurity news and topics.


 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management
 Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security










