Contents:
In this article, we’re going to tackle another data security-related topic – SOAR vs SIEM. So, without further ado, let’s see who wins today’s match. Enjoy!
Key Takeaways:
- Complementary Roles of SOAR and SIEM;
- Distinct Features and Functions;
- Pros and Cons of Each System;
- Deployment Considerations;
- Integration and Collaboration.
SOAR vs SIEM
So, who would win if we were to pit SOAR vs SIEM? To make a long story short, there’s no winner here, simply because there’s no competition. SIEM and SOAR are, what you might call, the two sides of the same coin which, in our case, is security. To better understand their similarities, differences, and what each side brings to the table, let’s list their features and capabilities.

At first glance, one would argue that there’s no discernable difference between SIEM and SOAR. Let’s try sharpening the contrast a bit with some pros and cons.


One final aspect to take into consideration is coverage. Both SIEM and SOAR are designed to operate in on-prem setups and in the cloud. Below you’ll find the pros and cons associated with each approach.
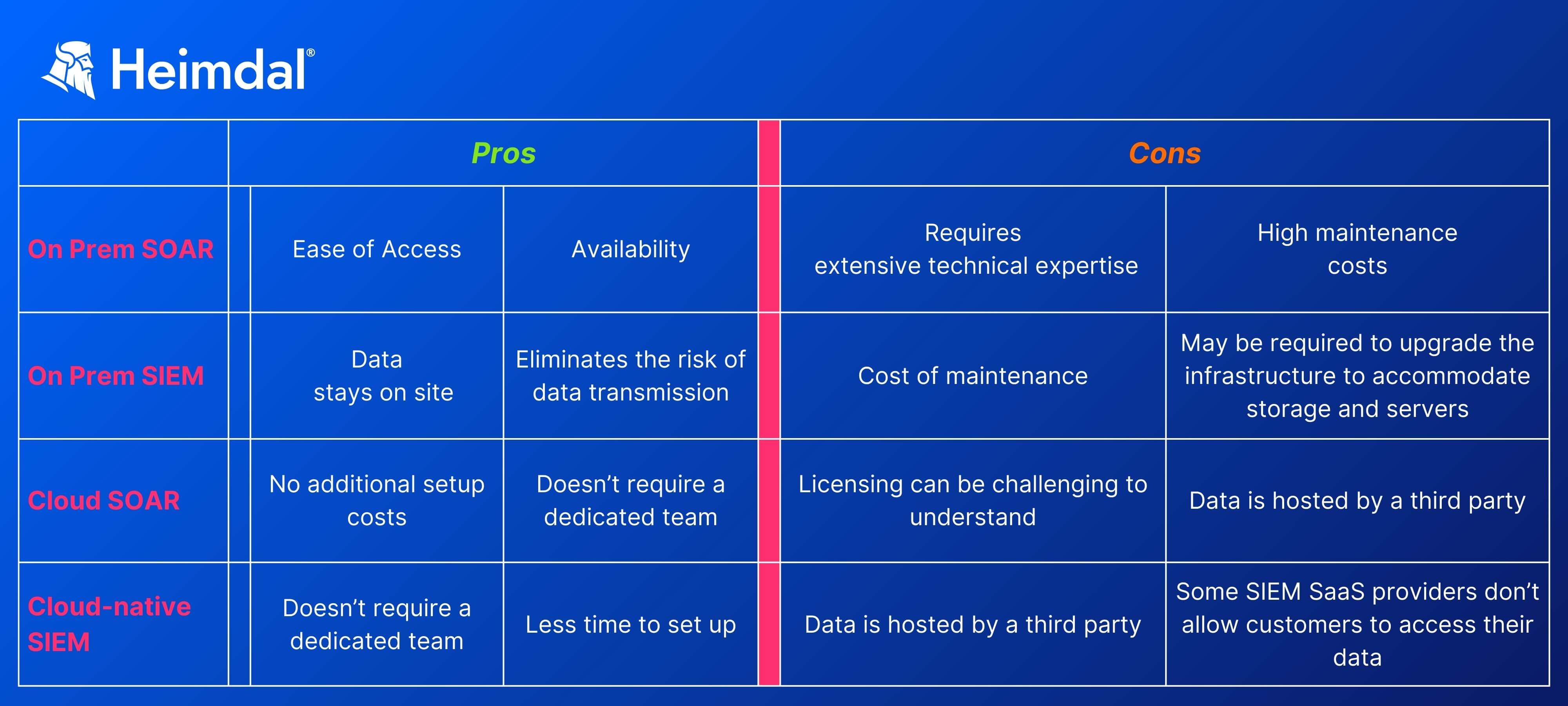
To sum everything up: in the SOAR vs SIEM contest, both of them win. Keep in mind that both of them have their roles set in stone: SIEM is all about data aggregation and alerting, while SOAR helps us set in motion all the security cogs needed to prevent, contain, or mitigate a threat.
Before concluding this article, it’s essential to circle back to the foundation of SOAR and SIEM.
What is SOAR?
A little refresher on SOAR – coined by Gartner, this concept is used to describe a security-centric architecture that focuses on Incident Response (IR) via automated workflows, processes, and procedures.
Intel-gathering is the cornerstone of any solution that falls under SOAR; this feature empowers the teams to gather threat intelligence from multiple sources, including SIEM. Oftentimes, SOAR(s) are deployed on top SIEM solutions, thus leveraging their data-gathering and automatic signaling abilities.
For additional information on how SOAR works and how it can add to your overall security, be sure to check out my other article on Security Orchestration Automation and Response Basics.
One more aspect I want to add before moving on to SIEM – SOAR doesn’t replace SIEM in the same manner as SIEM can’t replace a SOAR solution. Both ends were engineered to work in tandem; SIEM is the data mining and signaling component, while SOAR provides the necessary, interventional framework.
What is SIEM?
SIEM-based solutions are employed to aggregate and normalize data from across multiple sources.
For instance, your run-of-the-mill SIEM can gather firewall logs, proxy or web filtering logs, logs from miscellaneous security solutions (e.g., Sandbox, DLP, IPS/IDS, router NetFlow, etc.), network telemetry (i.e., data generated by products that do Deep Packet Inspection), Windows auth, information produced by endpoint-based security products, and, threat intelligence.
Now, before I scoot, here are a couple of things you may want to try out if you’ve decided to take the SIEM and SOAR road.
Baselines and standards
To have a detection & response baseline, you’ll need some standards. The same rules of engagement apply to both SIEM and SOAR. In the case of the former, you’ll need to set detection and alarm thresholds. For the latter, be sure to iron out those workflows before they go online.
Data Hygiene
Don’t let that data simply pile out. Put in place purging procedures and figure out what to discard and what to keep.
Human factor
Automation may be what defines both SIEM and SOAR, but this doesn’t leave the human factor out of the picture. Most of the fine-tuning and setup must be done manually.
SOAR + SIEM
Sounds like overkill, especially when you consider the financial aspects, but you can run SOAR and SIEM at the same time. Heimdal®’s eXtended Detection and Response (XDR) centralized monitoring and incident response hub brings you the same detection, response, and mitigation capabilities as any SIEM+SOAR combo.
Conclusion
The SIEM+ SOAR duo is an incredibly flexible threat identification and data gathering tool that will aid you in your threat-hunting effort, adding value to your company, while driving down costs.

- Granular telemetry across endpoints and networks.
- Equipped with built-in hunting and action capabilities.
- Pre-computed risk scores, indicators & detailed attack analysis.
- A single pane of glass for intelligence, hunting, and response.
If you liked this article, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, YouTube, and Instagram for more cybersecurity news and topics.


 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management
 Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security











