Contents:
Using EDR for cyber threat hunting has become essential since the attackers started using automation and AI to outpace traditional defenses.
In response, security teams began to actively search for hidden threats before they caused damage. Instead of waiting for alerts, cyber threat hunters investigate anomalies, connect data points, and uncover sophisticated attacks.
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools support proactive threat hunting by providing real-time visibility, automated detection, and powerful analytics to uncover hidden threats.
To explore how an EDR solution enables effective threat hunting, I spoke with Heimdal’s Threat Hunter Alex Gurgu and Cybersecurity Expert Jacob Hazelbaker. Their insights drive the discussion in this article.
How can threat hunters use EDR?
To understand how threat hunters can use an EDR solution to boost the organization’s security, I went to the source. I’ve asked my colleague, Alex Gurgu, to explain how the process goes. Alex is a threat hunter in Heimdal’s MXDR team. Here’s what he shared with me.
Using EDR for threat hunting – A four-step process
Data collection
The EDR tool collects endpoint data about suspicious behavior from various endpoints, including detecting infected files, blocking suspicious DNS requests, and more. Using it gives the threat hunter real-time visibility into unusual activities.
Alert analysis
The threat hunter analyzes the alert’s origin and the actions that followed after terminating malicious processes. This step helps determine if the alert is an isolated incident or part of a larger attack. Smart security tools automate at least a part of the investigation alert triage process.
Data correlation
Just like putting together the pieces of a puzzle, the threat hunter tries to understand if and how those alerts could be connected. The effectiveness of this phase depends on the threat hunter’s experience and analytical skills.
Stop the attack and remove the threat
Now the threat hunter needs to make sure the compromised endpoint is first isolated and can’t spread any malware and then sanitized. Next, he checks that communication with the phishing domain is blocked, the old, compromised, passwords changed with strong ones and all the suspicious files removed.
A real-life example of EDR supporting threat hunting
The threat hunter gets an alert for a suspicious activity on a client’s account. On the dashboard, he sees a list of all the detections on that account:
- DNS requests from phishing domains
- infected files
- brute force attempts
- encryption processes blocked by the ransomware module
Some of those alerts might not seem very dangerous. The problem is that most of the time they are related. The threat hunter uses all this endpoint data and their own experience and starts checking all the modules. Then they put the information together and see how it fits into a story:
- client clicks on a phishing domain that looks like a social platform
- the domain asks for the client’s credentials and also gets their IP address
- several brute force attempts follow
- someone is trying to log into the client’s endpoint by using some credentials
- the brute force detection stops, which can mean two things:
- the attacker failed and gave up
- the attacker gained access to the endpoint, so he doesn’t need to continue his brute force attempts
For the second case, the story keeps going. The next alert could come from the ransomware module:
- unknown source tries to deploy malware or encrypt existing files
For the threat hunter, putting all these details together brings the answers to:
- where did the encryption process come from
- why is it happening
- who’s doing the action
Sure, they could just block the process without thinking about those questions. But the attacker would still have access to the affected endpoint. They could use a more advanced ransomware to try encryption again.
Comprehensive visibility helps get to the root of the incident and stop the attack completely, not just block parts of it.
Threat hunting challenges that unified EDR solves
Traditionally, each of the actions in the example above would be picked up by a standalone solution. This would make it uniquely difficult to understand the full journey the hacker has taken, explained Cybersecurity Expert Jacob Hazelbaker:
Imagine you got five different vendors for your cyber security stack. You’re in one tab on your browser and then the other four log themselves out. Now you got to do the MFA on your phone again to get back logged in.
So, I would say one of the hardest parts of cyber threat hunting and one of the keys that really ties into EDR, is having it unified into one place with one screen where you can look at it.
Because that not only gives you context into what the antivirus sees, for example, but also the DNS security. What does it see? What does the ransomware encryption protection portion of it see?
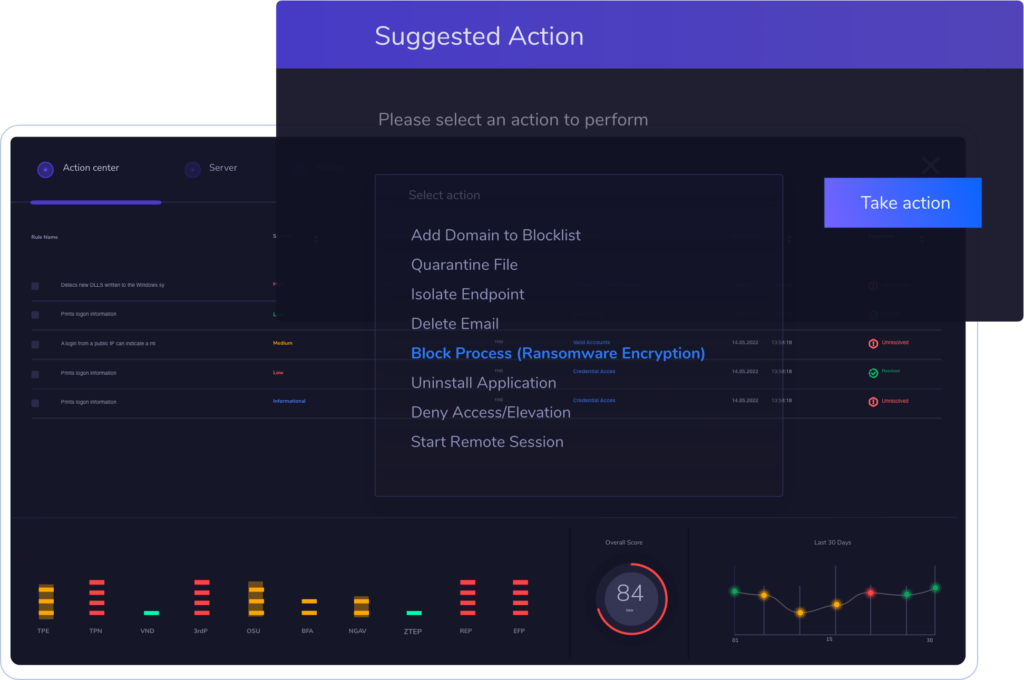
Instead of having all these different tabs that are constantly logging you out of them, you can have it under one dashboard, in one screen, like our Threat Hunting Action Center.
So, in the absence of a unified EDR platform, to join the dots, the security team would need to log in and out of four different dashboards and manually decide what actions are linked. If they don’t, it’ll be impossible to determine the root cause of the attack and remove the hacker.
With an extended EDR (XDR) platform, all these signals are surfaced in the same dashboard, making it instantly clear that they’re linked, and form four stages of the same attack. This lets security professionals quickly understand the scope and risks of an alert, so they can identify the right response.
Read more: EDR Implementation: Essential Features, Considerations, and Best Practices
Why is threat hunting an important part of the cybersecurity strategy?
Most organizations think of cybersecurity tools like an insurance policy, a necessary cost to reduce your risk. At the same time, the tools they were investing in took a primarily reactive approach, focusing on removing known threats from IT environments. Threat detection usually meant finding cyber threats that had already penetrated your system.
Today, it’s clear this mindset is outdated. Threat actors use AI and automation just like security engineers do. Mass scanning for vulnerabilities, domain generation algorithms and other similar tools increased the diversity and risk level of cyber threats. They made it harder to anticipate and prevent risks.
So, the focus must move to a more proactive approach. In short, it’s about being able to detect malware that was not yet reported as such. The goal is to prevent the hacker from gaining a foothold into your system, not only detect and remove the cyber threats once they get in.
This makes cyber threat hunting a crucial pillar of the cyber defense structure. But for cyber threat hunters to excel, they need real-time access to data about all things happening inside and on the outskirts of the system. Best EDR solutions are designed not just to detect security threats. They empower threat hunters with real-time intelligence, automation, and advanced analytics.
Read more: What Makes Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) Important? With Solid Use Cases
What capabilities of EDR support threat hunting?
Endpoint detection platforms have been a fundamental pillar of cybersecurity for several years. Over that time, a core set of tools and functionalities has evolved across most products:
Malware detection
An antivirus is perhaps the most important and fundamental tool in an Endpoint Detection and Response’s arsenal. Its goal is to identify malicious activity in the IT environment, including keylogging, data exfiltration tools, botnets, spyware, and more.
Detecting malware is nothing new. In fact, the antivirus has been the bedrock of cybersecurity products for decades. But traditionally, they worked by comparing suspicious files with a list of known, reported threats. By design, this approach can’t identify unknown threats. Therefore, advanced EDR tools incorporate a NextGen Antivirus solution. NGAVs use AI-powered anomaly analysis to detect hidden threats.
Ransomware Encryption Protection (REP)
Ransomware is just one type of malware. The methods to detect and protect against it are largely like the last section. The key difference is this: With ransomware, the stakes are much higher. Therefore, you need a special set of tools to detect and stop malicious encryption processes in time.
REP tools use behavior analysis to see if an encryption process is legitimate or not. The more advanced tools also use AI and machine learning to detect evidence of unknown threats.
Brute force protection
‘Brute force tactics’ is an umbrella term for several unsophisticated tactics that threat actors use to guess user credentials. Generally, they’ll use common passwords (e.g. ‘Password 123’) across all accounts until one works. Also, they use bots to create random strings of characters until they find the right password.
EDR solutions feature several straightforward protections against these techniques. This can include blocking IP addresses that fail to log in multiple times, or limiting the number of login attempts to a specific account. Other effective protections include requiring users to set and regularly change strong passwords, as well as use of multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Automated detection and response
Another crucial feature of EDR tools is the ability to automate incident responses for common risk signals. This allows security teams to focus their attention on a small number of the highest-risk alerts.
Here’s a common example. Employees sometimes log in to accounts from new devices or locations. This isn’t inherently suspicious, but you should implement additional security controls, since the risk is heightened.
Automation can help by identifying these situations and automatically requiring an additional stage of authentication, usually via MFA. It does this without requiring manual intervention from the security team – which would be a poor use of their time and create unnecessary delays and friction for the end user trying to sign in.
Read more: 8 Benefits of Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR) You Should Know [2024]
Key EDR features to look for
As we’ve discussed, there’s a lot of difference in the quality of EDR products available on the market today. But often, it’s not just about the feature set on offer. Increasingly effective cybersecurity is as much about approach as it is tangible features.
So how can you tell if a cybersecurity product is the right one for you? Here are some crucial EDR functions you should look out for:
A single pane of glass
Particularly in larger organizations, security teams often have multiple security dashboards. It can be a real struggle just to stay logged into all of these – you might have one tab on your browsers, others as desktop apps and they’ll log themselves out periodically. I would say that one of the hardest parts of cyber threat hunting is not just having it, but having it unified into one place and one screen. Then, you’ve got the full context of every alert in one window.
– Jacob Hazelbaker, Business Development Representative, Heimdal
Today, the most effective cybersecurity products are increasingly starting to consolidate functionality from different tools into a single dashboard.
Traditionally, if a hacker combined phishing, vulnerability exploitation, or malware in a single attack – each tactic would be picked up by a different product. This makes it difficult for IT teams to understand how all these alerts are linked, and what the hacker is really up to. By bringing all these risk signals into a single, integrated dashboard, it’s much easier for security practitioners to quickly see the context and start the right incident response process.
AI and machine learning
These days, the hackers trying to get into your organizations are almost certainly going to leverage AI models. Malicious actors will do everything they can to both attack corporations and scale those attacks beyond what we’ve previously seen.
Therefore, it’s vital that your security tools also use these new technologies to defend you from novel cyber-attacks.
– Jacob Hazelbaker, Business Development Representative, Heimdal
AI and machine learning are hugely important in a modern EDR solution or XDR tool. By analyzing activity across an endpoint, these tools help security analysts detect malicious activity and launch the incident response process in time.
To explain this in more detail, let’s consider phishing. If a hacker creates a convincing-looking phishing email, there will be small differences that the average end user might not see.
That could include layout differences, a few changed characters in the email address, or it being sent from Micros0ft rather than Microsoft. Machine learning algorithms are very effective at spotting these tiny differences.
This is the basis of a much more effective and proactive approach to security, across phishing, malware, ransomware, DNS connections, and much more. In doing so, these tools can detect suspicious activity that hasn’t been seen before, because even emerging threats will display anomalous behavior. Without this, a modern EDR/XDR tool can’t hope to create a genuinely proactive approach.
Rich context and telemetry data
A lot of security vendors, including Heimdal, now offer extra context and insights for certain threats. If it finds a particularly malicious file that’s quite well known, it’ll often link off to the relevant result in VirusTotal.
This gives you fast insights into why this file was flagged and what the cybersecurity community as a whole knows about that specific threat. This is absolutely crucial for effective threat hunting – you need a good EDR solution that not only shows you alerts but also gives you deeper insights.
– Jacob Hazelbaker, Business Development Representative, Heimdal
Most risk signals can and should be managed by automated rules. But for the small percentage of particularly unusual behavior, it’s important for human security experts to take the reins.
When they do, time is of the essence for them to understand the threat and diagnose the right response. To do that, they need information and context – and they need it quickly.
Here, security teams need as much information as they can get to understand the risk and define the response. One way to do this is through threat intelligence integration from public cybersecurity databases like VirusTotal, which can be surfaced in the integrated security dashboard.
Security experts can therefore have access to the collective insights of the entire cybersecurity community from their main security dashboard. This makes it much quicker and easier to understand the true scope of unusual threats.
Prioritizing the most critical cyber threats
Automation helps to detect false positives or other issues that aren’t as critical. In my opinion, all critical detections should be handled by a human. But automation can help to get rid of those excess detections that aren’t as important.
– Alex Gurgu, Business Development Representative, Heimdal
The layout of a security dashboard can make a huge amount of difference to your overall security posture.
Let’s pretend that your security team has 100 alerts in a day. 95 of these are common, low risk issues, five are unusual, and only one is critical.
If your IT team has to respond to all 100 alerts individually, the chances of them catching that one critical alert in time are vanishingly slim. But if 95 of the simplest issues are dealt with through automation, you’ve taken a huge amount of work off the security team’s plate, without affecting overall risk.
That’s why automation is such an important part of an effective IT product. The ideal product also needs to have a low number of false positives, so you can reduce unnecessary work to a minimum. Then, you should ensure the experts can quickly identify the most advanced attacks at a glance. This will help them focus their attention where it’s most needed.
Heimdal: Taking EDR to the next level
On its own, an EDR solution is an effective defense against a whole range of hacking techniques. But as I’ve explained, the best products on the market take EDR a step further, creating a single integrated hub for all your endpoint security requirements.
Heimdal takes this further than any other threat detection and response provider and also leaves room for flexibility. Our EDR platform is unified and modular. This means that you can either subscribe for all the tools in this kit or pick only those that you need for the moment.
Here’s what the most comprehensive EDR solution on the market offers:
- Patch and asset management
- Privileged Access Management
- Email & collaboration security
- DNS security
- Ransomware Encryption Protection
Want to find out more about cyber threat hunting and our endpoint protection platform? Get in touch to request your bespoke pricing quote.
FAQs: EDR for advanced threat hunting
What is advanced threat detection?
Real time threat detection tools scan your IT environment for known threats and types of malicious behavior. While useful, this can’t effectively protect against novel, emerging threats.
Advanced EDR tools take a much more fundamental approach, using AI-powered anomaly analysis to detect malicious activity and threat patterns. Also, these tools feature richer telemetry insights, and a broader scope of cybersecurity capabilities than traditional cybersecurity tools.
What role does EDR play in the big picture of advanced threat hunting?
Endpoint Detection and Response can improve cyber threat hunting through real-time monitoring, advanced detection, and behavior analysis. This helps identify new threats, analyze attack patterns, and offer swift incident response. Best EDR tools include automations for common risk signals, and advanced telemetry data.
How do analysts tell benign anomalies from malicious activity?
Security analysts use behavioral baselines and threat intelligence feeds to assess raw data such as logs and network traffic. By correlating this information with known indicators of compromise, they can distinguish legitimate deviations from true malicious activity.
Can EDR tools actively stop threats or only help after an attack?
EDR solutions do more than post-incident analysis — they can also mitigate threats in real time. They analyze data and endpoint behavior, then automatically respond to malicious activity.
If you liked this article, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and Youtube, for more cybersecurity news and topics.










 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management  Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security