Contents:
Also known as operational security or procedural security, OPSEC is a security and risk management process that prevents sensitive information from falling into the hands of malicious actors. Originating in the military, OPSEC became a popular practice in the private sector as well, helping organizations to protect customer data, address cyberespionage, and information security.
OPSEC is also defined as being a method for spotting seemingly innocent behaviors that can unintentionally give away sensitive information to a malicious actor.
The use of risk management to identify potential risks and vulnerabilities in business operations, operational procedures, and the software and hardware that employees utilize is a vital component of OPSEC.
Why Is OPSEC Important?
Operational Security challenges IT and security teams into viewing their operations and systems from the perspective of a threat actor. OPSEC teams can identify problems they may have overlooked by viewing systems and operations from a different angle, which can be essential to putting the right countermeasures in place to protect their most sensitive data.
To avoid the accidental disclosure of sensitive or confidential information, a robust OPSEC program is essential. Organizations can use it to keep the specifics of their upcoming operations, capabilities, and goals private. The secret to accomplishing this, though, is knowing what this data is about, where it is kept, what level of security is used to secure it, what would happen if it were compromised, and how the organization would react.
The OPSEC Process Explained
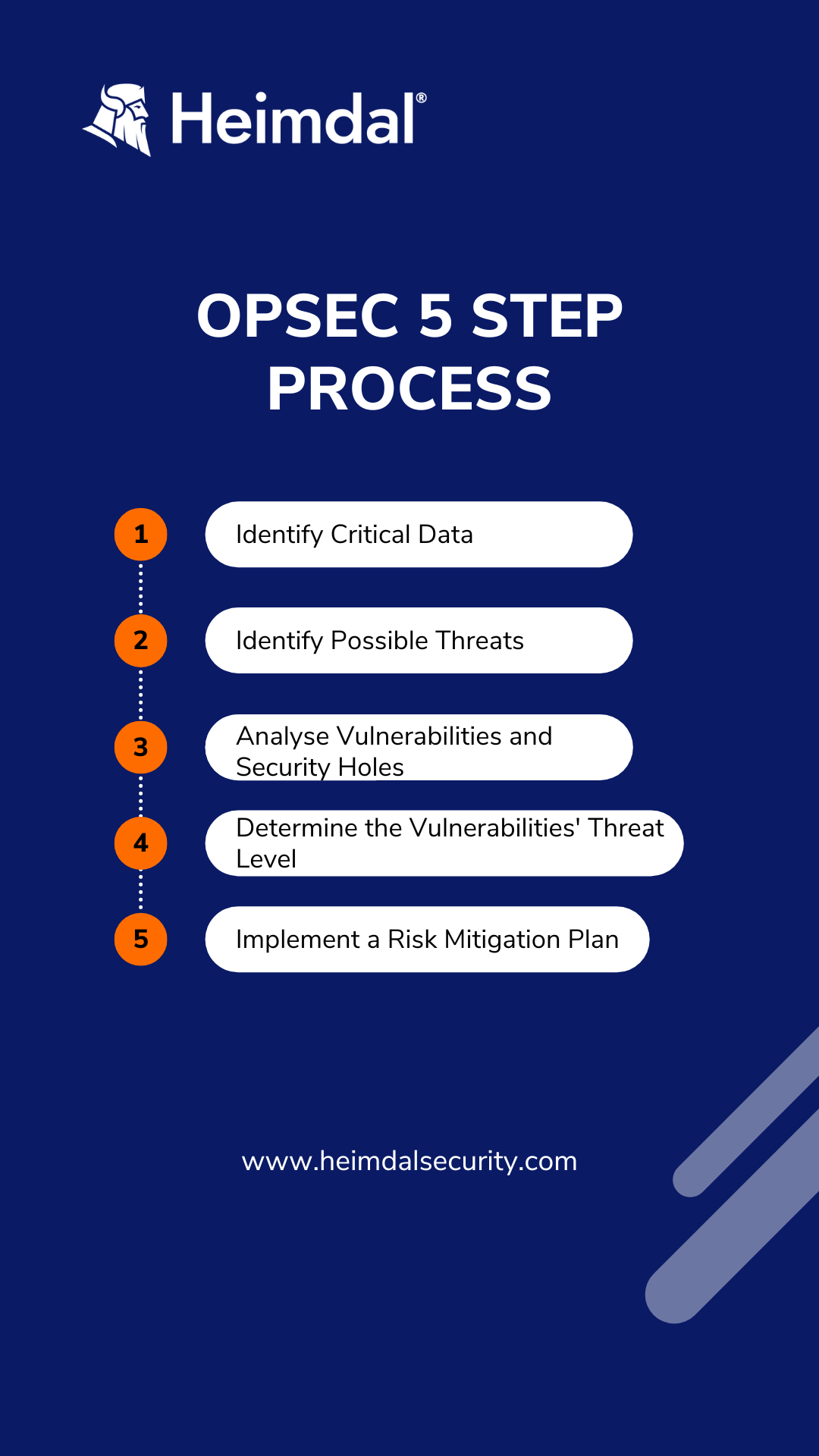
The operational security process is most commonly split into the following five steps:
1. Identify the Critical Data
Identify which data could be harmful to your business if it were to fall into threat actors’ hands. Such data can be customer information, financial data, employees’ information, intellectual property, and the list can go on.
2. Identify the Possible Threats
Now, with the sensitive data identified, you need to analyze them and further identify what determines the potential threats presented to the data. Such threats can be represented by malicious actors, third parties that might want to steal the data, competitors looking to gain a competitive advantage, or even negligent employees to name a few.
3. Analyze Vulnerabilities and Security Holes
The next step is to analyze potential vulnerabilities that may be found in your organization’s systems and could potentially be exploited by threat actors. This involves evaluating the procedures and technological solutions used to protect their data and spotting any openings or vulnerabilities that an attacker might try to take advantage of.
4. Determine the Threat Level of Each Vulnerability
Once you have identified the vulnerabilities, it is time to assess the risks associated with each one. You should rank the vulnerabilities based on the likelihood of attackers targeting them, the level of damage that may occur if the vulnerabilities are exploited, and the time necessary for fixing the damage and mitigating the vulnerability.
5. Implement a Plan for Risk Mitigation
After following the previous steps, you now have all the knowledge necessary to create a strategy to reduce the hazards highlighted. Putting in place countermeasures to get rid of threats and lessen cyber hazards is the last stage of OPSEC. These frequently involve upgrading hardware, developing regulations for protecting sensitive data, and educating staff members on security best practices and corporate data policies.
Best OPSEC Practices
To make sure your OPSEC strategy is effective and well-rounded, you should take into consideration the following best practices:
- Restrict Device Access: Organizations should allow access to devices only where it is absolutely required. As a general rule of thumb, network device authentication should be employed for access and data sharing;
- Change Management Processes: In the event that network modifications are made, organizations must put in place appropriate change management procedures that their staff can follow. Organizations must be able to properly audit and monitor the alterations, therefore these changes must be managed and logged;
- Follow the Principle of Least Privileged: The principle of least privileged (POLP) is a cybersecurity best practice based upon granting the minimum required access a user needs to perform an assigned task. This practice is essential in improving the security level of the organization, since it minimizes the attack surface, limits the risk of malware, and prevents insider threats;
- Prevent Human Error: One of the most common causes of data breaches is actually the human error. Train your employees, secure your systems with strong password policies, and additionally, implement two-factor authentication to add an extra layer of security to your data. Furthermore, when transferring data, or for employees working remotely, use VPNs to ensure that the data is securely encrypted;
- Incident Response Planning: No organization wants to think about the worst-case scenario, but in case it happens, you should be prepared. Even with OPSEC measures in place, you must still have an incident response plan ready for a rapid response against the threat.
How Can Heimdal® Help Your Organization
An important first step to ensure that your company’s software and hardware are safe is to keep them up to date. Performing this task manually can be a burden for an IT team, based on the number of machines that need to be verified.
Luckily, Heimdal’s Patch & Asset Management solution comes to your help. It is a fully automated patching solution that will make the problem of manual patching obsolete. As an on-the-fly solution, you will have access to the software at any time and from any location in the world. The system is fully customizable to fit the specific needs of your organization, and it can patch any Microsoft and Linux OS, third-party software, or proprietary software.

Heimdal® Patch & Asset Management Software
- Schedule updates at your convenience;
- See any software assets in inventory;
- Global deployment and LAN P2P;
- And much more than we can fit in here...
Conclusion
In conclusion, operational security or OPSEC is an important part of any organization’s cybersecurity strategy. It is a proactive approach to protecting sensitive information from potential threats and attacks. By taking the necessary steps to ensure that these security measures are in place, organizations can reduce their risk of becoming victimized by cybercriminals.
If you liked this article, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and Youtube, for more cybersecurity news and topics.


 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management
 Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security










