Contents:
As security concerns grow, organizations need to adopt more sophisticated access control systems. These mechanisms are critical for businesses everywhere in order to guarantee that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data.
According to Future Market Insights,
The access control market is expected to strengthen its boundaries at a steady CAGR of 12.4% during the forecast period. The market is expected to hold a share of US$ 19.05 billion in 2023 while it is anticipated to cross a value of US$ 61.31 billion by 2033.
But what is the difference between popular access control systems such as Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC), and Policy-Based Access Control (PBAC)?
This article covers everything you need to know about RBAC, ABAC, and PBAC, including:
- What Is Role-Based Access Control?
- What Is Attribute-Based Access Control?
- What Is Policy-Based Access Control?
- RBAC vs ABAC vs PBAC
- Which Access Control Is Best Suited for Your Organization?
What is RBAC?
In my exploration of the ‘RBAC vs ABAC vs PBAC’ debate, I aim to clearly define each security concept and discuss its potential benefits for your organization.
In computer security, Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is an approach to restricting system access to authorized users. Let`s briefly go over some of the RBAC’s key characteristics:
- It is based on the concept of roles, which are usually assigned to users by a system administrator. A role defines a set of permissions that can be assigned to one or more users.
- RBAC can be used to implement the Principle of Least Privilege (POLP), whereby each user is only given the permissions they need to perform their job. This reduces the risk of accidental or malicious misuse of privileges.
- RBAC is also easy to manage, as it does not require knowledge of the underlying system internals. This makes it well-suited for use in large organizations with many users and complex systems.
You can find an in-depth approach to Role-Based Access Control in this article.
What is ABAC?
ABAC, or Attribute-Based Access Control, is a newer security model that is gaining popularity. It uses attributes, or pieces of information about users, to control access to resources. This means that rather than defining roles and permissions ahead of time, ABAC can dynamically control access based on who is trying to access what.
Examples of parameters in ABAC include:
- User ID/role/department
- The time, location, and device information
- The name, creator, and file type of the resource in question
ABAC has many benefits over traditional models like RBAC and PBAC. For one, it’s much more flexible and can be tailored exactly to an organization’s needs. Additionally, it’s easier to implement and manage, since there are no predefined roles or permissions.
If you’re looking for a more modern and flexible approach to security, ABAC is worth considering! Check out a more detailed analysis here.
What is PBAC?
PBAC is a type of authorization model that relies on policies. Unlike Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC), which focus on fixed traits of users and resources, Policy-Based Access Control (PBAC) takes a flexible, context-driven approach to authorization.
One advantage of PBAC is that it can be used to enforce very fine-grained access control policies. Additionally, PBAC can be used to support risk-based decision-making. For example, a policy could allow a user to read a file only if the user has been authenticated with two-factor authentication.
When it comes to the benefits of PBAC, they look something like this:
- Define and enforce security policies consistently across an organization.
- Reduce the administrative overhead associated with managing access control permissions.
- Improve security by allowing administrators to quickly and easily revoke access to resources when needed.
- Enable auditing and reporting of user activity for compliance purposes.
We discussed Policy-Based Access Control in a previous article that you can find here.
The Ultimate Comparison – RBAC vs ABAC vs PBAC
Each of these types of access control has its own strengths and weaknesses, so it’s important to understand the differences before choosing an access control model for your organization.
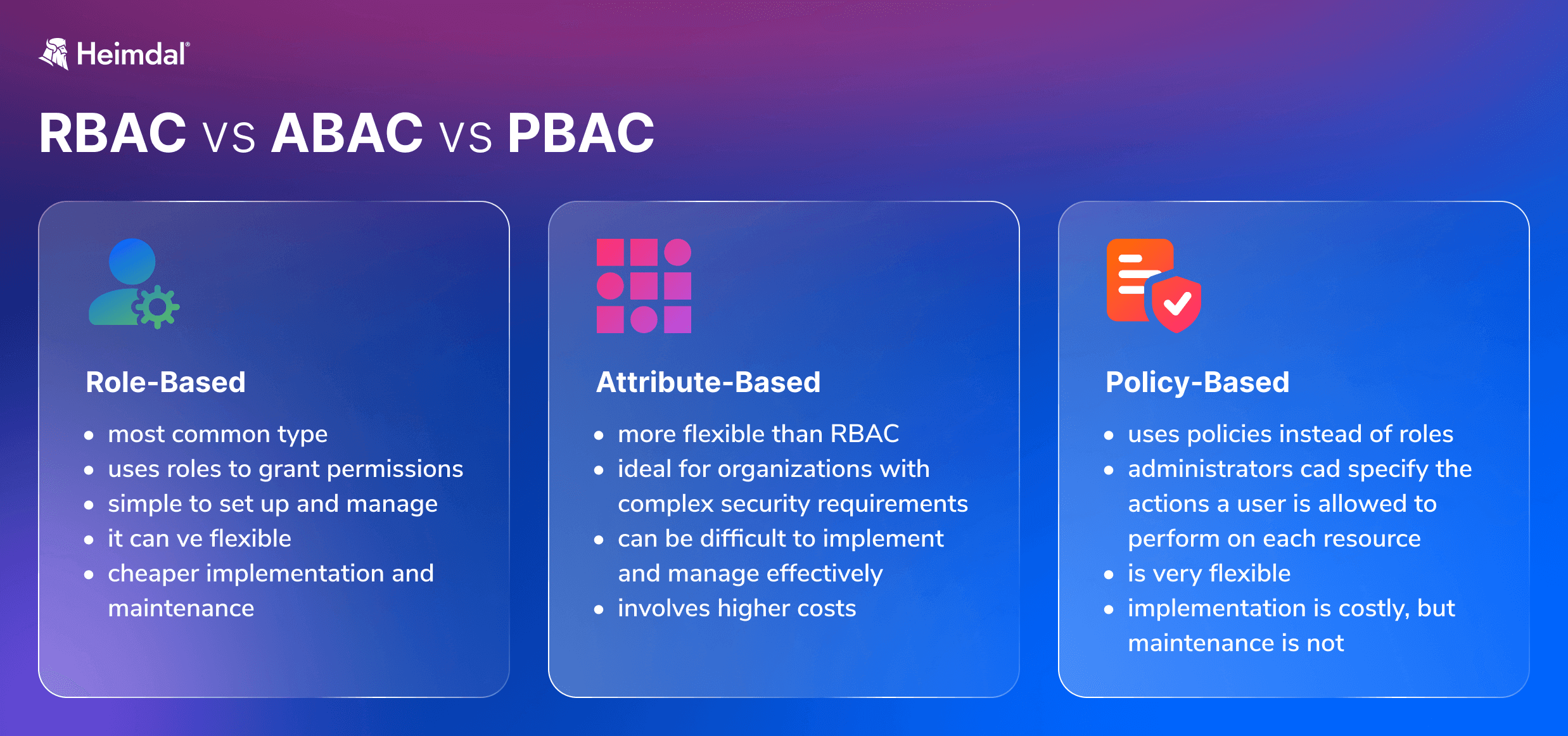
RBAC
The most common type of access control, as it uses roles to grant permissions to users.
For example, a user with the “admin” role might have permission to create, edit, and delete files, while a user with the “guest” role might only have permission to view files. RBAC is simple to set up and manage, but it can be inflexible if you need to give different levels of access to different users.
ABAC
Attribute-Based Access Control is more flexible than RBAC because, as the name suggests, it uses attributes instead of roles to determine permissions. Attributes can be anything from a user’s location or job title to the sensitivity of the data they’re trying to access. This makes ABAC ideal for organizations with complex security requirements.
As a drawback, ABAC can be difficult to implement and manage effectively. The difference between RBAC and ABAC stems from the way each method manages access. Unlike RBAC, which grants access according to predefined roles, ABAC is a security policy that relies on a combination of attributes to match users with the resources they need to do a job.
PBAC
It is similar to ABAC in that it uses policies instead of roles to determine permissions. However, Policy-Based Access Control goes one step further by allowing administrators to specify exactly what actions a user can perform on each resource. For example, an administrator could allow a user to read and write files, but not delete them. Suppose regulatory requirements or other security demands primarily determine your access controls, and you need maximum flexibility to apply those controls over different business contexts. In that case, PBAC is a good choice.
A comparison between three access control systems: RBAC, ABAC, and PBAC
How to Choose the Best Access Control System for Your Organization
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to the question of which access control model is best for an organization. The decision of which model to implement must be made based on a careful analysis of the organization’s specific needs and requirements.
When considering which model to choose, here are the most important questions that need to be thoroughly considered:
- What are the organization’s main objectives?
- How important is security?
- How well can the system effectively protect system resources without sacrificing accessibility?
- What is the nature of the data and assets that need to be protected?
- Who are the users that need access to these resources?
- What level of granularity is required in terms of user permissions?
- Are there any compliance requirements that need to be considered?
The answers to these questions will help organizations narrow down their options and choose the most appropriate access control model for their specific needs.
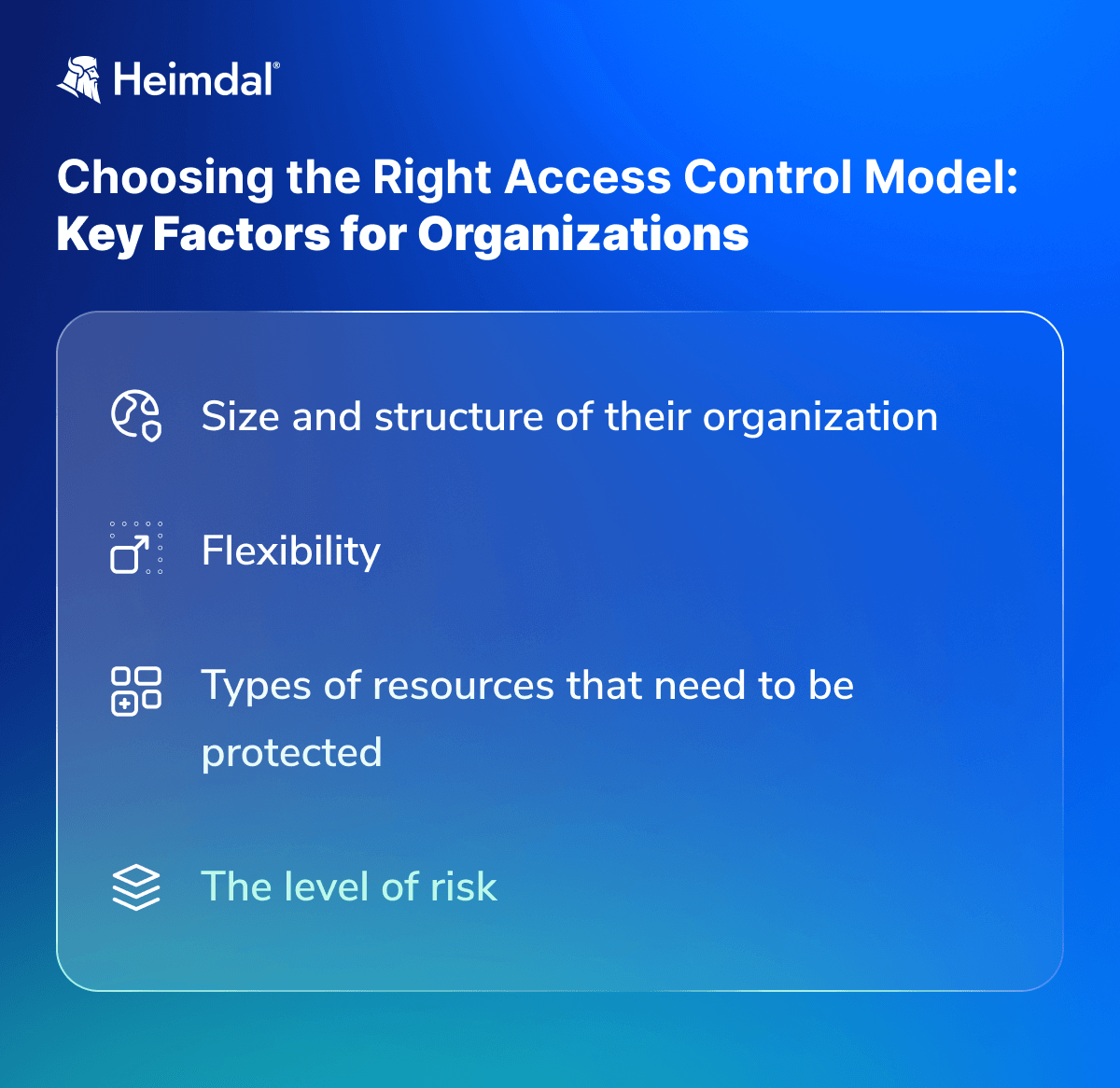
Here are a few factors to consider:
- First of all, the size and structure of your organization should play an important role in the decision-making phase. If you have a large and complex organization, then a more sophisticated security model, such as ABAC or PBAC, may be more appropriate. If you have a smaller and simpler organization, then a less complex security model, such as RBAC, may suffice.
- With modern IT infrastructure, flexibility is a huge benefit as roles and contexts change. Some organizations require access control systems that can adapt to changing conditions daily, while others prefer rigid, secure approaches.
- The second factor to consider is the types of resources that need to be protected. If sensitive data needs to be tightly controlled, then a more fine-grained security model, such as ABAC or PBAC, may be more appropriate.
- Another factor to consider is the level of risk involved. If you choose between a more robust security model, such as ABAC or PBAC, or a less robust one in the shape of RBAC, keep in mind that an overly rigid access control system can prove to be more of a detriment than a benefit if not configured properly, regardless of how secure it is.
4 Aspects to Consider When Choosing between RBAC, ABAC, and PBAC
In the end, choosing the right security model depends on your specific organization’s needs. What works for one organization might not work for another.
How Can Heimdal® Help Businesses?
Our Privileged Access Management solution allows administrators to manage user permissions easily. Your system admins will be able to approve or deny user requests from anywhere or set up an automated flow from the centralized dashboard. Another noteworthy characteristic of Heimdal`s Privileged Access Management (PAM) solution is that it automatically de-escalates on threat detection, making it the only one on the market with such capabilities.
Further, you can add the Application Control module into the mix, and you will be able to perform application execution approval or denial or live session customization to further ensure business safety.
Managing user permissions and access levels is not only a matter of saving your employees’ time but also a crucial cybersecurity infrastructure project.

Heimdal® Privileged Access Management
- Automate the elevation of admin rights on request;
- Approve or reject escalations with one click;
- Provide a full audit trail into user behavior;
- Automatically de-escalate on infection;
Wrapping Up…
Keeping implementation and maintenance costs low while protecting your data is possible with the right solution. While all of these frameworks facilitate authorization and limit access to digital resources, their functioning significantly impacts enterprise cybersecurity and related expenditures. RBAC, ABAC, and PBAC all have their advantages and disadvantages depending on the situation. It is important to consider which would be best for your specific needs when making a decision.
Hopefully, this article has helped you understand the differences between these three types of access controls so that you can make an informed decision about which one will serve your business’s security needs most effectively.
If you liked this article, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube, for more cybersecurity news and topics.










 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management  Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security








