Contents:
Risk-based vulnerability management (RBVM) exceeds the efficiency of legacy vulnerability management by far, being a more strategic and smart approach to protecting critical assets. Read on to learn more about what this concept refers to, what are its components, and how to implement a risk-based cybersecurity approach strategy.
What Is Risk-Based Vulnerability Management? Definition
Vulnerability Risk Management, or Risk-based vulnerability management (RBVM), is a cybersecurity strategy in which organizations emphasize software vulnerabilities remediation according to the risk they pose. A risk-based vulnerability management strategy has several components.
- It uses threat intelligence to identify the vulnerabilities attackers are discussing, experimenting with, or using, and to generate risk scores based on the likelihood of exploitation.
- It is mindful of the business context of multiple assets as an intrusion into some network segments may be more harmful or probable than others.
- It combines risk assessment and asset criticality, thus focusing patching efforts on the vulnerabilities that are most likely to be exploited and that reside on the most critical systems.
A risk-based approach focuses on the likelihood of a vulnerability being exploited, rather than just on the severity of potential consequences if it is exploited.
What Is a Security Vulnerability?
A security vulnerability is a flaw in the design, implementation, operation, or management of a system that can be exploited by an attacker to violate the system’s security policy. Security vulnerabilities are often documented as notes, bugs, glitches, or exploits.
A good example of this was when Facebook (Meta) was hacked and millions of people’s data were leaked online. The hacker was able to find out what people liked on Facebook and then used that information to send them targeted ads.
Types of Security Vulnerabilities
The following are some of the most common types of security vulnerabilities:
Software vulnerabilities
Software vulnerabilities are usually found in the coding or design of the software. These may allow attackers to take control of computers remotely without authorization, perform unauthorized actions, or access sensitive information like passwords and credit card numbers.
Hardware vulnerabilities
Hardware vulnerabilities are normally flaws in the hardware design that allows attackers to bypass security features and gain access to sensitive data or resources on devices like smartphones and laptops.
Network vulnerabilities
Network vulnerabilities include weaknesses in network protocols that allow attackers to intercept data as it is sent over the internet, or eavesdrop on conversations between people using email.
How Risk-Based Vulnerability Management Works
Risk-based vulnerability management works by means of tools companies use to perform an assessment of current vulnerabilities and to establish their risk level to critical business assets. This process involves some essential steps:
Providing visibility
As a first step of the risk-based vulnerability management process, enterprises should make sure that they have visibility over cloud/hybrid-based environments, traffic, and endpoints and identify and map all of their assets in order to efficiently determine what must be secured. RVBM helps with defining the operational landscape, including traditional assets, mobile, web apps, cloud, container, IoT, and OT, thus facilitating a comprehensive overview of the related threat landscape.
Security gaps identification
The following step is represented by the identification of security gaps through scanning and monitoring for attack vectors. You must become aware of the assets’ status in relation to which vulnerabilities they own, what misconfigurations exist, and so on. An important characteristic of this step is that the process should be regular and cover a nearly complete attack vector spectrum in accordance with the continuous emergent vulnerabilities.
Assessing the risk context
This is the moment when the risk-based vulnerability management strategy comes into play, as once the flaws were identified, not they should be prioritized in relation to their severity level, if and how might they be exploited and what will be the potential damage along with what are the current security tools of the companies in relation to this.
Remediating the problem with an RBVM tool
The vulnerabilities were identified and prioritized based on risk level, now they should be remediated. This can be done efficiently with an RBVM tool that will work on three areas: it will make sure that the vulnerability identification process is continuous, providing an accurate and updated overview of what’s at risk in your organization, it will provide risk-based patch management in accordance with the determined risk context and finally, it will let you carry out the vulnerability remediation process effectively and effortlessly.
Automate the Patch Management Process with Heimdal®
Find out more 30-day Free Trial. Offer valid only for companies.Legacy Vulnerability Management vs. Risk-Based Vulnerability Management
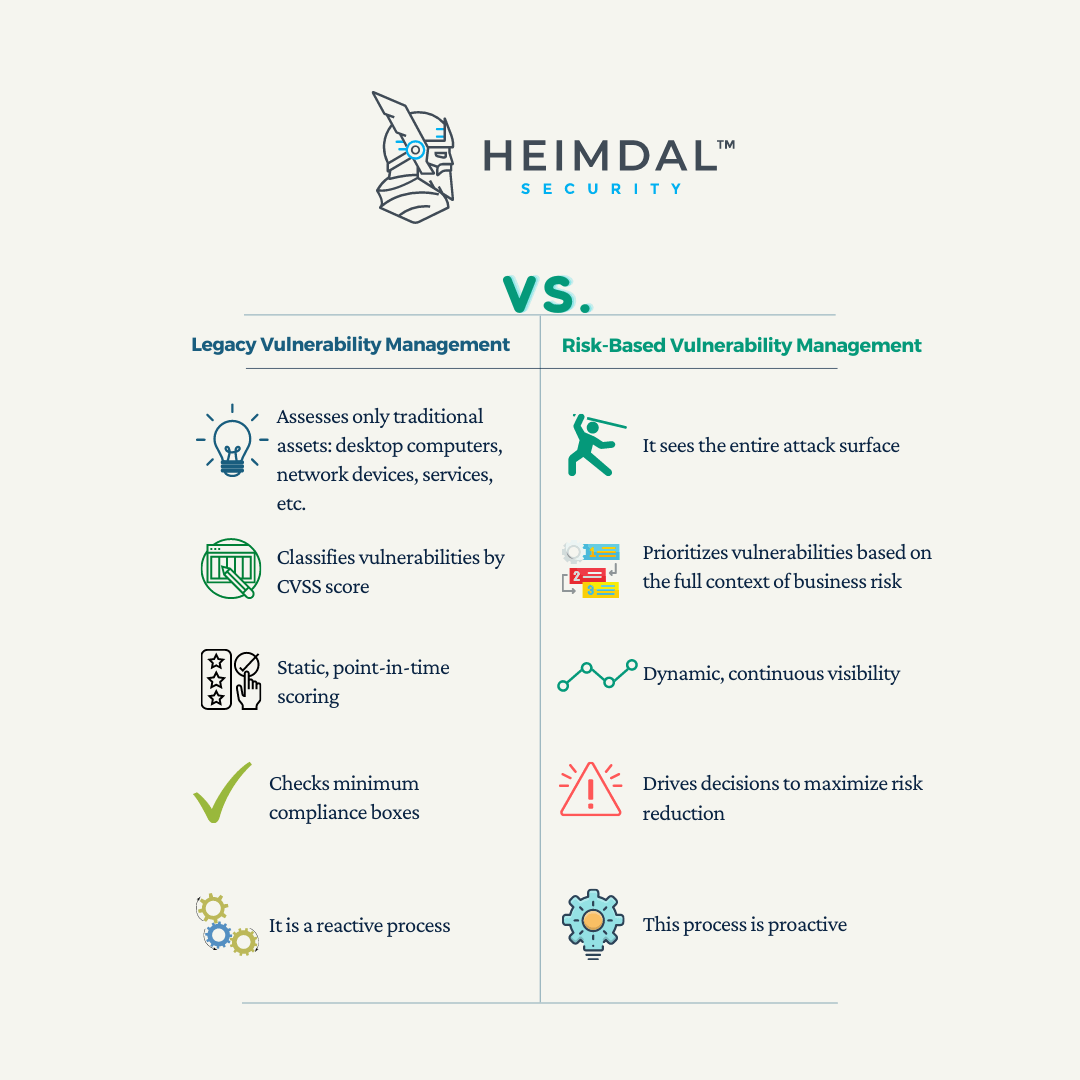
Unlike legacy vulnerability management, risk-based vulnerability management doesn’t just discover vulnerabilities. It helps you comprehend vulnerability risks with threat context and potential business impact awareness.
There is a clear delimitation between legacy vulnerability management and RBVM, as the first process is reactive, concentrating on traditional infrastructures, system silos along CVSS score. While, the second one is the opposite, being defined as a proactive process, more dynamic, and in continuous development, as it focused on the vulnerabilities themselves and the risk they pose to a business, not merely on their severity level.
| LEGACY VULNERABILITY MANAGEMENT | RISK-BASED VULNERABILITY MANAGEMENT |
|---|---|
| Assesses only traditional assets | Sees the entire attack surface |
| Classifies vulnerabilities by CVSS score | Prioritizes vulnerabilities based on the full context of business risk |
| Static, point-in-time scoring | Dynamic, continuous visibility |
| Checks minimum compliance boxes | Drives decisions to maximize risk reduction |
Risk-Based Vulnerability Management Statistics
VulcanCyber analyzed the response of 200 technology decision-makers (C-Suite, VP, Director, Manager) from North America in the period between September 23 – October 17, 2021. Here are the statistics they pushed in relation to the risk-based vulnerability management strategy:
- 86 % of respondents use vulnerability severity to prioritize vulnerabilities, while 70% voted for threat intelligence and 59% for asset relevance.
- 71% use the common vulnerability scoring system to score and prioritize vulnerabilities while 59% use OWASP Top Ten and 47% use scanner reported severity.
- 78% of the participants say that high-ranked flaws should be given a lower rank, while 69% say the opposite, that low-ranked vulnerabilities should have a higher score.
- Their main concern falls on data exposure (54%), broken authentication (44%), and security misconfigurations (39%).
Four Reasons Why Risk-Based Vulnerability Management Is Needed
Risk-based vulnerability management is needed because it helps the IT vulnerability management team prioritize which system vulnerabilities are the most critical a thus which need immediate remediation, letting them implement a strategy based on precedence.
Craig Lawson, a Gartner’s VP Analyst, emphasized the importance of vulnerability risk management in the context of risk mitigation.
What’s important is turning ‘whether a platform gets patched’ into ‘whether the specific risk of platform vulnerability has been sufficiently mitigated.
Here are 4 reasons why RBVM is important:
#1 The number of vulnerabilities is growing day by day
Keeping up with the number of vulnerabilities that emerge day by day can become tiresome for security teams and trigger business disruptions, that’s why an RBVM strategy is important in controlling properly and addressing each critical flaw.
#2 Everybody’s moving to the cloud
Since cloud technologies have started to gain more and more ground, this means more assets connected to the Internet. More connected assets obviously mean more exposure risk that can only be efficiently managed with risk-based vulnerability management.
#3 The wave of “working from home” trend
With more and more employees working from home, security teams need to be aware of what software employees use in their daily tasks. The efficiency of an RVBM plan lies in the adoption of a tool that helps with the identification of unknown assets.
#4 Hackers shifted their focus from high CVSS to medium or low CVSS
Threat actors are no longer targeting so often high-severity flaws in accordance with the CVSS score. They have shifted their focus instead on medium to low-vulnerabilities which serve as an entry point. They do this because they know these flaws are not paid enough attention to comparing to those ranked as severe.
This also enforces the fact that an RBVM approach is more practical, as it addresses vulnerabilities by risk context this also includes their exploitation likelihood, while traditional vulnerability management only focuses on CVSS ranking.
Benefits of Risk-Based Vulnerability Management
#1. The ability to identify what to fix first
This first step represents a win-win for both teams. Clearing the traditional disagreements that can often exist between IT and security teams, everyone can understand what is a priority and what is not – and why.
#2. Security teams no longer have to generate extended patch lists
Instead, they are confident that they are taking the right actions to protect the organization. In the meantime, IT teams know that they can concentrate on a clearly defined set of cybersecurity concerns that can be remediated without adversely impacting application or web services availability.
#3. Security and IT teams can work hand-in-hand across multiple business units
As they are able to spend less time chasing highlighted vulnerabilities that actually don’t pose a particular threat to their organization, they can now prioritize remediating those vulnerabilities that actually represent the greatest risk. As far as cyberthreats are concerned, they are able to leverage their newfound efficiencies to focus instead on other strategic projects.
#4. RBVM platforms enable these teams to clearly communicate their strategies
More exactly, besides enabling improved collaboration between security and IT teams, they can report how they are lowering risks for the organization as a whole. What’s more, they can support risk-intelligent decision-making going forward in the context of the organization and its IT infrastructure.
With the proper cybersecurity knowledge and practices, as well as reliable services, RBVM will come at hand. As always, Heimdal™ Security can help you with the right solutions. If you want to know more about which of our company products are best suited for your needs, don’t hesitate to contact us at sales.inquiries@heimdalsecurity.com.
Best Practices on Implementing a Risk-Based Vulnerability Management Approach
A multi-perspective RBVM approach
Vulnerability prioritization should be done from several points of view in an RBVM approach, which means that factors like vulnerabilities severity, if they are currently exploited, what’s their critical level reports to the business, and how much the impacted system is exposed, should be taken into account.
According to Lawson, one best practice that really works and mitigates risk faster is to switch the focus and address vulnerabilities exploited in the wild.
One of the biggest changes you can make is to focus on the vulnerabilities that are being exploited in the wild. That should be the No. 1 goal and will drive down the most risk the fastest.
Compensating controls and remediation measures should come together
Compensation controls that can perform virtual patching should be combined with remediation solutions like a Patch and Asset Management Tool, a technique that will make your strategy to reduce the attack surface truly efficiently maintaining at the same time at minimum the organization’s operational impact.
Our Patch & Asset Management tool lets you automate your vulnerability management, covering patches from Microsoft to third-party and proprietary ones. You benefit from features like on-demand update, advanced scheduling, patching flows updating by means of command-line scripting, and many more. The best part about our tool is the vendor-to-end-user-waiting-times, this meaning that you have the released patch fully repackaged, tested, and ready to be deployed in your system in less than 4 hours from the release.
An RBVM approach should answer the 4W
An RBVM approach should answer the 4Ws in order to prove efficient:
- What is the attack surface of an organization?
- What are the most critical assets a company should focus on?
- Where are the gaps?
- What’s the threatening likelihood of a vulnerability?
Building a context-based risk score based on the 5 basic vulnerability management categories
A context-based risk score should be built in accordance with the 5 basic vulnerability management categories which are vulnerability, asset, network, organization, and external threat environment. Thus, companies should establish the individual features of a flaw starting from the CVSS score, then analyzing the asset where the flaw is located and whether this asset has a critical status or encompasses critical data, then the particular network characteristics where the asset is connected should be investigated to see if the asset is connected to the Internet and how the policies around it impact its susceptibility to a cyberattack.
Then, to properly assess a context-based risk score, it should be defined what is the relation of the identified asset and vulnerability to the company’s business objectives and finally, the external threat environment should not be overlooked, but instead establish if the flaw has any relation whatsoever with social feeds like the dark web and if it fears the publishing of a future potential exploit.

Heimdal® Patch & Asset Management
- Create policies that meet your exact needs;
- Full compliance and CVE/CVSS audit trail;
- Gain extensive vulnerability intelligence;
- And much more than we can fit in here...
Wrapping Up
With the proper cybersecurity knowledge and practices, as well as reliable services, RBVM will come at hand. As always, Heimdal™ Security can help you with the right solutions. If you want to know more about which of our company products are best suited for your needs, don’t hesitate to contact us at sales.inquiries@heimdalsecurity.com.
If you have any comments on this article, we’ll be happy to hear your opinion, so you may drop a comment below. As always, if you want to keep up to date with everything we post, don’t forget to follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, Youtube, and Instagram for more cybersecurity news and topics.
This article was initially drafted by Cezarina Dinu in February 2021 and updated by Andra Andrioaie in January 2022.










 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management  Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security








