Contents:
As we all know, an email’s journey across the internet includes stops at numerous servers and routers. Sometimes, at any of these stops, malicious actors may come across the email message and read its contents or insert a bogus answer, impersonating the two parties who are communicating. For instance, this could lead to the theft of login credentials or the redirection of traffic to a phishing website.
This tactic is known as a Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attack, and it can be difficult to detect, but it can be prevented by using S/MIME’s encryption and digital signatures.
But first things first!
What Is S/MIME?
S/MIME or Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extension is a technology widely used by corporations that enhances email security by providing encryption, which protects the content of email messages from unwanted access. It also adds digital signatures, which confirm that you are the authentic sender of the message, making it a powerful weapon against many email-based attacks.
In a nutshell, S/MIME is a commonly-used protocol for sending encrypted and digitally-signed email messages and is implemented using S/MIME certificates.
S/MIME Uses
S/MIME can be used to:
- Check that the email you sent has not been tampered with by a third party.
- Create digital signatures to use when signing emails.
- Encrypt all emails.
- Check the email client you’re using.
How Does S/MIME Work?
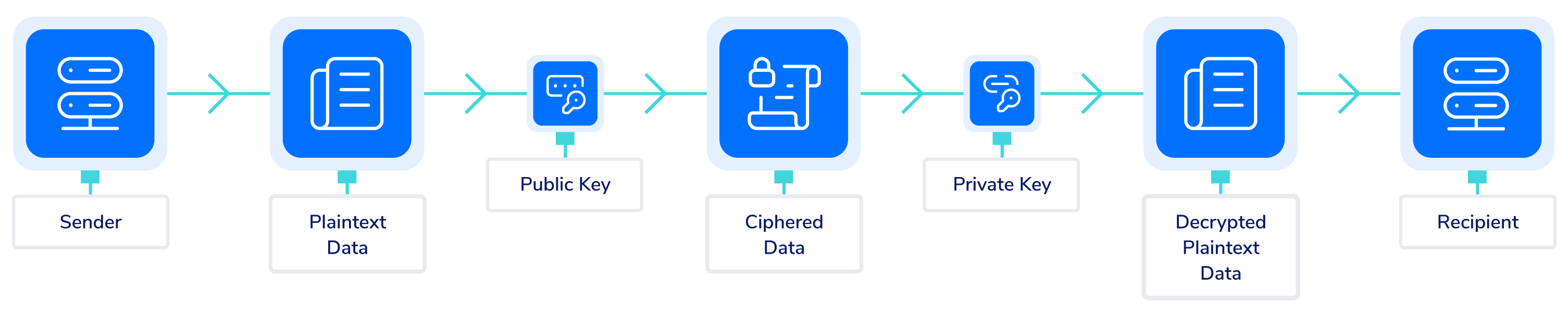
To operate, S/MIME employs mathematically related public and private keys. This technology is based on asymmetric cryptography. Because the two keys are mathematically related, a message that was encrypted with the public key (which is, of course, published) can only be decrypted using the private key (which is kept secret).
When someone clicks “send” on an email, S/MIME sending agent software encrypts the message with the recipient’s public key, and the receiving agent decrypts it with the recipient’s private key. Needless to say, both the sender and the recipient must support S/MIME.
The email message decryption process can only be done with the private key associated with it, which is supposed to be in sole possession of the recipient. Unless the private key is compromised, users can be confident that only the intended recipient will have access to the confidential information contained in their emails.
Simply put, S/MIME encryption muddles emails so that they can only be viewed by receivers who have a private key to decrypt them. It prevents others, particularly malicious actors, from intercepting and reading email messages as they are sent from senders to recipients.
You may be aware that SMTP-based Internet email does not provide message security. An SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) internet email message can be read by anyone who sees it as it travels or views it where it is stored. S/MIME uses encryption to tackle these issues.
Message encryption provides two distinct security benefits:
Confidentiality
The purpose of message encryption is to keep the contents of an email message safe. The contents are only visible to the intended recipient, and they remain private and inaccessible to anyone else who might obtain or view the message. Encryption ensures message confidentiality while in transit and storage.
Data integrity
Message encryption, like digital signatures, offers data integrity services as a result of the operations that make encryption possible.
As I mentioned before, S/MIME also adds a digital signature to an email. This guarantees that the sender has permission to send emails from a specific domain.
S/MIME Digital Signatures
Digital signatures are the most commonly used service of S/MIME. As the name indicates, they are the digital equivalent of the conventional, legal signature on a paper document. S/MIME digital signatures protect against email spoofing attempts by confirming the sender’s identity, making sure that the message content has not been tampered with, and verifying that the sender actually sent the email message.
Security capabilities offered by digital signatures:
Authentication
A signature validates the answer to the question “who are you?” by allowing that entity to be distinguished from all others and proving its uniqueness. Authentication ensures that a message was sent by the individual or organization claiming to have sent it. This reduces the likelihood of email spoofing, which is common in phishing scams.
Nonrepudiation
A signature’s uniqueness prevents the sender from denying that they sent the message. This is useful for purchases and transactions, legal documentation, and criminal investigations, among other things.
Data integrity
When the receiver of a digitally signed email validates the digital signature, the recipient is assured that the received email message is the same one that was signed and sent and that has not been tampered with while it traveled.
What Is a S/MIME Certificate and How Does It Work?
An email signing certificate, which you can obtain from a certificate authority, is required to sign and encrypt your email. This certificate can be used to digitally sign your emails. Once you purchase it, it will automatically get added to your email.
All senders and receivers must have a digital certificate that binds their identity to a public key. Typically, an administrator is in charge of configuring S/MIME and issuing digital certificates.
Why Need a S/MIME Certificate?
- S/MIME certificates ensure that the emails you send are only accessible by the intended recipient.
- They employ asymmetric encryption.
- Public and private keys will be used to encrypt and decrypt emails, ensuring that the emails you send cannot be read by anyone other than the receiving party.
- S/MIME certificates protect emails by preventing hackers from accessing or changing their contents.
- Offer both digital signatures and encryption.
- While asymmetric encryption keeps your data private, digital signatures provide authentication and message integrity.
- S/MIME certificates are installed on email clients.
How to Send a S/MIME Encrypted Mail
Gmail
When a user composes a message in Gmail, a lock icon shows up next to each receiver who has S/MIME configured. If the user intends to send the email to more than one recipient, and each of those recipients supports a distinct level of encryption, Gmail will use the lowest level of encryption supported by all recipients.
Outlook
When writing a single message in Outlook, users can choose “Encrypt with S/MIME” from the Options menu. To digitally sign or encrypt every email by default, users can select encryption, sign, or both from the Settings menu.
Conclusion
S/MIME Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extension protects sensitive and confidential information from accidental and purposeful data leaks, and it informs the receiver if a malicious actor has tampered with the digital signature in any way. The digital signature also verifies the identity of the sender and protects the recipient from spoofing attempts.
The advantages listed above are important not only for businesses to protect their customers’ email accounts and sensitive data but also for individuals. As you know, malicious software, such as viruses, trojans, and other threats, is usually distributed via email.
How Can Heimdal™ Help?
Heimdal Security has developed two email security software aimed against both simple and sophisticated email threats: Heimdal Email Security, which detects and blocks malware, spam emails, malicious URLs, and phishing attacks, and Heimdal Email Fraud Prevention, a revolutionary email protection system against employee impersonation, fraud attempts – and BEC, in general.
For example, you may want to consider Heimdal Security’s Heimdal Email Fraud Prevention, the ultimate email protection against financial email fraud, C-level executive impersonation, phishing, insider threat attacks, and complex email malware. How does it work? By using over 125 vectors of analysis and being fully supported by threat intelligence, it detects phraseology changes, performs IBAN/Account number scanning, identifies modified attachments, malicious links, and Man-in-the-Email attacks. Furthermore, it integrates with O365 and any mail filtering solutions and includes live monitoring and alerting 24/7 by our specialists.
If you liked this article, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, Youtube, and Instagram for more cybersecurity news and topics.


 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management
 Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security










