Contents:
The importance of Windows patch management in the context of modern cybersecurity cannot be overstated.
This article provides a comprehensive guide, exploring every facet of managing updates for Windows systems, including an overview of third-party patch management tools.
Key Points
- What Is Windows Patch Management?
- Why Microsoft Patch Management Software Is Essential for Windows Devices.
- What Is a Patch?
- The Windows Patch Management Process.
- Benefits of Managing Windows Patches.
- Challenges in Windows Patch Management.
- Automated Patch Management Limitations.
- Windows Patch Management Best Practices.
- How to Implement Windows Patch Management Using Heimdal® Patch & Asset Management?
- FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions).
What Is Windows Patch Management?
Windows patch management is an essential IT process that involves managing the patches and updates to Windows operating systems and applications across all Windows devices.
Such updates are essential for maintaining security, optimizing performance, and fixing bugs in the system.
Regular patching is crucial for ensuring operational efficiency and strengthening cybersecurity defenses.
Section takeaways:
- Multiple Methods – Utilize Windows Update, WSUS, and third-party tools, depending on the organization’s size and needs.
- Centralized Control – WSUS offers centralized control for larger networks, ensuring consistency in patch deployment.
- Comprehensive Solutions – Third-party tools provide comprehensive coverage, including patches for non-Microsoft software.
- Customization and Control in the Endpoint Management System – Choose the method that offers the right level of customization and control for your organizational needs.
- Hybrid Approaches – Consider a hybrid approach for complex environments to cover all patch management requirements effectively.
Why Microsoft Patch Management Software Is Essential for Windows Devices
Microsoft patch management software plays a critical role in keeping your Windows devices secure and compliant.
By centralizing updates and allowing IT teams to deploy patches quickly, a patch management tool helps close vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
Whether you use native Microsoft solutions or third-party options, streamlining the patching process is key to maintaining endpoint health and reducing downtime.
What Is a Patch?
A software patch is an update released to address specific issues in a program, such as bugs, security vulnerabilities, or performance enhancements.
Microsoft frequently releases patches to improve its software’s performance and security, ensuring that systems are protected against the latest security risks and function optimally.
Types of Windows Patches
Windows patches come in various forms, each serving a distinct purpose.
Critical updates address significant vulnerabilities that could be exploited by cyber threats.
Security updates are released to specifically target known security flaws and mitigate potential threats.
- Critical Updates.
- Security Updates.
- Microsoft Quality Updates.
- Updates.
- Update Rollups.
- Definition Updates.
- Feature Updates.
- Drivers.
- Tools.
The Windows Patch Management Process
The Windows patch management process is a crucial component of maintaining system security and functionality.
It involves various strategies and tools to ensure that all Windows systems in an organization are kept up to date with the latest patches and updates.
The process can be conducted through several means, each catering to different needs and scales of operation.
Windows Update
- Individual Systems – Windows Update is typically used for individual systems or small networks. It provides automatic software updates and security updates to the OS and other Microsoft products.
- User-Friendly – This method is user-friendly and requires minimal technical knowledge, making it suitable for personal use or small businesses.
Windows Server Update Services (WSUS)
- Centralized Management – WSUS allows for centralized management of updates in a corporate environment. It gives IT administrators control over the deployment of updates within their network.
- Customization – Administrators can choose which updates are approved for installation, schedule updates, and receive reports on update compliance across the network.
Third-Party Patch Management Tools
These tools are designed to cover not only Windows patch management but also updates for third-party patching, offering a truly comprehensive patch management software solution for all endpoints.
Many third-party tools offer advanced features like automated patch deployment, prioritization of critical updates, and detailed reporting.
Combining Methods
In larger organizations, a combination of these methods might be used to achieve optimal patch management.
This could involve using WSUS for Windows and third-party tools for other software.
Patch Tuesday
Patch Tuesday is a well-known term in the IT world, referring to the specific day each month when Microsoft releases software updates.
Benefits of Managing Windows Patches
Effective Windows patch management brings critical benefits, enhancing both system security and operational efficiency.
Regular patching not only fortifies defenses against cyber threats but also ensures compliance with industry standards and improves overall system performance.
Section Takeaways
- Security: Regular patching is essential for protecting systems from cyber threats and vulnerabilities.
- Performance: Patches improve system efficiency and reduce the likelihood of crashes and slow-downs.
- Compliance: Staying updated with patches ensures adherence to regulatory standards, avoiding potential penalties.
- Cost-Efficiency: Proactive patch management can save costs by preventing expensive IT emergencies and system downtimes.
- Hardware Longevity: Regular patching contributes to extending the life of hardware components.
- Zero-Day Protection: Patching reduces the risk of zero-day attacks by keeping systems updated against recent vulnerabilities.
- User Satisfaction: A well-maintained system enhances the overall user experience, increasing productivity and satisfaction.
- Innovation Readiness: Regular updates prepare systems to integrate new technologies and features, keeping the organization at the forefront of technological advancements.
1. Enhanced Security
The most significant benefit of a diligent Windows patch management process is the enhancement of system security.
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity threats, keeping systems up-to-date with the latest patches is critical.
Each patch addresses specific vulnerabilities that, if left unchecked, could be exploited by cyber attackers.
These vulnerabilities range from minor loopholes to critical security breaches that can compromise the entire network. By applying patches regularly, organizations can:
- Protect against malware, ransomware, and other malicious software.
- Close security gaps that could be exploited by hackers.
- Prevent data breaches that could lead to significant financial and reputational damage.
- Improved System Performance.
Patches often include improvements and optimizations that enhance the overall performance of the OS and applications.
This means that regular patching can lead to:
- Faster system response times.
- Reduced crashes and system hang-ups.
- Enhanced efficiency in software and hardware interaction.
2. Compliance with Regulations
Many industries are governed by regulatory standards that require the maintenance of a secure and updated IT environment.
Regular patch management ensures compliance with these standards, helping organizations avoid legal and financial penalties.
This is particularly critical in sectors like healthcare, finance, and government, where data privacy and security are paramount.
3. Reduced IT Costs
While it might seem counterintuitive, effective patch management can lead to long-term cost savings.
By proactively addressing potential issues, organizations can avoid the costs associated with system downtimes, data breaches, and expensive emergency IT interventions.
4. Extended Hardware Lifespan
Regular patching can also contribute to extending the lifespan of hardware.
By optimizing software performance and ensuring compatibility, patches can reduce the strain on physical components, thus prolonging their usability.
5. Protection Against Zero-Day Attacks
Zero-day attacks exploit unknown vulnerabilities.
Regular patching reduces the window of opportunity for such attacks by ensuring that systems are safeguarded against recently discovered vulnerabilities.
6. Enhanced User Experience
For employees and end-users, a well-maintained system translates to a smoother, more efficient user experience. This can lead to:
- Increased productivity.
- Reduced frustration with IT systems.
- A more streamlined workflow.
7. Support for New Technologies and Features
Patches often introduce support for new technologies and enhanced features, especially in Windows machines. Staying up-to-date with patches means organizations can leverage these advancements for improved business processes and competitive advantage.
Challenges in Windows Patch Management
In Windows patch management, organizations face significant challenges, including managing timely updates and addressing compatibility issues.
These challenges are crucial to overcome for maintaining robust security and system integrity.
1. Balancing Timing and Operational Needs
One of the primary challenges in Windows patch management is timing.
Finding the right balance for rolling out updates is crucial to minimize disruption.
This involves:
Scheduling Updates
Timing the deployment of patches to avoid peak business hours.
Minimizing Downtime
Ensuring that updates do not significantly interrupt business operations.
Emergency Patching
Dealing with the need to immediately apply critical patches, which can disrupt planned workflows.
2. Complexity of Patch Management
The process of patch management is often complex, involving various steps that can pose challenges:
- Identifying the Right Patches. Deciding which patches are relevant and necessary for specific systems.
- Patch Testing. Ensuring that new patches do not cause system instability or incompatibility issues.
- Managing Diverse Environments. Tailoring patching strategies to diverse IT environments with different operating systems and software.
3. Resource Constraints
Many organizations face constraints in terms of resources, which can hamper effective patch management and the patching process:
- Limited IT Staff: Smaller teams may struggle to keep up with the volume of patches released.
- Budget Limitations: Budget constraints can limit the ability to implement advanced patch management tools or solutions.
4. Ensuring Compliance
Ensuring compliance with various standards and regulations while managing patches can be challenging, particularly for industries that are heavily regulated.
5. Patch Compatibility Issues
Not all patches are universally compatible with every system configuration, leading to potential issues:
- Software Incompatibility. Patches might not be compatible with certain applications or custom software.
- Hardware Limitations. Older hardware might not support the latest patches, leading to security vulnerabilities.
- User Resistance. Often, users may resist installing updates due to concerns about changes in functionality or usage disruptions.
Automated Patch Management Limitations
While automated tools simplify patch management, they are not without their limitations.
These include:
- Overdependence on Automation. Overreliance on automated tools can lead to missed manual checks and balances.
- False Positives/Negatives. Automated systems might incorrectly identify or overlook certain patches.
- Cybersecurity Threats. The ever-evolving nature of cybersecurity threats means that patch management strategies must continuously adapt, which can be challenging.
Windows Patch Management Best Practices
Adopting best practices in Windows patch management is essential for safeguarding IT infrastructure and optimizing system performance.
These practices, including automation and regular testing patches, play a pivotal role in maintaining a secure and efficient network environment.
As cybersecurity expert Joseph Shenouda says:
The burden that comes with manually patching systems falls off your shoulders once you embrace Patch automation.
Section takeaways
- Embrace Automation. Automating patch management enhances efficiency and reduces human error.
- Prioritize Risk. Focus on patches that address the most critical vulnerabilities first.
- Test Before Applying. Conduct thorough testing of patches in a controlled environment.
- Develop Clear Policies. Maintain comprehensive and clear patch management policies.
- Educate User. Keep users informed and educated about the patch management process.
- Conduct Regular Audits. Regularly audit the patch management process for compliance and effectiveness.
- Integrate with Security. Ensure patch management is part of a broader security strategy.
- Prepare for Recover. Have robust backup and disaster recovery plans in place.
- Collaborate with Vendors – Work closely with vendors to understand and manage patches effectively.
1. Emphasizing the Role of Automation
Automating the patch management process is one of the most crucial best practices. Automation streamlines the process, ensuring timely updates and reducing the likelihood of human error. This involves:
Utilizing Patch Management Software
Implementing software that automatically detects, downloads, and installs necessary updates.
Scheduled Updates
Configuring updates to be deployed during off-peak hours to minimize disruption to operations.
Consistency and Reliability
Ensuring that patches are consistently applied across all systems to maintain network integrity.
2. Prioritization of Patches
With the sheer volume of patches released, prioritizing which patches to apply first is critical. This involves:
Risk Assessment
Risk assessment consists of evaluating the severity of the vulnerabilities each patch is meant to address.
Critical Patches First
Applying patches that address critical vulnerabilities as soon as possible.
3. Testing Before Deployment
Before deploying patches network-wide, it is best to test them in a controlled environment. This helps to:
Identify Potential Issues
Ensuring that patches do not cause system instability or compatibility problems.
Minimize Disruption
Reducing the risk of widespread issues within the live environment.
4. Comprehensive Patch Policies
Developing and maintaining clear patch management policies is essential. These policies should:
Define Procedures
Outline how and when patches are to be applied.
Assign Responsibilities
Clearly state who is responsible for various aspects of patch management.
Establish Guidelines for Exceptions
Provide procedures for handling exceptions, such as incompatible patches.
5. User Education and Communication
Keeping users informed about the importance of patch management and how it affects them is vital.
This involves:
Regular Communication
Updating users on upcoming patches and any potential impact.
Training Sessions
Providing training on the importance of updates and how to handle them.
6. Regular Audits and Compliance Checks
Regularly auditing the patch management process ensures compliance with internal policies and external regulations. This involves:
- Reviewing Patch Logs. Checking patch history to ensure that no systems are overlooked.
- Compliance Reporting. Generating reports that demonstrate compliance with regulatory standards.
- Integration with Overall Security Strategy. Patch management should be integrated into the broader IT security strategy. This ensures that it works in tandem with other security measures to protect the network.
6. Backup and Disaster Recovery Planning
Ensuring that there are adequate backup and recovery plans in case a patch causes system issues is crucial for minimizing potential damage.
7. Vendor Management
Working closely with vendors to understand the patches they release and their implications can enhance the effectiveness of patch management.
How to Implement Windows Patch Management Using Heimdal® Patch & Asset Management?
Patch management for Windows OS can become significantly more efficient when using a unified management tool.
Heimdal’s solution notably shortens the waiting time from vendor release to deployed patch. With Heimdal® Patch & Asset Management you can apply Windows patches through our Microsoft update module quicker than you’d say “patch” because our product provides the shortest vendor-to-end-user waiting time.
This means that every patch is ready to be deployed (being already tested, adware-cleaned, and repackaged) in less than 4 hours from the release in your Heimdal® Cloud.
Our Heimdal® Patch & Asset Management, will help you deploy patches automatically, will see any software assets in your inventory, alongside their version and number of installs, deploy updates for Windows, Linux operating system, macOS, third-party, and custom software to your endpoints anywhere in the world, and create inventory reports for accurate assessments and compliance demonstrations.
Everything can be easily controlled from our intuitive dashboard.
How does the Patch & Asset Management – Microsoft Updates module work?
The Microsoft-Updates Module looks for both the installed and available Windows Updates on an endpoint, then this will be reported to the Heimdal® Dashboard, where the role of the administrator comes into play as he can perform deployment of available Windows Updates using 2 methods: manual deployment and installation or automatic deployment and installation.
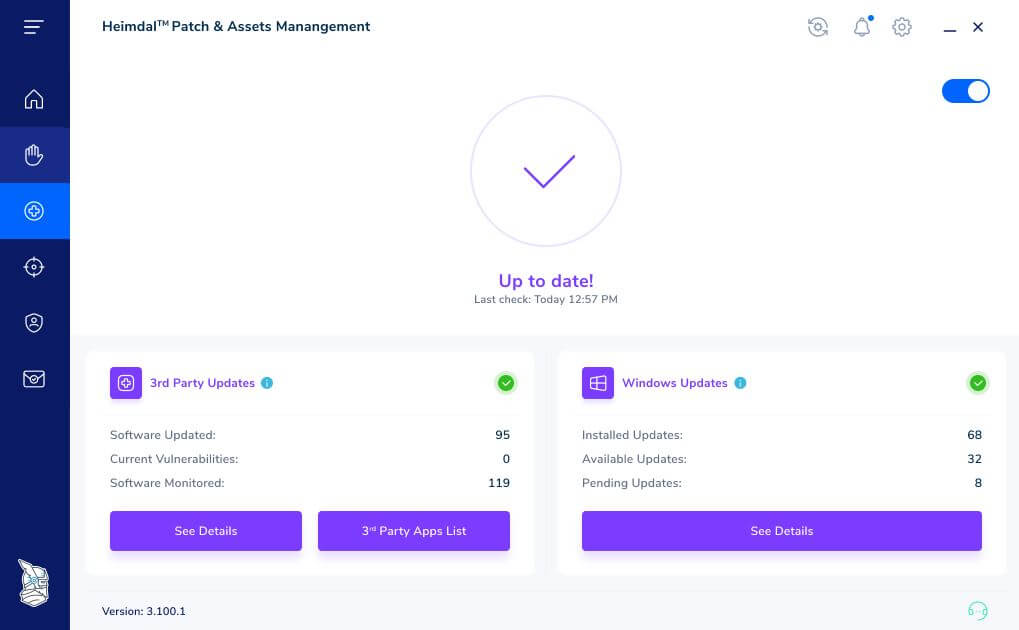
In the Heimdal® Agent, you can view installed, pending, and available updates across all Windows server operating and desktop systems, supporting full visibility into your patch lifecycle.
The Microsoft Update view will show you:
- Installed Windows updates, pending and available with information about Title, KB, Severity, Endpoints, Servers, CVE, CVSS, Products, and Categories.
- Updates per endpoint with data related to Hostname, Username, and Updates per Endpoint.
- A compliance view with information about Hostname, Username, Number of Updates, Highest Severity, Operating System, Oldest patch date, Last Seen, and Status.
Last, but not least, our tool makes deploying patching effortless, even Microsoft Optional Quality Updates that are usually hard to implement, showing a challenging management nature. Our patch management tool also lets you patch software across other operating systems, such as macOS and Linux operating system.
These are just some features of Heimdal®’s tool on patch & asset management. You can find more by visiting our website!
Conclusion
In conclusion, Windows patch management is a critical aspect of maintaining software integrity and security in any organization.
With the right strategies and tools, such as Heimdal®’s solutions, managing patches becomes a more manageable and efficient process.
Frequently Asked Questions (F.A.Q.)
What Is Windows Patch Management?
Windows patch management is the process that involves managing the updates and patches for Windows operating systems and applications.
Such updates are essential for maintaining security, optimizing performance, and fixing bugs in the system.
What Are Some Best Practices for Windows Patch Management?
- Automation: Using patch management software to automate the process of detecting, downloading, and installing updates.
- Prioritization: Assessing the severity of vulnerabilities and prioritizing critical patches.
- Testing: Testing patches in a controlled environment before wide deployment to avoid system instability or compatibility issues.
What Is WSUS Patch Management?
WSUS is essentially just a role assigned on any Windows Server.
Through the internet, the WSUS server obtains patches and updates from Windows Update.
Administrators must authorise patches for deployment after they have been downloaded to WSUS.
If you liked this article, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and Youtube, for more cybersecurity news and topics.










 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management  Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security








