Contents:
An Intrusion prevention system (IPS) is an automated network security tool that continuously monitors your network traffic stream, to detect and prevent threats and malicious incidents.
The main functions of an IPS are to gather and log essential information, detect suspicious behavior, attempt to stop the activity and finally report to system administrators.
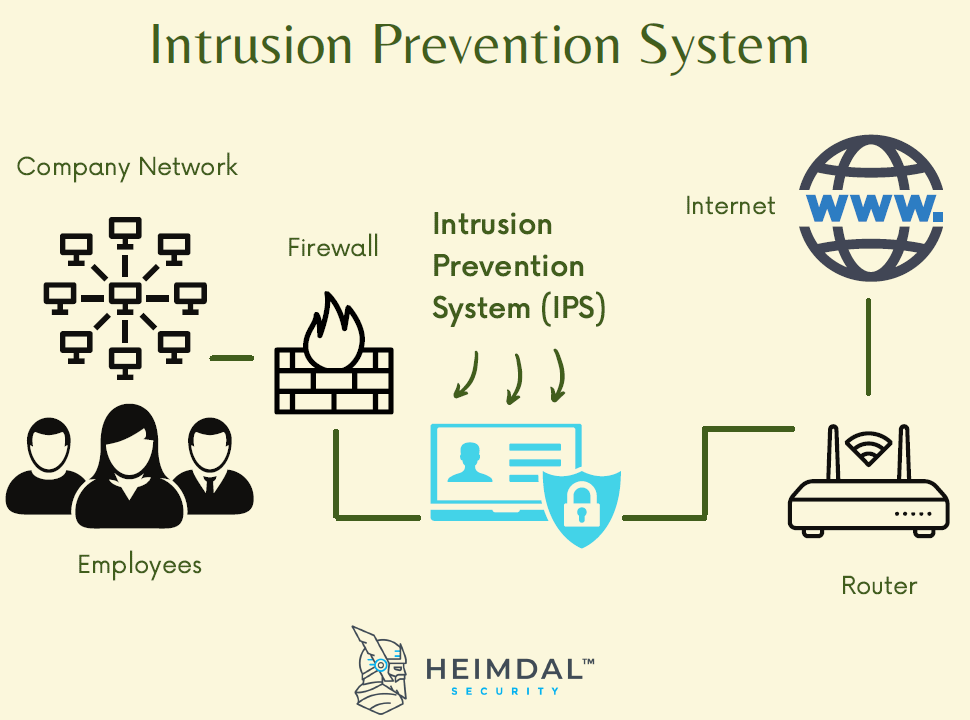
Apart from monitoring networks and preventing threats, IPS security is also an excellent method of preventing employees and network guests from violating corporate security policies.
Types of Intrusion Prevention Systems
IPS systems can be classified into several major types:
- NIPS. Network-based intrusion prevention systems look for questionable traffic by analyzing the entire network’s protocol activity.
- WIPS. Wireless intrusion prevention systems work in the same way as NIPS, but they’re looking across the entire wireless network.
- HIPS. Host-based intrusion prevention systems are secondary software packages that look for malicious activity and analyze events within a single host.
- NBA. Network behaviour analysis is interested in the network traffic and tries to identify threats that produce suspicious traffic flows.
Detection Methods used by an IPS
An Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) is designed to prevent various types of malware: viruses and worms, exploits, Denial of Service (DoS) attacks and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, and it does so by using various approaches:
- Signature-Based. This approach relies on predefined signatures of common network threats. If the IPS system finds an attack that matches a certain signature or pattern, it immediately takes the necessary actions.
- Anomaly-Based. As you might guess, the anomaly-based approach looks for any abnormal or unexpected behaviour. When an anomaly is detected, the IPS system blocks its access to the target host.
- Policy-Based. The policy-based approach makes use of the security policies that the administrators need to configure according to the network infrastructure and each company’s security policies. In this case, if the IPS system discovers an activity that violates a security policy, it triggers an alert to notify the system administrators.
When it comes to intrusion countermeasures, an intrusion prevention system can:
- configure a firewall to increase protection;
- replace malicious parts of an email, for example (like fake links), with warnings about the content that was removed;
- notify system administrators about possible security breaches by sending automated alarms;
- drop the detected malicious packets;
- block traffic from suspicious IT addresses;
- reset connections.
What Is the Difference between IDS and IPS?
IDS stands for Intrusion Detection System and refers to devices or applications that monitor networks or systems looking for malicious activities or policy violations.
The main difference between an IPS system and an IDS system is that:
- IPS systems control the access to IT networks by monitoring intrusion data and taking the necessary actions to prevent an incident or attack.
- IDS systems do not block attacks– they only monitor networks and, if they detect potential threats, they send alerts to system administrators.
Moreover, an IDS system requires a human or another system to look at the results it finds, while an IPS system requires its database to be continuously updated with the new threat information.
IDS systems can be divided into network intrusion detection systems (NIDS) and host-based intrusion detection systems (HIDS). “A system that monitors important operating system files is an example of a HIDS, while a system that analyzes incoming network traffic is an example of a NIDS.”
Another way of classifying IDS systems is according to the detection approach:
The most well-known variants are signature-based detection (recognizing bad patterns, such as malware) and anomaly-based detection (detecting deviations from a model of “good” traffic, which often relies on machine learning). Another common variant is reputation-based detection (recognizing the potential threat according to the reputation scores).
The Key Benefits of an Intrusion Prevention System
- Automation
Nowadays, companies need a pretty high level of security to ensure safe communication, and the ability to prevent intrusion by having an automated solution that can take the necessary actions with minimal IT intervention and low costs is a nice advantage.
- Achieve Compliance
Investing in cybersecurity is not only a necessity but also a requirement of compliance. By choosing an IDS or IPS system you will, simultaneously, gain peace of mind because your network will be safe from multiple online threats and check off a box on the compliance sheet because you’ll address a significant number of CIS security controls.
- Enforcing Policies
IPS/IDS solutions can help you configure internal security policies at the network level. For example, you can use it to block other VPN traffic if you support only one VPN.
Heimdal’s approach to IPS
Our Heimdal™ Threat Prevention can help you reduce more than 90% of the advanced forms of malicious software by stopping threats at the perimeter level. This Network Prevention, Detection, and Response tool offers complete DNS protection and is powered by our AI-driven, “Character-Based” Neural Network intelligence, using advanced Machine Learning algorithms to deliver HIPS/HIDS and IOA/IOC capabilities that detect even concealed malware.

Heimdal® Network DNS Security
- No need to deploy it on your endpoints;
- Protects any entry point into the organization, including BYODs;
- Stops even hidden threats using AI and your network traffic log;
- Complete DNS, HTTP and HTTPs protection, HIPS and HIDS;
Final Thoughts
In today’s world, cyber-attacks only become more sophisticated, so the technologies we use to prevent them must try to be one step ahead. In terms of network protection, IPS security can help you achieve this.
However you choose to proceed, please remember that Heimdal Security always has your back and that our team is here to help you protect your home and your company and to create a cybersecurity culture to the benefit of anyone who wants to learn more about it.










 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management  Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security








