Contents:
Ransomware gangs have been forced to reduce their targeting scope and increase the productivity of their attacks as a result of the last year’s many law enforcement operations that resulted in the arrests and takedown of notorious ransomware campaigns.
Although prominent members of some well-known ransomware groups have been detained, most of the notorious Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) gangs keep operating, perfecting their strategies for maximum damage.
So, What Changed?
Coverware, an organization that helps businesses remediate ransomware, released an analysis based on ransom negotiation data from Q4 2021, which revealed that ransomware groups are now asking for higher ransom payments rather than increasing the frequency of their attacks.
According to BleepingComputer, the average ransom payment in Q4 2021 was $322,168, which means a 130% increase over the previous quarter. The median ransom payment figure was $117,116, a 63% increase compared to Q3.
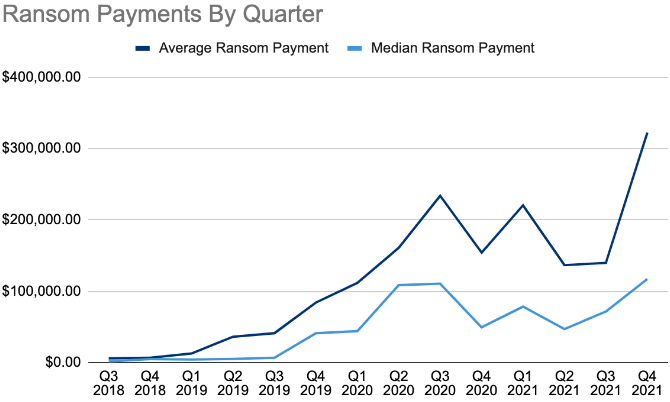
Malicious actors are now trying new strategies, as interrupting major organizations’ activities triggers investigations and creates political conflicts on a global scale.
Threat actors target businesses that are large enough to pay fairly substantial ransom demands but not so large or critical to cause them more geopolitical problems than profits.
Fewer Attacks on Large Companies
In terms of personnel count, it appears that organizations with more than 50,000 employees have encountered fewer attacks, as threat actors have chosen to target mid-sized businesses.
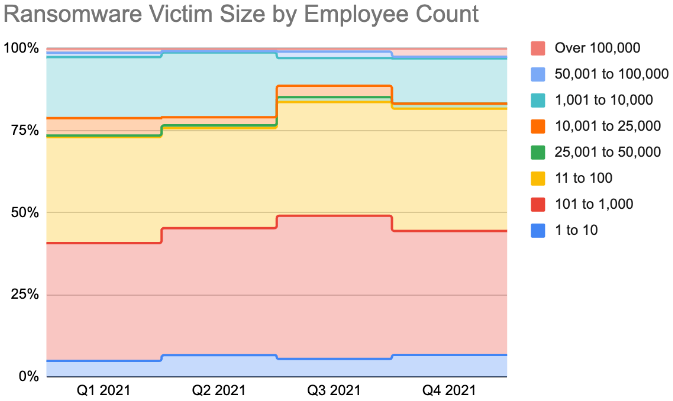
Although medium and large organizations continue to be impacted, ransomware remains a small business problem with 82% of attacks impacting organizations with less than one thousand employees.
Given that the top three ransomware gangs use double-extortion methods, it’s not surprising at all that 84% of all incidents in Q4 also included theft of private information.
The Most Common Ransomware Gangs in Q4 2021
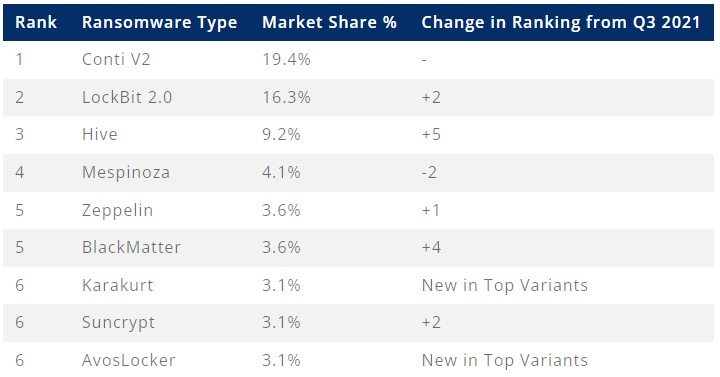
Conti was the most commonly observed variant in Q4 2021, being responsible for 19.4% of all detections, LockBit 2.0 was second with 16.3%, and Hive was third with 9.2%.
Besides statistical data on cybercriminals’ behavior, Coveware collects information on actors’ tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) leading up to ransomware deployment, Here are the top 5 from 2021:
- Persistence: 82% of ransomware incidents had persistence TTPs observed, a growth of 34% points from Q3.
- Lateral Movement: 82% of ransomware attacks involve lateral movement with the most common types being Remote Services observed in 39% of cases, Exploitation of Remote Services observed in 38% of cases, and Lateral Tool Transfer observed in 23% of cases.
- Credential Access: 71% of ransomware cases observed Credential Access tactics via either Brute Forcing observed 78% of the time or OS Credential Dumping observed 22% of the time.
- Command and Control: 63% of ransomware attacks observed some form of Command and Control with Remote Access Software being the most common tactic.
- Gathering data: Collection tactics were observed in 61% of cases, with Archive Collected Data being the most common.
Another significant shift in strategy relates to the initial compromise vector. As ransomware actors turn their attention to abusing security flaws, RDP access, which was once a widely-bartered item on the dark web, is continuously dwindling.
According to BleepingComputer, the most abused network entry flaws on Microsoft Exchange and Fortinet firewall appliances in Q4 2021 were CVE-2021-34473, CVE-2021-26855, and CVE-2018-13379.
How Can Heimdal™ Help?
In the fight against ransomware, Heimdal Security is offering its customers an outstanding integrated cybersecurity suite including the Ransomware Encryption Protection module, that is universally compatible with any antivirus solution, and is 100% signature-free, ensuring superior detection and remediation of any type of ransomware, whether fileless or file-based (including the most recent ones like LockFile).
If you liked this article, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, Youtube, and Instagram for more cybersecurity news and topics.










 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management  Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security








