Patch management tools identify software applications running on outdated versions.
This can make your infrastructure vulnerable to cyber-attacks.
To counter this trend, we’ll discuss the best free and/or open-source patch management tools and how they can improve your apps’ health and cyber-resilience factor.
Why are Open Source Patch Management Tools Important?
Open-Source patch management tools are vital because they close critical security gaps.
Edgescan’s 2024 Vulnerability Statistics Report uncovered several interesting facts regarding the importance of patching.
Why is Heimdal one of the best PATCH MANAGEMENT solutions?
Learn by booking a free trial here!
8 Best Open Source Patch Management Tools
To help you get started on your way towards true vulnerability management, here are eight of the best free and/or open-source patch management tools.
These will give you a sense of what your enterprise needs and who out there cut you the best deal.
Bonus Tool: Heimdal® Patch & Asset Management
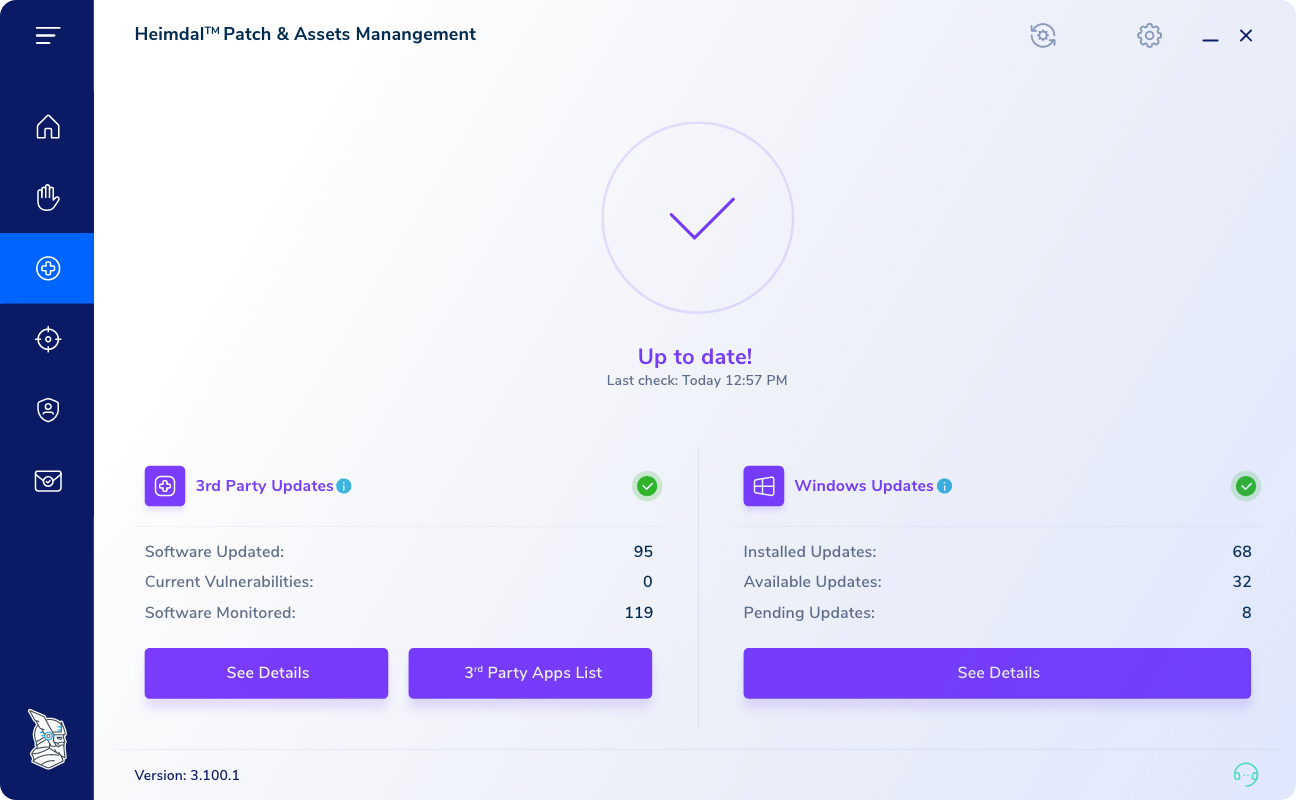
Screenshot from Heimdal the Patch and Asset Management’s dashboard.
Heimdal®’s Patch & Asset Management is neither free nor open-source, but we do we have a 30-day, no strings attached trial.
If you’re interested in giving us a try, book a demo now.
Why is Heimdal One of the Best Patch Management Solutions?
Here are some reasons why you should try out our patch management solution.
KEY FEATURES
- Centralized Console.
Streamlines patch management through an integrated dashboard. Enables efficient control and overview of software inventories.
- Customizable Patching Options.
Allows customization of patching schedules, prioritization of user groups.
- Support for Over 180 Applications.
Includes ready-to-use support for a wide range of third-party applications, ensuring extensive coverage.
- Swift Patch Deployment.
Industry-leading time frame from vendor to user, with a waiting period of less than 4 hours.
- Policy and Compliance Control.
Automates software deployment configurations while ensuring compliance standards.
- Infinity Management Add-On.
Provides extra automation capabilities for internal software or applications through command-line scripting.
- Ensured Continuous Compliance.
Ensures compliance with key industry standards and regulations.

Infographic describing what Heimdal Patch & Asset Management is ideal for versus less suitable for.
PROS
- Automates patching for various software, enhancing efficiency.
- Manages software assets and vulnerabilities effectively.
- Easy setup, intuitive interface, with strong support.
- Customizable update policies and rollback capabilities.
- Compatible with multiple operating systems.
CONS
- Reporting capabilities can be inconsistent, with some users finding errors in report data.
- Admin portal can be difficult to navigate initially.
#2 PDQ Deploy
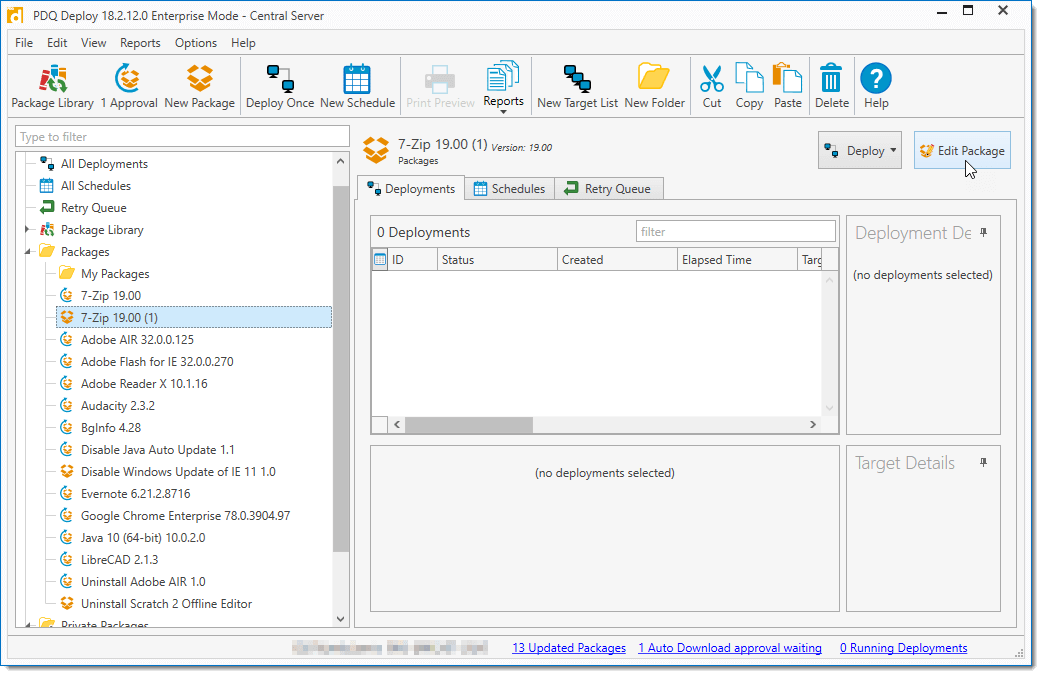
A patch management tool for Windows that can update 3rd party apps and deploy custom scripts.
The solution comes with a package library of over 200 popular applications ready-to-deploy.
KEY FEATURES
- Automatic Download & Scheduling
Manages software updates via the PDQ Deploy package library, ensuring timely deployment.
- One-Click Deployment
Allows rapid installation of multiple applications using the nested package feature.
- Patch Prioritization & Scheduling
Enables customized patching strategies by prioritizing critical updates.
- Inventory Scan
Detects and lists the latest available software updates for efficient patch management.
- Failed Patch Queue
Automatically resumes interrupted updates after connectivity issues are resolved.

Infographic describing what PDQ Deploy is ideal for versus less suitable for.
PROS
- User-friendly interface that simplifies deployment tasks, making it accessible for small IT teams.
- Allows deployment of custom scripts and packages, offering flexibility.
- Integrates well with Active Directory for targeting specific machines or groups.
- Offers a free version with basic features, making it suitable for small-scale operations.
CONS
- Limited reporting features compared to more comprehensive solutions.
- Lacks built-in vulnerability assessment tools, requiring additional software for full endpoint security.
- Not suitable for large-scale environments without the enterprise version.
#3 Comodo
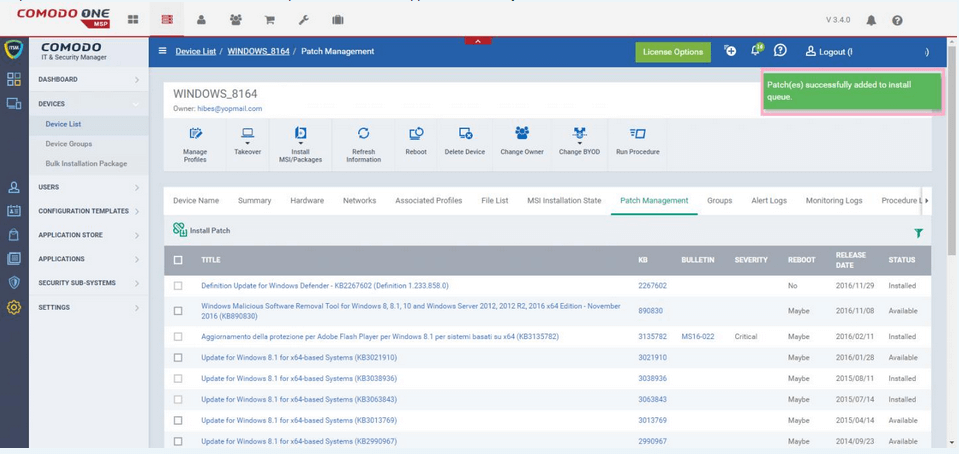
Screenshot from Comodo One.
Comodo addresses vulnerabilities that create security weaknesses or system unavailability.
It manages patches for Windows, Linux, and third-party applications.
KEY FEATURES
- Change Tracking & Implementation
Monitors and applies system updates to maintain security and performance.
- Patch Deployment
Automates installation and distribution of patches across multiple systems.
- Audit & Vulnerability Assessment
Provides tools to assess patch status and identify system vulnerabilities.
- Compliance
Ensures all devices and software are updated and meet security standards.
- Endpoint Discovery
Identifies all managed devices in the network for seamless patch deployment.

Infographic describing what Comodo is ideal for versus less suitable for.
PROS
- Provides integration with Comodo’s other security products, like antivirus and firewall.
- Supports a wide range of software, including Windows OS and third-party applications.
- Centralized dashboard for easy management across all endpoints.
CONS
- Can be difficult to configure, especially for non-technical users.
- Customer support has mixed reviews, with some users citing slow response times.
- The user interface can be cluttered and overwhelming.
#4 Miradore
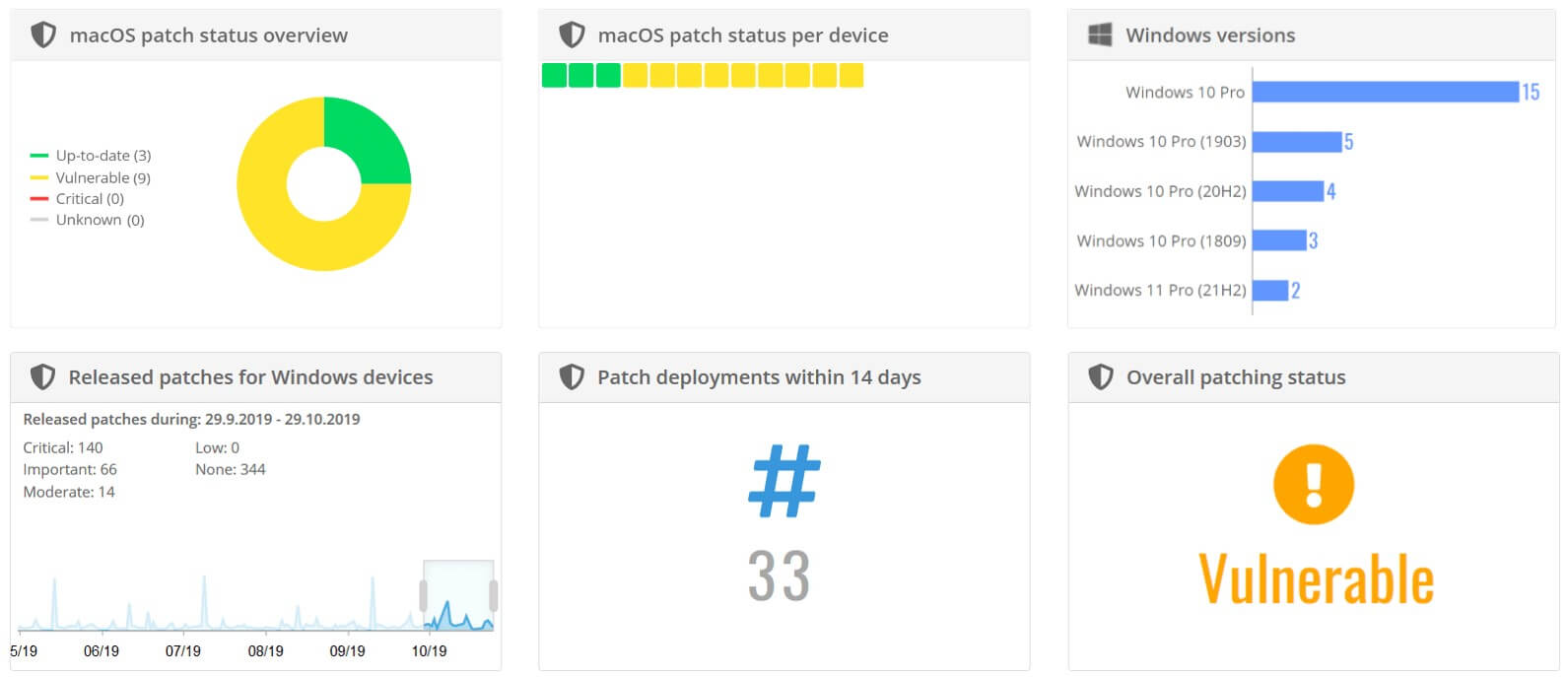
Screenshot from Miradore.
Miradore offers a streamlined approach for maintaining Windows and Mac security and performance.
It focuses on automating the patch management process.
KEY FEATURES
- Automated Patch Management
Streamlines patching for Windows and macOS devices, reducing complexity.
- Detailed Reporting & Insights
Provides in-depth reports on patch releases and installation status.
- Broad Software Support
Covers nearly 100 vendors, ensuring extensive application compatibility.
- Patch Lifecycle Management
Handles detection, reporting, testing, and deployment of updates.
- Security & Compliance
Mitigates vulnerabilities while ensuring compliance with HIPAA, GDPR, and other standards.

Infographic describing what Heimdal Patch & Asset Management is ideal for versus less suitable for.
PROS
- Cloud-based solution that simplifies the management of Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android devices.
- Offers mobile device management (MDM) capabilities alongside patch management.
- Suitable for smaller organizations with budget-friendly pricing.
CONS
- Limited advanced features for complex enterprise environments.
- Does not support as many third-party software patches compared to other solutions.
- Reporting and analytics capabilities are basic.
#5 Local Update Publisher
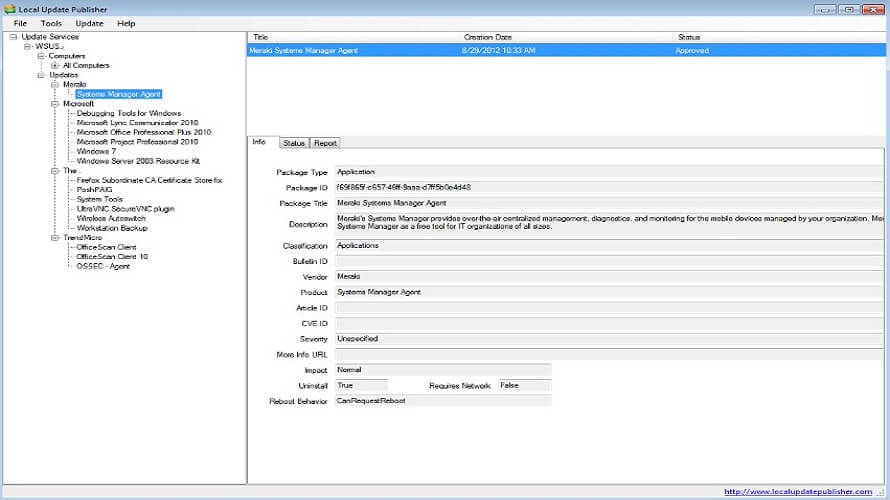
Screenshot from Local Update Publisher.
Is an open-source tool designed to deploy app and updates in a domain or workgroup via a WSUS API.
KEY FEATURES
- Application Publishing
Deploys applications to a domain or workgroup for centralized management.
- Custom Installation Rules
Defines installation behavior to control software deployment.
- Installation Tracking
Monitors the progress of installations for better oversight.
- WSUS Group Integration
Allows approvals and management within WSUS groups.
- WSUS Infrastructure Support
Utilizes existing WSUS setup, supporting multiple parent and child servers.

Infographic describing what Local Update Publisher is ideal for versus less suitable for.
PROS
- Integrates directly with Microsoft’s WSUS (Windows Server Update Services), making it familiar for Windows environments.
- Allows deploying patches for third-party applications through a known interface.
- Free, open-source solution suitable for budget-conscious organizations.
CONS
- Requires knowledge of WSUS to set up and maintain.
- Lacks the more advanced features found in commercial solutions, such as extensive reporting and automation.
- Limited to Windows environments.
#6 Ansible
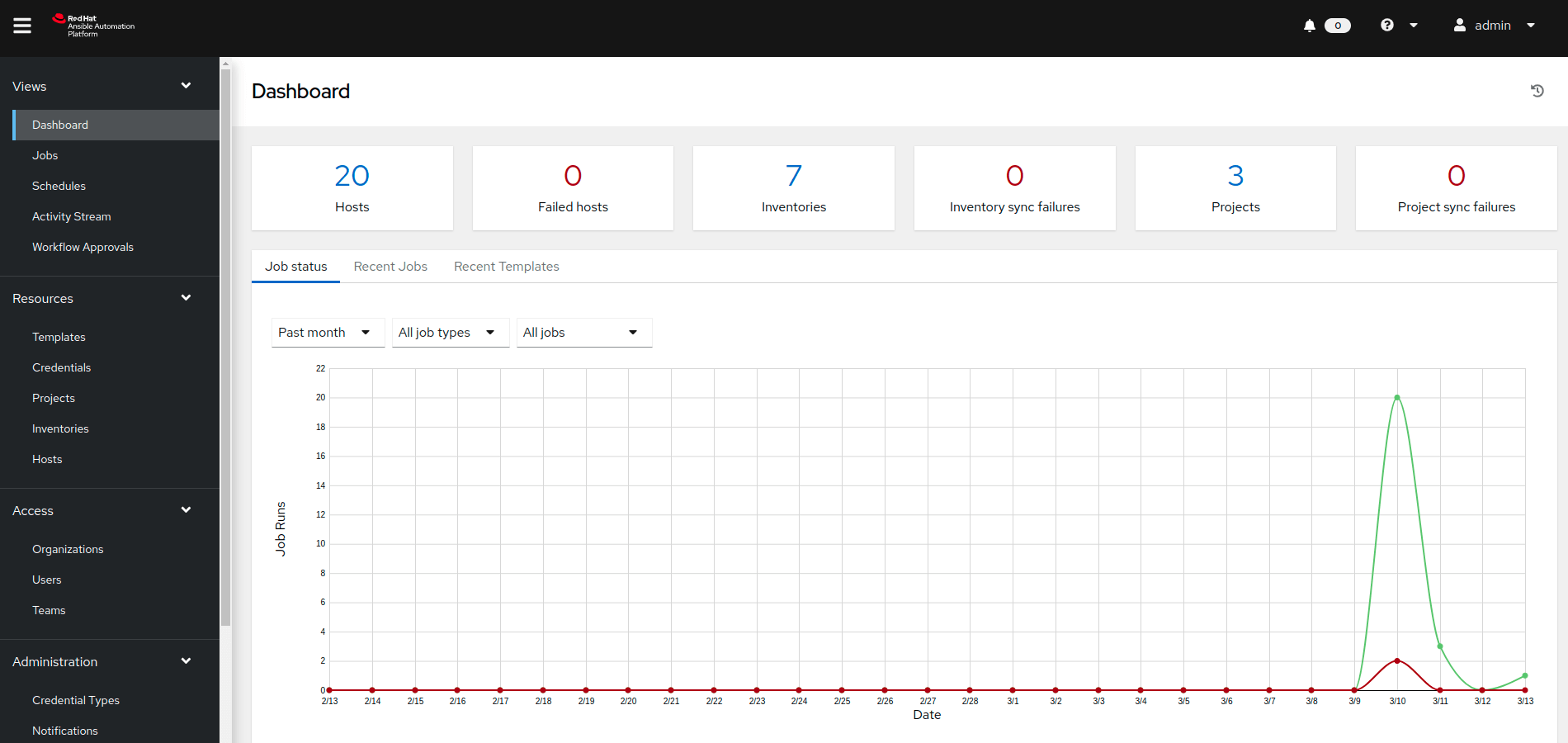
Screenshot from Ansible.
Is an open-source IT automation engine. Use Ansible to automate tasks across various systems and platforms.
Also, it can enhance efficiency and consistency in managing updates and installations.
KEY FEATURES
- Automated Patch Management
Handles patching and updates across various Linux distributions, ensuring system consistency.
- Task Automation Modules
Provides modular automation for a wide range of IT processes.
- Agentless Architecture
Uses SSH to connect and execute tasks without requiring an agent on managed nodes.
- YAML-Based Playbooks
Orchestrates complex IT workflows with easily customizable playbooks.
- Ad-Hoc Command Execution
Supports on-the-fly automation for single-use tasks without requiring a full playbook.
- System Maintenance
Manages system updates, restarts, and reconnections to keep software up to date.

Infographic describing what Ansible is ideal for versus less suitable for.
PROS
- Open-source and highly flexible, suitable for a variety of automation tasks beyond patch management.
- Uses playbooks, which allow users to customize automation tasks in a detailed manner.
- Works across various platforms including Windows, Linux, and macOS.
CONS
- Requires scripting knowledge, which may pose a learning curve for new users.
- Lacks out-of-the-box patch management functionalities compared to dedicated solutions.
- Limited built-in reporting and alerting features.
#7 SysWard
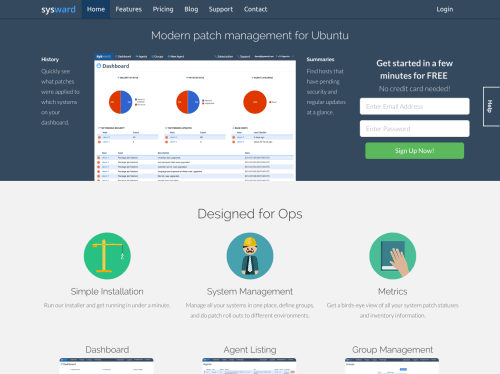
Screenshot from SysWard patch management.
Brings ease of use and efficiency to Linux server patch management.
KEY FEATURES
- Multi-OS Support
Compatible with various Linux distributions for flexible patch management.
- Simplified Server Management
Optimized tools for handling mixed server environments efficiently.
- System-Wide Overview
Monitors pending updates, patch failures, and inactive hosts.
- Critical Alerts & CVE Notifications
Provides real-time security alerts via email and chat based on installed packages.
- Patch Tracking & Safe Deployment
Uses groups and tags for structured, environment-specific patch rollouts.
- One-Click Upgrades & Filtering
Allows quick software updates and precise package management.

Infographic describing what SysWard is ideal for versus less suitable for.
PROS
- Provides automated patch management and remote monitoring capabilities.
- Includes an easy-to-use dashboard that helps in managing updates.
- Offers additional features such as antivirus integration and device monitoring.
CONS
- Limited brand recognition and community support compared to more established solutions.
- May not offer as many integration options with other IT tools.
- Reporting features are not as comprehensive.
#8 OPSI (Open PC Server Integration)
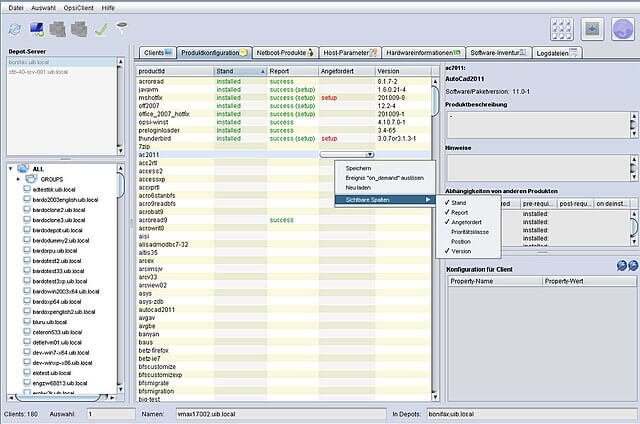
Screenshot from OPSI dashboard.
OPSI is an open-source device management tool that offers key automatic patching features.
This tool is compatible with Windows, Linux, and macOS.
KEY FEATURES
- Automatic Software Distribution
Deploys applications and updates across multiple systems seamlessly.
- Patch Management
Automates the process of detecting, testing, and applying patches.
- OS Installation
Supports both package-based and image-based automated OS deployments.
- Configuration Management
Ensures system settings and configurations remain consistent across devices.
- Hardware & Software Inventory
Tracks system components and installed applications for better asset management.

Infographic describing what OPSI is ideal for versus less suitable for.
PROS
- Open-source solution with strong community support.
- Offers extensive configuration options for deploying software and managing updates.
- Suitable for Linux environments, with cross-platform support.
CONS
- Complex setup process requiring technical expertise.
- User interface is not as polished as commercial products.
- Documentation can be lacking for newer users.
#9 GFI LanGuard
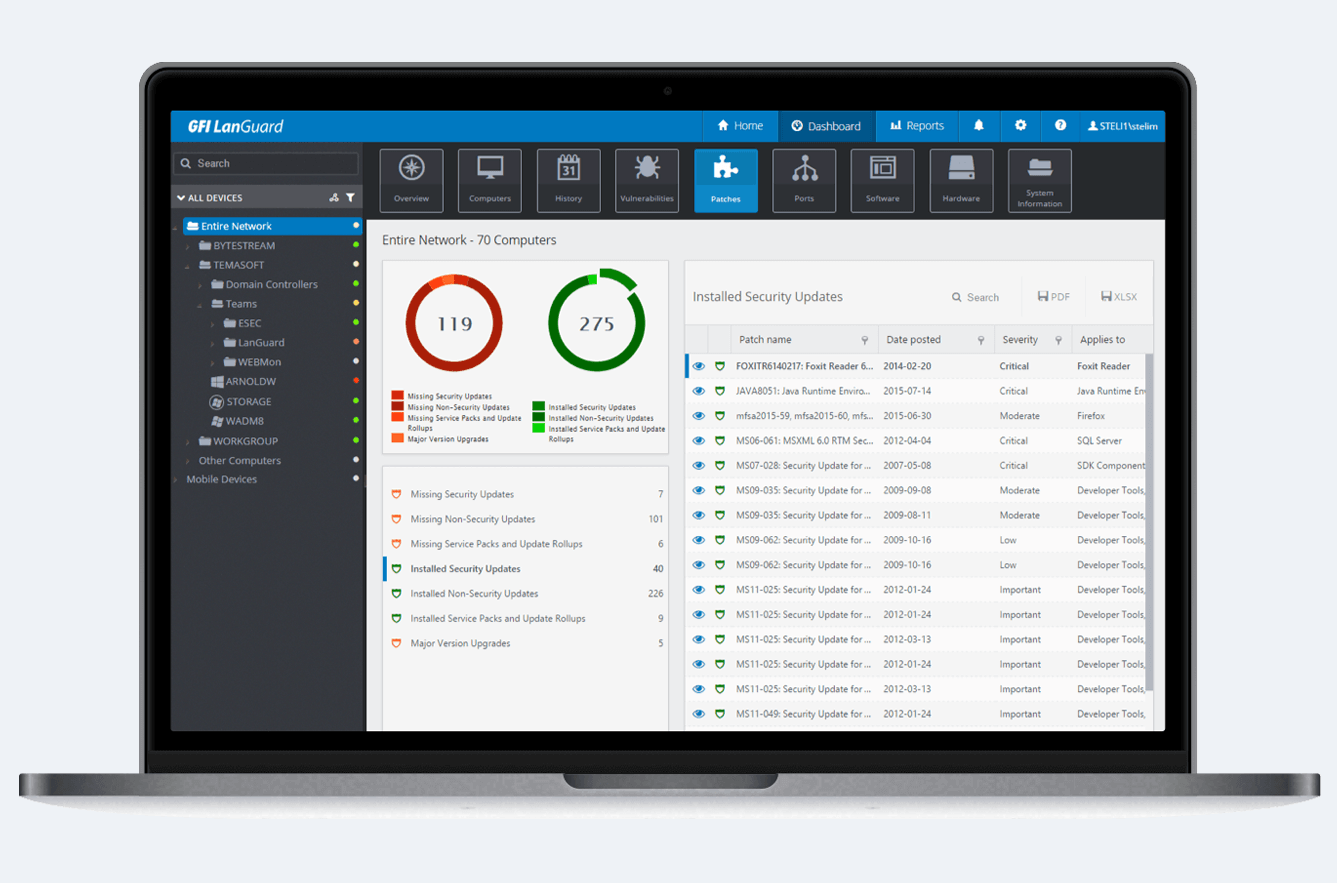
Screenshot from GFI LanGuard.
An endpoint protection software which enables you to discover and close vulnerabilities.
It allows admins to scan networks or perform scans on demand and balance processing load via agents.
The tool can also balance the processing load using agents.
KEY FEATURES
- Network Scanning
Performs on-demand and automated scans to detect vulnerabilities.
- Patch Deployment
Installs Microsoft Windows and third-party updates across endpoints.
- Mobile Device Management (MDM)
Supports Android and iOS setup while identifying mobile vulnerabilities.
- User-Friendly Dashboard
Provides a web-based interface for easy logging, reporting, and endpoint control.
- Auto-Download & Patch Identification
Detects and downloads missing updates to maintain system security.
- Compliance & Security Standards
Meets industry standards like SANS Top 20 and OVAL for vulnerability assessment.

Infographic describing what GFI LanGuard is ideal for versus less suitable for.
PROS
- Combines patch management with network security scanning, offering a holistic approach.
- Supports a wide range of third-party applications and OS patching.
- Provides detailed reports and compliance auditing features.
CONS
- User interface can be outdated and less intuitive.
- Higher pricing compared to other solutions, especially for smaller organizations.
- Setup and configuration can be time-consuming.


 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management
 Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security










