Advanced threats can bypass basic detection methods. That’s why organizations need modern, multilayered endpoint protection strategies.
Open-source EDR tools (Endpoint Detection and Response) can protect your digital ecosystem against next-generation threats that antivirus-based systems can’t detect.
In 2026, adversaries use fileless malware, living-off-the-land binaries (LOLBins), and advanced social engineering. To respond, you need visibility into what’s happening at the endpoint, and open-source EDR tools can help close that gap.
Here’s a comprehensive list of the most popular open-source EDR tools available today.
What is Endpoint Detection and Response?
EDR is a strategic approach to malware, emphasizing digital prevention, screening, and detection over mitigation.
It’s undoubtedly a huge leap from traditional the detection & remediation approach, based on post-intrusion behaviour.
Advanced malicious content is specifically engineered to inflict as much damage as possible after infiltrating your endpoint, network, or both.
Under EDR, digital forensics become the backbone of threat detection.

- Morten Kjaersgaard, Founder & Chairman, Heimdal
Open Source EDR Tools
Open-source Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools provide an essential layer of defense, empowering organizations to detect, investigate, and respond to threats effectively.
Let’s explore some of them together.
#Bonus tool: Heimdal® Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
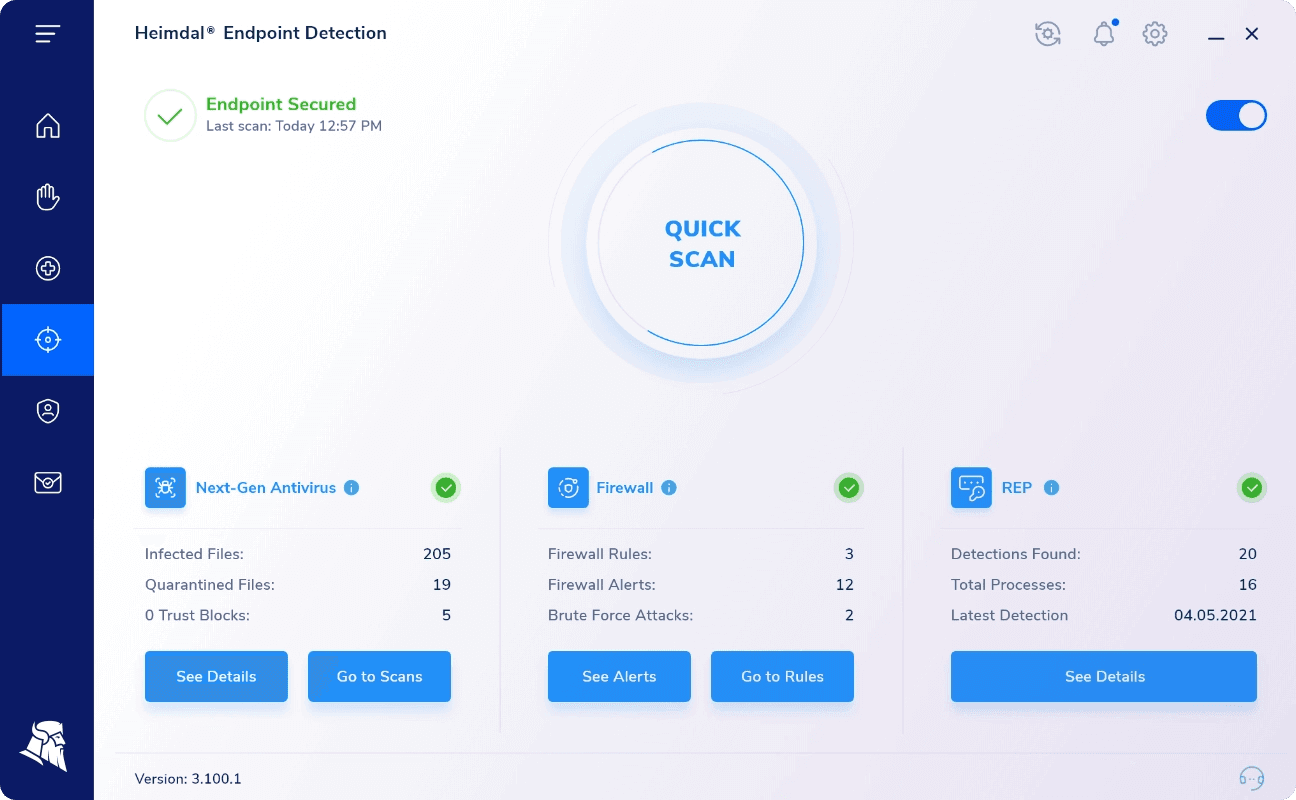
While Heimdal®’s EDR solution isn’t open-source, it offers advanced NGAV + XTP with MDM capabilities that go far beyond what most open-source tools can provide.
It delivers threat hunting, sandboxing, behavioral analysis, and automatic device isolation, making it ideal for organizations seeking enterprise-grade protection with centralized management.
The users has a 30-day, no strings attached trial.
If you’re interested in our EDR approach, book a free demo today.
Key Features
- Threat Prevention.
- HyperAutomated 3RD Party and Windows.
- Patching, Without WSUS License Costs.
- Next-Generation Antivirus.
- Ransomware Encryption Detection.
- Email Security.
- Remote Support Tools.
- Email Fraud Prevention.
- Active Directory Management.
- Advanced Threat Analytics.
- Office Suite.
- VPN/Direct Access.
- Privileged Access Management.
- Application Control.
1. OSSEC
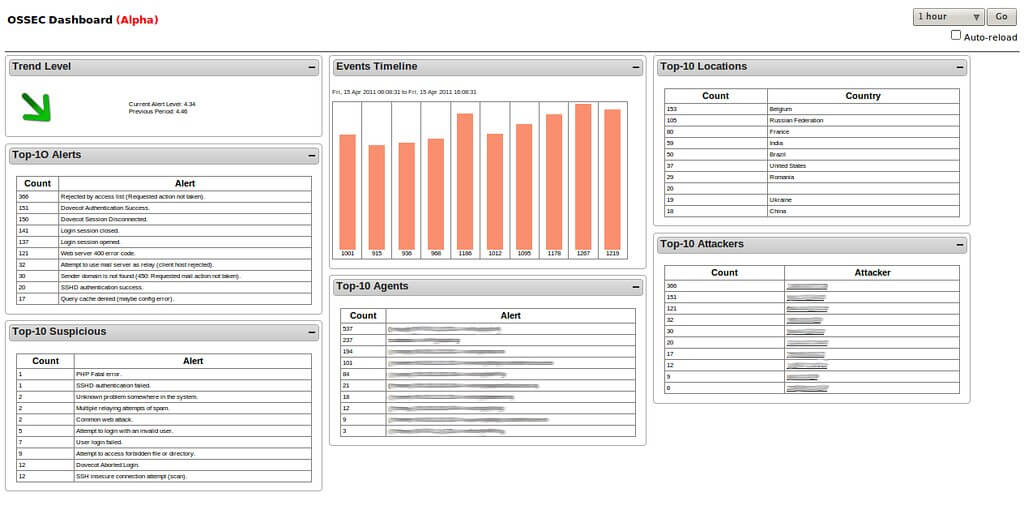
An open-source and free software that offers HIDS (Host-based Intrusion Detection System), HIPS (Host Intrusion Prevention System), log analysis, real-time Windows registry monitoring, and other EDR features.
OSSEC is mostly addressed to large enterprises, SMBs, and governmental agencies.
Key Features
- LIDS (Log-based Intrusion Detection).
Scans and analyses log data coming from multiple endpoints.
- Malware and Rootkit Detection capabilities.
Process- and file-level scanning to detect dormant or active malicious applications, rootkits included.
- Active response.
Firewall policy benchmarking, support for integrating with/in 3rd party apps.
- FIM (File Integrity Monitoring).
Real-time windows and file registry monitoring. Capable of producing forensic copies.
- System inventory.
Information-gathering platform. Able to retrieve various types of software and hardware data.
- Compliance.
Offers compliance with many of the common industry standards such as CIS and PCI-DSS.
- Cross-platform compatibility.
The software is compatible with Windows, Linux, OpenBSD, macOS, Solaris, and FreeBSD. OSSEC doesn’t support Android or Mac OSX.
2. TheHive Project
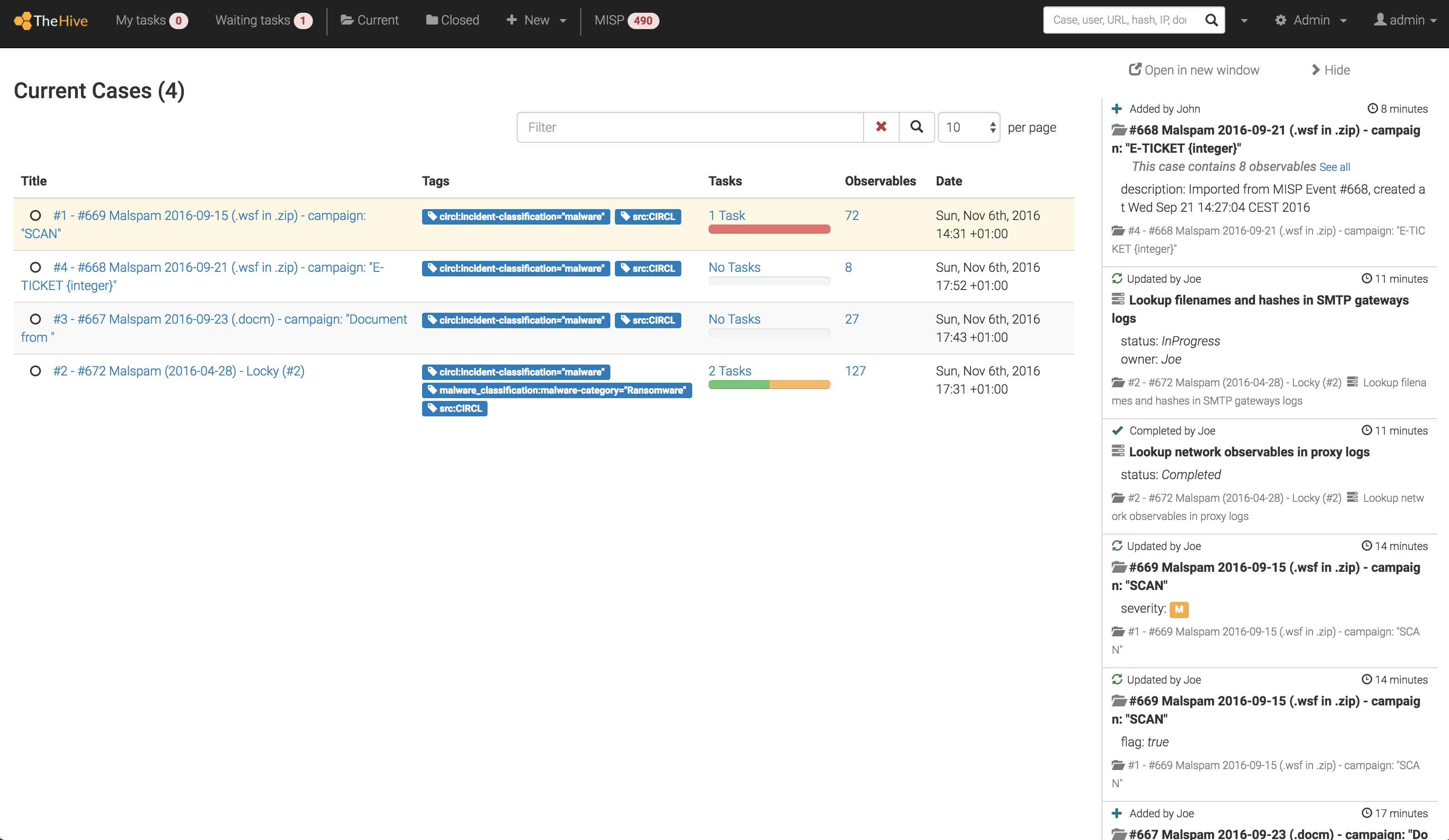
TheHive Project aggregates open-source, scalable, and free solutions to aid CERTs, SOCs, and CSIRTs in drafting security incident reports faster and elaborate actionable strategies.
In addition, it offers collaboration features such as live streaming, real-time information, and task assignments.
Key Features
- Dynamic dashboard.
It’s cloud-hosted architecture allows real-time collaboration.
- Advanced filtering options.
Capable of handling hundreds of observables. Users can import, create alerts based on any event or alarm, and customize filters.
- Forensics and Incident Response.
Cortex grants an overview of the observables via a web interface.
Other forensics and incident response features: custom scrips, AP integration, advanced containment functions.
- Cross-analysis.
Draft incident reports using analyzers from popular web services such as PassiveTotal, Google’s Safe Browsing, Onyphe, Shodan, VirusTotal.
- Python API.
TheHive4py’s Python API is an EDR tool that grants the investigator access to sources such as SIEM and/or email.
3. osQuery
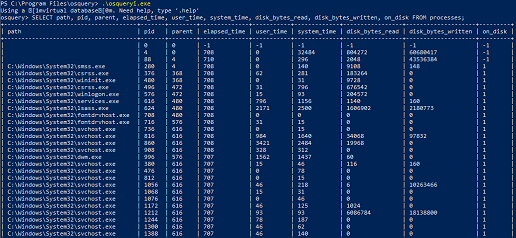
osQuery is an open-source, Apache-based device querying software that increases the visibility over your connected devices.
The product uses basic SQL commands to create complex relational data models, simplifying investigations and/or audits.
Key Features
- Interactive querying console.
Comprehensive SQL-powered console that gives you a bird’s eye view of your OS.
- Modular codebase.
Language binding is available. All components are modular and developed using open-source APIs.
- Powerful host-monitoring daemon.
Osqueryd, osQuery’s daemon can aggregate all query results and help you generate logs.
- AWS logging.
The solution can log results from Amazon AWS Kinesis Streams and Kinesis Firehose.
- File integrity monitoring.
osQuery allows users to collect file events from specific files and directories.
- YARA scanning.
Capable of outputting yara_events queries. Users can also perform on-demand YARA scans.
- Anomaly detection.
Post-deployment, the tool can establish a baseline, allowing you to threat-specific activity via scheduled queries.
- Process auditing.
osQuery can log process executions and network connections in real-time. Auditing is available for Linux and macOS via BPF, Audit, OpenBSM or EndpointSecurity.
- Cross-platform compatibility.
The software is compatible with Windows, macOS, CentOS, FreeBSD, and Linux (with some limitations).
- Enterprise-grade features.
osQuery is intended for SMBs and enterprises.
4. Nessus Vulnerability Scanner
Nessus Vulnerability Scanner is a COM port scanner useful for detecting system vulnerabilities.
Though not fully EDR, it’s very efficient in identifying security breaches.
Key Features
- Custom scripting and multiple plug-ins.
The agent also allows multiple plug-ins: server detection, processor information, Microsoft Windows ARP table, recent file history, Windows scan not performed with Admin Privileges, Microsoft Windows Last Boot Time, etc.
- Patching indicator.
The port scanner will offers suggestions on how to resolve the vulnerability.
- In-depth vulnerability scanning.
Will perform up to 1,200 checks to detect system vulnerabilities.
- Cross-platform compatibility.
Nessus is compatible with devices running Linux, Windows, and macOS.
5. SNORT
An open-source intrusion prevention software that allows the user to identify e-threats through packet logging and real-time network traffic analysis.
Key Features
- Multi-mode deployment.
SNORT can run in three modes: sniffer, packet, and NIDS
- Tunneling Protocol Support for most common formats.
SNORT supports the following tunneling protocols: PPTP over GRE, MPLS, GRE, IP in IP, ERSPAN.
- Multiple NIDS Mode Output options
Supports multiple output options: Fast alert, Full Alert mode, Unsock (can send the alert to a Unix-type socket), No alert (disables alerts), Console (displays fast-type alerts on your screen), and CMG (displays alerts in the CMG style).
- Cross-platform compatibility.
Fully compatible with Fedora, Centos, FreeBSD, and Windows
6. Ettercap Project
Ettercap Project is an open-source EDR tool that simulates ARP Poisoning and Man-in-the-Middle attacks on LAN.
It has multiple security options such as network traffic interception, active eavesdropping for the most common protocol, network security auditing, and protocol dissection.
Key Features
- Dual-mode.
Ettercap Project can reconfigure the network interface to run in two modes. Both modes yield precious forensic information. The user can determine how the system will act and react during a MiM attack.
- OS fingerprinting.
Analyze how OS fingerprinting works in real time.
- IP-based filtering.
Use this option to filter incoming and outgoing packets by destination and IP source.
- Plug-in support.
Ettercap’s capabilities can be enhanced through publicly available APIs and plug-ins.
- Cross-platform support.
Ettercap Project is compatible with Linux, Solaris, BSD, MacOS X, and Microsoft Windows.
7. Infection Monkey
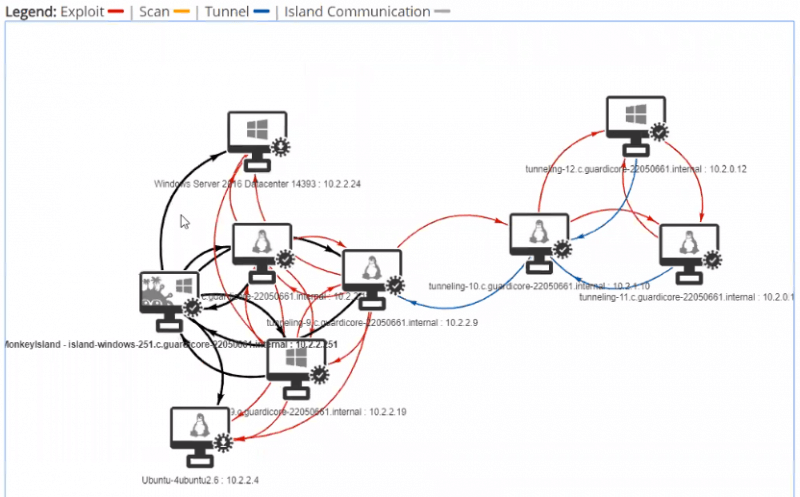
Infection Monkey is a free and open-source assessment tool that simulates system breaches.
This tools is designed for sysadmins who want to probe a company’s security infrastructure in search of vulnerabilities.
Key Features
- Run real-life infection scenarios.
Infection Monkey can simulate many types of malicious actions such as Shellshock, Sambacry, ElasticGroovy, Struts2, Weblogic, Hadoop, Credential Stealing, and Brute-Force logins.
- Advanced detection capabilities.
Guardicore’s tool boasts numerous detection methods such as Alerts on cross-segment traffic (check to determine if your global segmentation policies and rest are correctly enforced), tunneling (alerts the user if tunneling is detected), and credential analysis.
- Cross-platform compatibility.
The tool is compatible with Microsoft Windows, Linux, and macOS X.
8. Cuckoo Sandbox
Cuckoo Sandbox is an open-source sandboxing environment that allows the user to quarantine, analyze, and dissect files exhibiting malicious behavior.
Key Features
- Powerful file analyzer.
Can probe various file formats and types (documents, pdf files, executables, emails, etc.).
The engine also allows the user to execute Cuckoo Sandbox in VM-type environments.
- Advanced memory and network analysis.
Probe process memory using YARA and Volatility.
Network traffic can also be analyzed before dumping. It also applies to traffic encrypted with TLS or SSL.
- Cross-platform compatibility.
The tool is compatible with Microsoft Windows, Linux, Mac OS X, and Android.
9. GRR Rapid Response
GRR Rapid Response is an incident response framework used to perform remote live forensics on a large number of endpoints.
Key Features
- YARA.
YARA Library support is available.
- Powerful Search Features.
Search and download features for registry entries and files.
- Multiple client libraries.
Client libraries include Go, PowerShell, and Python.
- Automation.
Schedule tasks for your clients.
- Extensive monitoring capabilities.
The tool can help user monitor I/O usage, CPU, memory, and custom parameters.
- Cross-platform compatibility.
The tool is compatible with Microsoft Windows, macOS X, and most Linux builds.
10. MIG by Mozilla
Mozilla’s MIG is a free-to-use forensics platform for remote endpoints.
The tool is compatible with Windows, Linux, and Mac OSX. A beginner’s tool, but very helpful in providing accurate IOCs.
Key Features
- Log Analysis.
Runs real-time queries on logs, detecting threats without large data transfers.
- Memory & Network Inspection.
Scans live memory, processes, and connections for malware and anomalies.
- System Auditing.
Identifies misconfigurations, missing patches, and unauthorized changes.
- Vulnerability Management.
Detects outdated software and security flaws, aiding patching.
Conclusion
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) has become the next gold standard of cybersecurity.
Despite the slow and somewhat problematic adoption, companies and institutions have realized the importance of this extra security layer.
EDR tools such as the ones described in the article are reasonable first steps towards global tech assimilation.










 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management  Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security








