Contents:
Heimdal® has recently launched an investigation into a massive smishing campaign, deliberately targeting Romanian telecom customers. The data collected so far reveals that the threat actor or APT behind the fake customs invoicing smishing campaign is attempting to maliciously collect user PII by redirecting them to a cloned website via an SMS-delivered crafted URL.
Background and Findings
Acting on a tip sent by an anonymous subscriber, Heimdal® has uncovered a smishing campaign that appears to prey on Romanian cellphone users. Furthermore, based on our ongoing investigation, this malicious operation is not limited to a single mobile carrier, data shows that the very same message has been transmitted over several Romanian carriers. The attack displays, to a certain extent, similarities to other malicious operations tracked across Romania such as the Fan Courier Phishing Campaign or the ANAF Spearphishing Campaign.
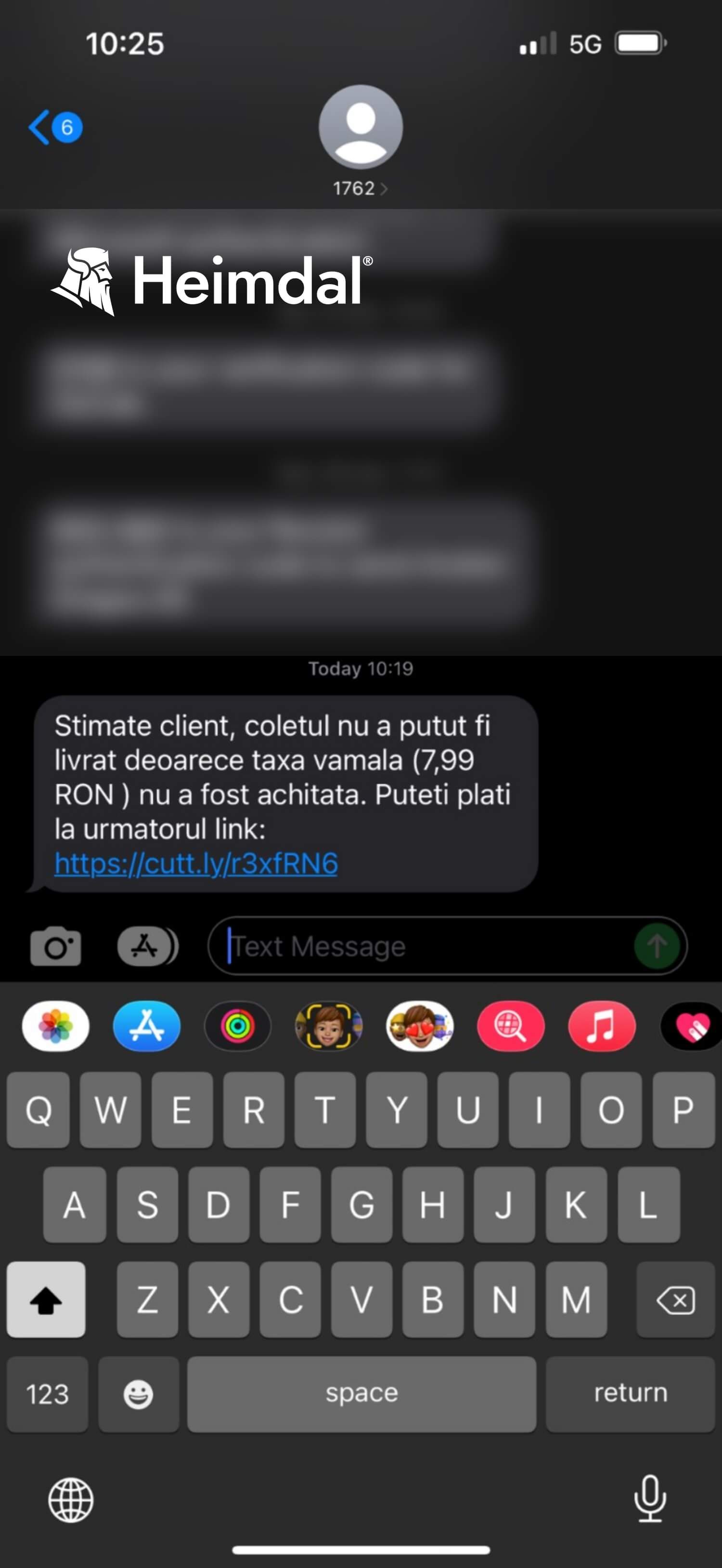
The attack scenario plays out in the following manner – the user receives an SMS with information on the status of a fictional package, presumably ordered from outside of the country. In addition, the client is also informed of the fact that the delivery has failed due to the fact that the customs fee for the said package was not paid. The user is provided with a pay URL and asked to pay off the customs fee of 1.63 euros in order to take possession of the package (see the screenshot below).
Translated from Romanian, the message read: “Dear customer, the packet’s delivery has failed due tothe fact that the customs fee (7.99 RON) was not cleared. You can pay by following this link (…)”
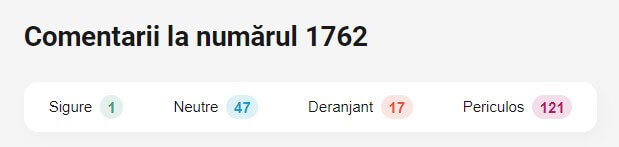
Before accessing the link, we did some background check on the phone number from which the SMS was sent. Multiple Romanian websites dedicated to evaluating the health and safety of homeland and external phone numbers have marked the “1762” call as “unsafe” (see image below).
The top section reads “Comments to 1762 phone number”. From left to right, the scoring labels read “safe”, “neutral”, “intrusive”, and “dangerous”. As you can see, 121 people have labeled the “1762” phone number as “dangerous”. For additional information and insights into this particular phone number and frequency across different mobile carriers, please review this article.
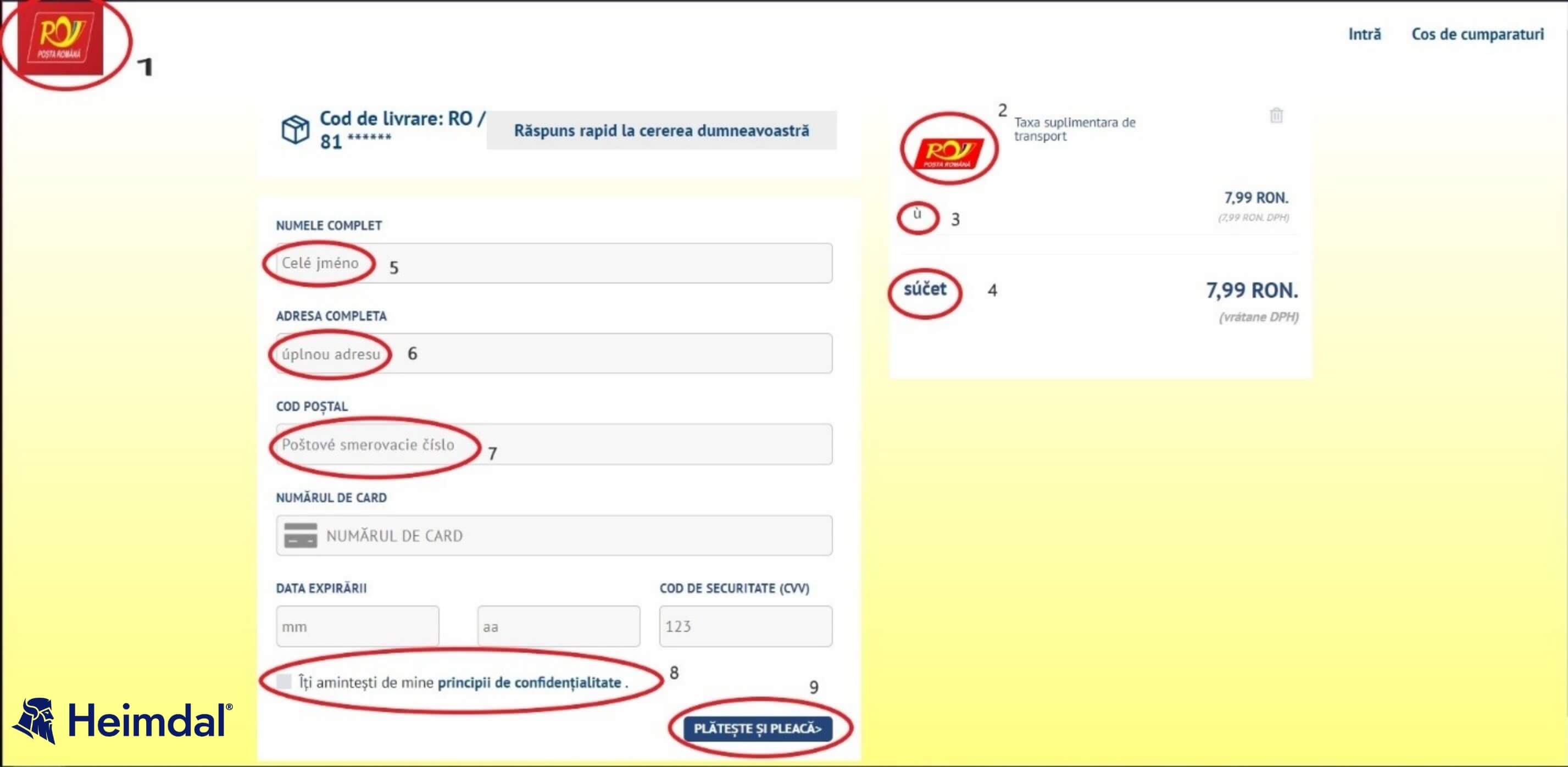
Upon accessing the enclosed URL, the user gets redirected to a page that resembles the Romanian National Post’s official website. A closer inspection of the payment page reveals several interesting elements.
First, let’s compare elements marked as “1” and “2”. If we pay closer attention to the two Posta Romana logos, we can distinctly see a difference between color pallets (i.e., the background of logo 1 is a darker shade of red, whereas logo 2’s background is plain red). Let’s move on to elements “2” and “3”. Would this have been a legitimate website, this section would have contained the Romanian equivalents of sub-total and total (i.e. the box on the right side of the screen reads “Additional transportation fees”).
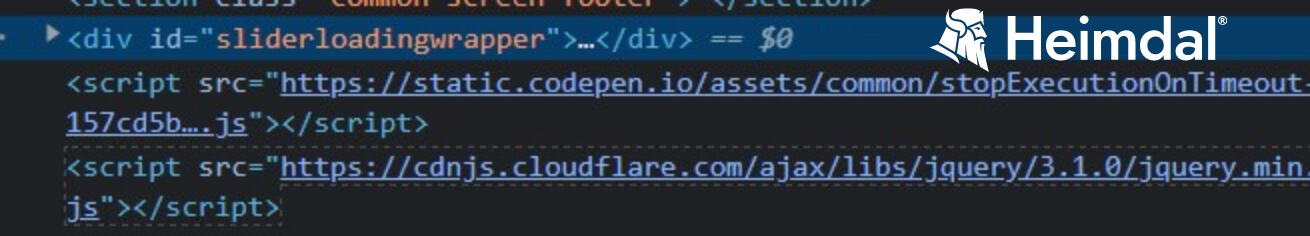
We can see that the fields marked as “2” and “3” are written in Polish. The same anomaly can be seen in elements “5”, “6”, and “7”. Let’s focus on elements “8” and “9”. Apart from the obvious orthographical and translational errors, these sections contain two scripted redirects
Let’s check out some off-page elements. Take a closer look at the URL field and tab composition.
The snapshot above reveals that the payment website lacks the SSL certificate and that the tab itself has nothing in common with the off- and on-page characteristics associated with Posta Romana’s legitimate website (see picture below for comparison).
Anti-phishing Cybersecurity Tips
Below, you will find a short, but comprehensive list of tips on how to guard yourself against phishing and smishing attempts.
Avoid opening suspicious-looking ads
Bear in mind that some Google ads you may come across are not malicious. However, this doesn’t mean that you should open everyone, just because the item looks interesting or was on your Wishlist (those can be tracked across apps and platforms). If you do open a link via SMS, make sure it has the HTTPS certificate – check for the padlock icon next to the link.
Deploy and employ next-gen anti-phishing protection
Some phishing attempts, such as the one we’ve discussed, employ a sophisticated anti-detection mechanism, allowing them to get past your antivirus. To counter these threats, you use an anti-malware solution that looks beyond the ‘file’ and ‘code’ levels.
Heimdal® Threat Prevention – Endpoint, Heimdal®’s award-winning DNS-filtering solution, can prevent threats from reaching your machine by blocking traffic to and from any malicious C&C server.
Leave a comment below if you enjoyed this article and make sure you follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube to keep up to date with everything we post!










 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management  Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security