Contents:
In this article, we’re going to tackle another data security-related topic – SOAR vs SIEM. SOAR stands for Security Orchestration Automation and Response. SIEM is short for Security Information and Event Management.
Key Takeaways:
- Complementary roles of SOAR and SIEM
- Distinct features and functions
- Key differences
- Pros and Cons of each platform
- Deployment considerations
- Integration and collaboration
SOAR vs SIEM
So, who would win if we were to pit SOAR vs SIEM? To make a long story short, there’s no winner here, simply because there’s no competition. SIEM and SOAR are the two sides of the same coin, and the best approach is having them work together.
To better understand their similarities, differences, and role in cybersecurity, let’s list their key features and capabilities.
SOAR Key Features
- Integration
- Automation and orchestration of security workflows
- Phase & object tracking
- Documentation
- Reporting
- Continuous tracking of physical and virtual assets
- Threat Intelligence
- Incident triage
- Forensics
- Disaster recovery
- Adds granularity when applied to RBAC
- Centralized view
- Playbook-based incident response
- Detect anomalies
- Ability to automate low-level security responses

SIEM Key Features
- Data Aggregation
- Data Correlation
- Advanced Reporting
- Raw data querying
- Data analytics to identify threats
- Dashboard visualization
- Retention of historical data
- Context-based data correlation
- UEBA (User and Entity Behavior Analysis)
- Incident timeline
- Real-time security monitoring
- Real-time notification and alerting
- Data protection capabilities
- Identity-based auditing
- Compliance simplification
While there are some similarities between SIEM and SOAR, let’s put their main differentiator into the spotlight.
A SOAR platform focuses on automating and orchestrating incident response while a SIEM solution collects security event data from different sources, then correlates and analyzes them.
Each security tool brings specific benefits and comes with certain downsides.

SOAR platform pros
- Some types of security responses can be fully automated
- Ability to centralize incident response processes
- Increased transparency
- Ability to integrate with SIEM and/or log management
- Scalability
- Multi-source threat intelligence
SIEM platform pros
- Increased digital ecosystem visibility
- Helps with compliance
- Easier forensics
- Data correlation
- Increased security
- The increased threat detection rate

Like all other cybersecurity tools, SIEM and SOAR are less performant when used for certain security operations. Here are some cons for each.
SOAR tools cons
- Challenging to set up and understand
- Requires technical expertise
- Support is limited in some cases
- Some types of integrations can be challenging
- Requires ample documentation prior to set up
- Lack of standardized performance metrics
SIEM tools cons
- Expensive
- Challenging to deploy
- Increased background noise generated by continuous data collections
- SIEM reports are difficult to understand
- Configuration-based efficiency
- Not manned 24/7
One final aspect to take into consideration when choosing between SOAR and SIEM solutions is coverage. Both tools are designed to operate in on-prem setups and in the cloud. Below you’ll find the pros and cons associated with each approach.
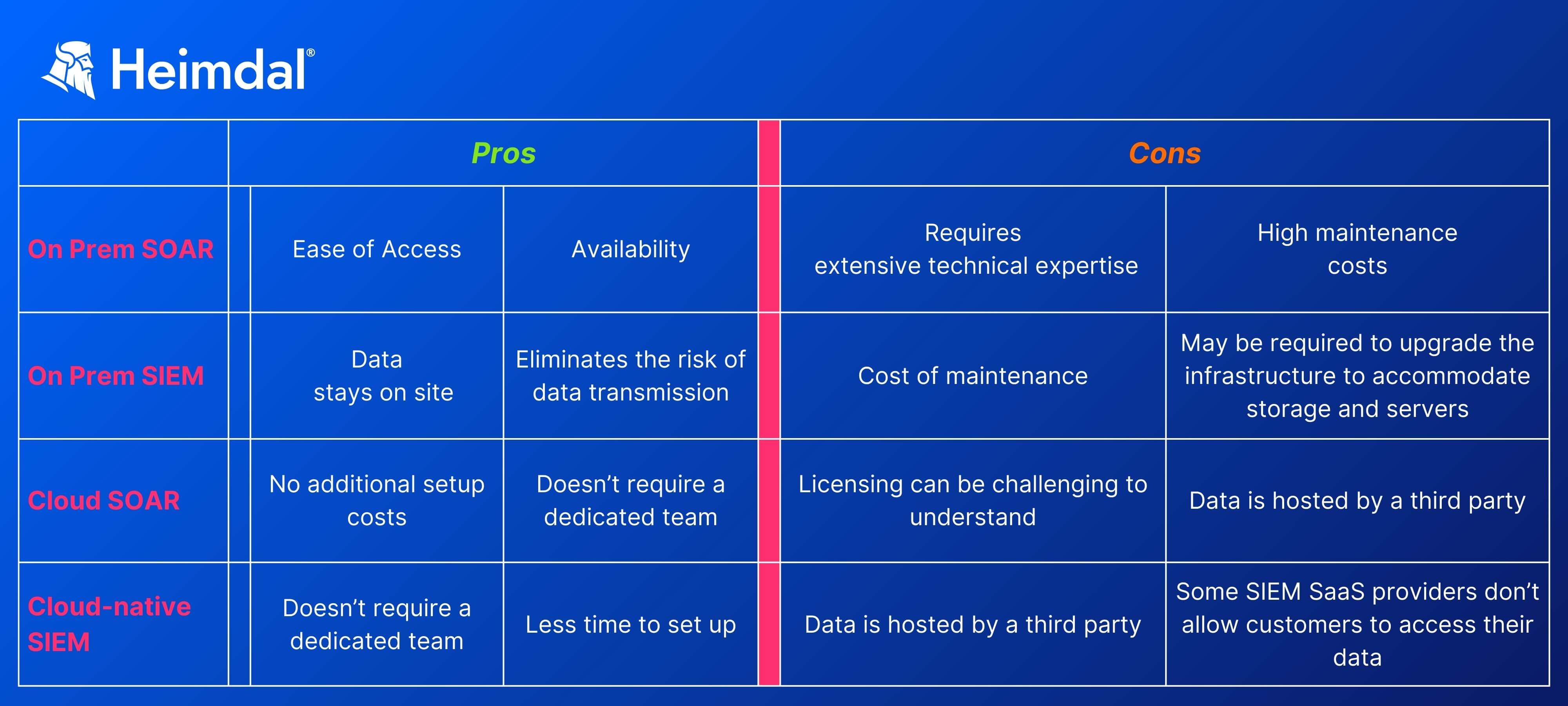
In the SOAR vs SIEM contest, both of them win, as each has its role in the threat detection and response process.
The SIEM system collects data from multiple sources and alerts the security team in case of a security incident. A SOAR platform helps set in motion all the security cogs needed to prevent, contain, or mitigate security threats.
To better understand the differences between SIEM and SOAR, let’s take a deeper view of each.
What is SOAR?
SOAR, a term introduced by Gartner, refers to a security-focused architecture that streamlines incident response (IR) through automated workflows, processes, and procedures. A SOAR platform’s role is to orchestrate, automate, and manage incident response workflows.
SOAR platforms pull in threat intelligence from various sources, including SIEM data, to give clearer, more useful alerts.
For more information on how SOAR solutions work and how you can use them for security automation, check out my other article on Security Orchestration Automation and Response Basics.
It’s important to understand that SOAR doesn’t replace SIEM. Security professionals use them in tandem to enhance the company’s security posture. SIEM is the data mining and signaling component, while SOAR automates incident response.
What is SIEM?
Security professionals use SIEM-based solutions to collect and analyze security data from multiple sources.
For instance, your run-of-the-mill SIEM can gather:
- firewall logs
- proxy or web filtering logs
- logs from miscellaneous security solutions (e.g., Sandbox, DLP, IPS/IDS, router NetFlow, etc.)
- network telemetry (i.e., security data generated by products that do Deep Packet Inspection),
- Windows auth
- information produced by endpoint-based security products
- threat intelligence
SIEM and SOAR solutions best practices
Now that you know what’s the difference between SIEM and SOAR, let’s see some best practices on how to use these solutions.
Baselines and standards
To have a detection & response baseline, you’ll need some standards. The same rules of engagement apply to both SIEM or SOAR. In the case of the former, you’ll need to set detection and alarm thresholds. For the latter, be sure to iron out those workflows before they go online.
Data hygiene
Don’t let that security data simply pile out. Put purging procedures in place and figure out what you should discard or keep.
Human factor
Although automation is a key feature of both SIEM and SOAR, it doesn’t mean the human factor is out of the picture. Most of the fine-tuning and setup must be done manually. A Security Operations Center could in fact integrate and use both solutions for better threat detection results.
SOAR + SIEM
Sounds like overkill, especially when you consider the financial aspects, but you can run SOAR and SIEM at the same time. Heimdal®’s eXtended Detection and Response (XDR) centralized monitoring and incident response hub brings you the same detection, response, and mitigation capabilities as any SIEM+SOAR combo.
Conclusion
The SIEM+ SOAR duo is an incredibly flexible threat identification, data gathering, and incident response tool that will aid you in your threat-hunting effort. A better security posture will add value to your company, while driving down costs.

- Granular telemetry across endpoints and networks.
- Equipped with built-in hunting and action capabilities.
- Pre-computed risk scores, indicators & detailed attack analysis.
- A single pane of glass for intelligence, hunting, and response.
If you liked this article, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, YouTube, and Reddit for more cybersecurity news and topics.










 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management  Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security









