Contents:
The Round-robin DNS is a load-balancing technique that helps manage traffic and avoid overloading servers. Load balancing means sending traffic to multiple servers for better performance and availability.
You can use the round-robin on single domain names that have multiple IP addresses assigned. Through this load-balancing technique, each time the domain name is resolved, it picks the returned IP address in a circular order.
The round-robin method distributes the traffic load evenly between the servers associated with the IP addresses, making the service fast and available.
Read on to find out:
- How Round-Robin DNS works
- Why use it: benefits & challenges
- How is Round-Robin DNS used for cyberattacks
How does Round-Robin DNS work?
Instead of using a specific load-balancing item of hardware to distribute traffic, when using a Round-robin DNS, an authoritative nameserver will do the balancing.
Round robin only works if the website’s or the service’s content is hosted on several redundant web servers. A redundant server is a replica of a system that incorporates lines of communication and network devices. If the primary DNS server goes down, it can act as the main operating system.
When repeatedly queried for an IP address, the DNS authoritative nameserver returns each time a different IP address. It picks those addresses in a rotational order:
- User no 1 makes a query for the example.com page and is pointed to the first IP address.
- User no 2 requests to access the example.com page and is taken to the second IP address.
- No 3 user asks to access example.com and is pointed to the third IP address.
- When user no 4 also makes a query for the example.com page he is sent to the first IP address. That is how the Round-robin algorithm goes.
A DNS server with a round-robin configuration has multiple different A records that point to the same domain name while displaying a different IP address. It operates in a loop. Each time it gets a query, the DNS server sends the IP address it most recently used to the back of the line.
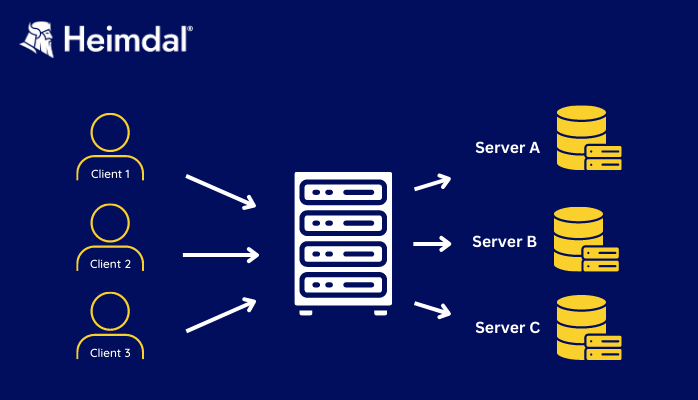
This way, the IP addresses in a round-robin DNS server work like the wheel spikes of a bike: each one gets to fall perpendicularly on the ground one after the other.
Why use Round-Robin DNS?
Using round-robin DNS as a load-balancing technique is both simple to understand and configure. However, it is not an ideal load-balancing method. This is because the round-robin algorithm doesn’t consider the server load or capacity. You`d rather need to use a load balancer for that.
The result is some of the clients might be directed to an already overloaded server.
Further on, let’s see which are the benefits and disadvantages of using Round-robin DNS to distribute DNS requests across a group of servers.
Benefits:
- It’s easy to set up.
- It’s cost-effective, as there is no need for extra hardware or software.
- The round robin method treats each DNS request equally, by the „first come, first served” principle, no matter whom the queries come from.
- It offers increased availability. If one of the servers goes down, it will automatically direct traffic to the other servers.
Disadvantages:
Unfortunately, Round-robin DNS also comes with a series of drawbacks.
- Uneven traffic distribution – Because of DNS caching and client-side caching, it doesn’t always succeed to evenly-distribute traffic. When a user makes a query to a high-traffic recursive resolver for a certain site, the resolver will cache the website’s IP and could continue to send a great amount of traffic to that one IP.
- No failure detection – If one of the multiple servers goes offline, the algorithm continues to use it and direct queries to it. Usually, its A record has to be removed manually from the loop. Otherwise, each time traffic is directed to the fallen server, one unlucky user will be denied service.
- Equal priority – There are also downsides to treating each request equally. With the Round-robin DNS technique, you can’t prioritize processes, no matter how important they are.
How is Round-Robin DNS used in cyberattacks
Cyberattackers leverage the Round-robin DNS load-balancing method for their fast flux evasion technique. Fast flux is a DNS-based avoidance technique that threat actors use to cover up their phishing and malware delivery websites.
Round-robin DNS enables them to associate multiple redundant web servers, that have distinct IP addresses, with a domain. To set up their fast flux obfuscation technique, attackers also set a very short TTL for these IP addresses. This way, once the TTL expires, the IP address in the cause will no longer be associated with that domain name. This gives the security team a harder time when trying to bring down malicious sites.
So, although it’s not a malicious tool, hackers can use Round-robin DNS as one.

Heimdal® DNS Security Solution
- Machine learning powered scans for all incoming online traffic;
- Stops data breaches before sensitive info can be exposed to the outside;
- Advanced DNS, HTTP and HTTPS filtering for all your endpoints;
- Protection against data leakage, APTs, ransomware and exploits;
How can Heimdal® help?
91% of online threats use the DNS. Threat actors launch DNS attacks to spread malware or conduct phishing campaigns. Neglecting to keep up with modern methods always comes with a price. In 2022, according to the IDC report, the average cost of a DNS attack was estimated to be $942,000. Money are not the only loss of victim organizations. Reputation damage in front of customers and employees is also a huge cost.
Yes, hackers keep coming up with new threats and obfuscation methods. Yet you can still win the fight against cyber criminality, if you choose the right cybersecurity partner. Heimdal’s DNS Security – Endpoint module is currently the best solution in the world to secure your machines without having to stop or slow down the workflow.
As part of this module, the DarkLayer Guard engine protects endpoints against malware, social engineering scams, and drive-by attacks. The product automatically filters all network packages based on DNS requests.
DarkLayer Guard’s unique 2-way traffic filtering engine supports fully customizable white/blacklisting. When a malicious domain is found, the solution swiftly blocks network communication to mitigate Zero Hour exploits, Ransomware C&Cs, next-gen attacks, and data leakages.
Wrap up
Round-robin DNS is one more example that hackers can leverage a totally legitimate tool or feature in harmful ways. While hackers use domain generation algorithms to enhance their chances to succeed and hide their footprints, security teams should also upgrade their prevention measures.
FAQs on Round robin DNS
How do I check my DNS round robin?
Open the command prompt window. Type “ping hostmane” and use the host name setup in the DNS Round Robin configuration. Press “Enter”. The IP address you receive in the four replies should match the IP address of one of the load balancing servers in the DNS Round Robin server group.
What is the difference between Round-robin DNS and load balancing?
Round Robin DNS cycles through a list of DNS servers and distributes traffic evenly. On the other hand, load balancing directs traffic to the least busy server for better efficiency.
Can Round-robin DNS replace hardware load balancing?
Round Robin DNS cannot substitute hardware load balancing. It doesn’t assess server health to distribute traffic effectively.
And if you liked this article, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube for more cybersecurity news and topics.










 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management  Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security







