Contents:
Separation of privilege is a privileged access management concept and refers to splitting up tasks and assigning rights to different parts of a system.
User privileges are segmented between various users and accounts. You can also apply separation of privileges to applications, system sub-components, tasks, and processes.
This means that different persons can run various parts of the system. Each of them has access to the areas they need to do their job and nothing more.
You can also use separation of privilege at a higher level, like isolating parts of the organization into distinct security domains. Thus, if one area of the system is breached, it won’t impact the security of another. Separation of privilege helps protect data integrity and increase safety and is a PAM best practice.
Organizations must be more aware of the risks associated with privilege escalation and take steps to mitigate them. Implementing least privilege principles is a crucial security measure.
The Principle of Least Privilege (POLP) means each account has the lowest level of privileges possible. So, as a system administrator, you only increase privilege rights for those who need them to perform their jobs.
The separation of privilege principle can be applied in a variety of ways. A common example is the use of privileged accounts.
What Is a Privileged Account
A privileged account has special permission to bypass normal security controls. For example, a privileged account can view and modify any file on the system, regardless of the file’s permissions.
Privileged accounts allow administrators to perform necessary actions that would otherwise be prohibited by general security controls. However, if they are not properly managed, they can turn into a risk factor. This is why you should have a strict policy in place for who and how can access and use them. Limiting access to sensitive information for general users is critical.
There are various types of privileged accounts. They can be associated with the employee`s identity, a contractor, vendor or auditor, a machine or an application. In order to access such an account, you`ll need to use privileged credentials: passwords, SSH keys, or DevOps secrets.
Here are some of the most important privileged account types.
Domain Administrator Accounts
Admin accounts have unrestricted access to all assets. You should try to reduce as much as possible the number of domain administrator accounts. Grant access to them only to a selected few.
Privileged User Accounts
This includes accounts with a variety of privileges that can be escalated or revoked over time. This type of accounts can be made for vendors, for example.
Local Administrator Accounts
A local administrator privileged account has complete control and access rights over a computer system. Its user can install software, change system settings, and access all files on that endpoint. It can become a risk when used for everyday computing.
Non-human Automation Accounts
Non-human automation accounts are tied to systems like apps, databases, or devices and they enable shared functionalities. Using them is practical, so it is pretty common. Although they don`t usually have full admin rights, their compromise can jeopardize other network assets. If hackers breach it, they can use it for lateral movement.
Cloud Accounts
The IT team uses Cloud accounts to manage workloads, instances, and resources. Their dynamic nature requires various privilege levels. Proper management of these accounts helps identify over-provisioning, outdated, or misused accounts, enhancing operational security.
Most of the times, hackers need access to a privileged account to run malware. So, they try to gain access to privileged credentials through phishing or other social engineering techniques, to compromise a company`s system.
Why Separation of Privilege Matters
In essence, separation of privileges helps prevent system and data breaches and limit damage when incidents occur. It helps maintain the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of critical systems and data.
Privilege separation is also a key factor in preventing lateral movement attacks. IT teams implement privilege separation to make sure that even if one area is breached, the others remain secure.
Imagine a computer with two user accounts: an administrator account with full privileges and a standard account with limited privileges. If an attacker gains privileges of a standard account, the impact wouldn`t be that important. They would only have limited privileges. However, if they gain access to the administrator account, they can take over the entire endpoint.
If a person with access to an administrator account clicks on a phishing email, threat actors can gain privileges of that account. This is much more dangerous than if the employee only logs in to a basic user account.
How Separation of Privilege Works
Imagine privilege separation like a cupboard with specific, locked-up drawers for each part of an IT environment. If an intruder breaks into one of the drawers, privilege separation will stop them from moving to the next one.
Similarly, employees, software, and system processes only have access to their own drawers, which is enough for them to perform.
You can implement privilege separation in various ways and here are four of the most common:
- separate administrative account functions from each other
- delimitate administrative and standard account capabilities
- split auditing and logging capabilities within administrative accounts
- separate system functions: view, read, write, edit, execute, etc.
In addition, implementing separation of duties ensures that tasks and privileges are distributed among multiple individuals or systems, reducing the risk of misuse or error.
You can also use other methods to implement privilege separation, besides using the principle of least privilege. Two of them are role based access control (RBAC) and access control lists (ACLs).
Role based access control
This method implies that you should analyze all the roles that employees, processes and technologies have inside or outside the organization. Assess what are the sensitive data that they need access to.
Further on, make sure you understand how responsibilities and tasks corelate for each specific position. Assign users to roles with specific permissions and keep in mind that systems should be isolated from each other.
Access control lists
An access control list is a set of rules that defines the users or systems that have access to a particular object or system. When installed on routers or switches, they filter and decide which traffic can access the network.
Sys Admins use them to control permissions to a computer system or computer network. Depending on their role, users with different levels of privilege can only access files in a certain way. For example, if you login as a network administrator you get complete permissions: read, write and edit for sensitive files. If you login on a guest account, you`ll only have read permissions.
 Privilege Access Management Tool Dashboard
Privilege Access Management Tool Dashboard
What Are the Benefits of SoP?
In addition to providing security, when configurated well, privilege separation can also improve efficiency. For example, if you have a group of users who all need access to the same data, but don’t need to be able to change it, you can give them read-only access. Set their account privileges to enable them to view the data, but to need someone`s approval before making any changes.
Some of the main benefits of the separation of privileges are:
- prevents breaches to happen
- stops intruders close to the point of compromise and prevents lateral movement
- ensures that only authorized users have visibility to and can edit sensitive data
- simplifies auditing and ensures compliance
The Limitations of SoP
Separation of privilege is a security measure that requires multiple people to approve an action before it can be completed. This prevents an employee from having too much control over sensitive information or systems. However, separation of privilege can also generate problems.
If you have a two person control process for all financial transactions, it will be hard to perform if one of those people is out sick or on leave. The whole system comes to a grinding halt. In addition, separation of privilege can lead to internal power struggles and turf wars as people jockey for position and influence.
Double check how different roles and departments interact, in order to avoid blockages and frustration. When people have too much of a hard time doing their jobs because of rules, they will try to find a way to work around them. As people can be extremely creative, this might result in security breaches.
How Can Heimdal® Help?
Heimdal® Privilege Escalation and Delegation Management can both escalate and de-escalate user rights and enables you to:
- remove permanent rights and grant rights as fast as you need it
- apply the Principle of Least Privilege (POLP), so users and applications will have just enough access to complete their tasks
- block untrusted applications in 1 click, with Full Zero-Trust Execution Protection
- deny privilege elevation for vulnerabilities with CVSS scores higher than 7, on unpatched endpoints
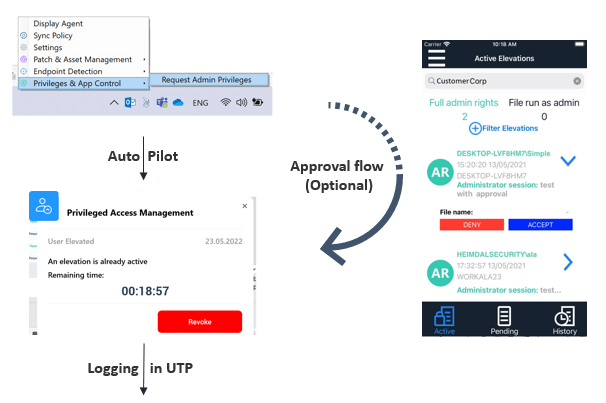
Your system administrators will be able to approve or deny user requests remotely or set up an automated flow from the centralized dashboard. Additionally, Heimdal`s privilege access management tool helps you achieve full compliance since it is NIST AC-1,6 compliant.
With Heimdal`s Application Control, you can approve or deny application execution, while also having the freedom to edit live sessions to make sure your business remains safe.

Heimdal® Privileged Access Management
- Automate the elevation of admin rights on request;
- Approve or reject escalations with one click;
- Provide a full audit trail into user behavior;
- Automatically de-escalate on infection;
In Conclusion…
Separation of privilege, dual control, and the principle of least privilege are best practices that all organizations apply. Well-implemented policies help prevent unauthorized individuals from accessing company sensitive information and reduce the impact of a successful attack.
Privileged Access Management plays a key role in protecting critical infrastructure from external and internal threats. Improper access controls can lead to data breaches and even ransomware attacks. Follow the best practices and use top cybersecurity tools when allowing system privileges to keep a safe digital environment.
If you enjoyed this article, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, or Youtube to keep up to date with everything we post!


 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management
 Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security










