Contents:
Event Viewer is a component of Microsoft’s Windows NT operating system that authorizes administrators and users to view the event logs on a local or remote machine. Applications and operating-system components can use this centralized log service to report events that have taken place, such as a failure to start a component or to complete an action. In today’s article we are going to focus on what is audit failure in Event Viewer, but first, let’s take a look at the audit failure matter.
Audit failure happens when an auditor digresses from the relevant professional standards in such a way that the opinion contained in his or her audit report is incorrect. Audit failures can create a less safe environment, leaving your company exposed to external attacks.
They are usually related to deficient auditory instruction, failure to practice adequate professional doubt in assessing management representations, not evaluating enough customer valuation estimates, primarily not being involved in any auditing activities in any way, and/or generating insufficient audit papers.
According to an American application security organization, the most common audit failures from which we all can learn are:
- Deficient prioritization from the top. If management doesn’t accept the significance of compliance, then its employees implementing and working on the controls won’t, either. Management’s way of looking at it sets up priority for the entire company, which drives resources and involvement.
- Insufficient documentation. The majority of the discoveries auditors identify are caused by documentation failures. As a solution, organizations should document what they’re doing in written policies, make sure everyone is instructed in the right procedures, and create a paper trail of the performance of the controls.
- Human error compounded by too many manual processes.
- Weak or missing risk assessment. Without a proper risk assessment, companies will squander resources on controls that don’t address the highest risk. This means missing or skimping on essential controls that transform into audit findings or create unwanted exposure for an organization.
- Internal assessment too self-congratulatory. Organizations should develop a proper autonomous internal audit program—one that has a distinct reporting form than the security and IT departments—or employ an independent assessor.
What is Audit Failure in Event Viewer?
A Windows system’s audit policy establishes which type of information about the system you’ll find in the Security log. Windows utilizes nine audit policy categories and 50 audit policy subcategories which you can enable or disable.
Their purpose is to provide you more granular control over which information is registered. Below you can see the main categories:
- Audit account logon events
- Audit logon events
- Audit account management
- Audit directory service access
- Audit object access
- Audit policy change
- Audit privilege use
- Audit process tracking
- Audit system events
An event in the Windows Security log has a keyword for either Audit Success or Audit Failure. The moment you permit an audit policy, you can authorize the policy to log Success events, Failure events, or both, depending on the policy. Only a few policies generate Failure events while Success events are generated by all nine audit policies.
Read along to find out what is audit failure in Event Viewer and what are the most common Event ID failures.
Most Common Event ID Failures
Windows Event ID 4771 – Kerberos pre-authentication failed
So when we ask what is Audit Failure in Event Viewer, we find out that in the Windows Event Viewer, the Audit Failure event is generated under the Security log.
The Event ID 4771 generates every time the Key Distribution Center fails to issue a Kerberos Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT). This problem can occur when a domain controller doesn’t have a certificate installed for smart card authentication (for example, with a “Domain Controller” or “Domain Controller Authentication” template), the user’s password has expired, or the wrong password was provided.
This event is logged on domain controllers only and only failure instances of this event are logged. Also, it is not generated if “Do not require Kerberos pre-authentication” option is set for the account.
Here is an example of Event ID 4771:
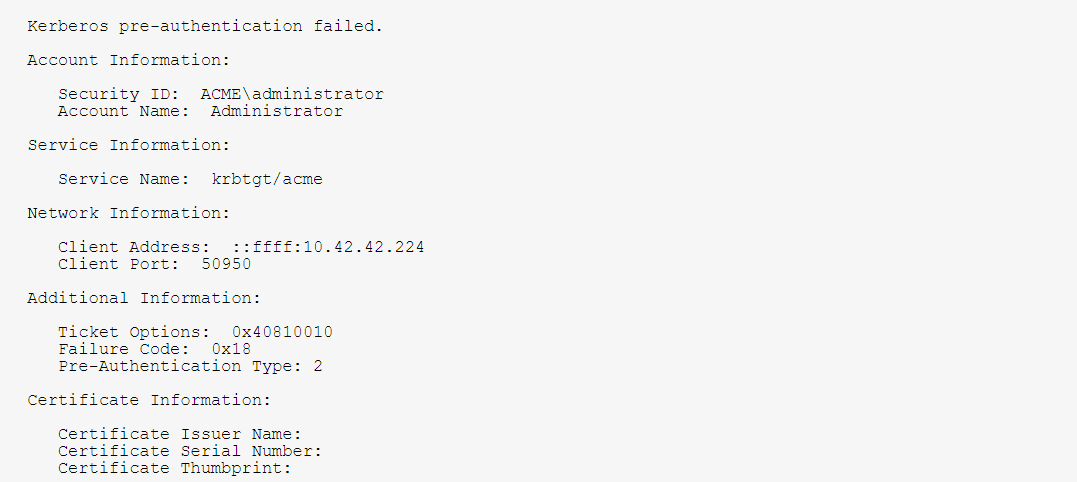
Windows Event ID 4625 – An account failed to log on
Another audit failure in Event Viewer is Event ID 4625 that generates if an account logon attempt failed when the account was already locked out. It also generates a logon attempt after which the account was locked out. It generates on the device where logon endeavor was made, for example, if logon attempt was made on the user’s computer, then the event will be logged on this device.
This event generates on domain controllers, member servers, and workstations.
Event 4625 applies to Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7, Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows 8.1, and Windows Server 2016 and Windows 10. Corresponding events in Windows Server 2003 and earlier included 529, 530, 531, 532, 533, 534, 535, 536, 537, and 539 for failed logons.
Here is an example of Event ID 4625:

Ways to Remedy Common Event ID Failures. Recommendations.
Security monitoring recommendations for 4771(F): Kerberos pre-authentication failed.
- You can track all 4771 events where the Client Address is not from your internal IP range or not from private IP ranges.
- If you know that Account Name should be used only from a known list of IP addresses, track all Client Address values for this Account Name in 4771 events. If the Client Address is not from the allow list, generate the alert.
- All Client Address = ::1 means local authentication. If you know the list of accounts that should log on to the domain controllers, then you need to monitor for all possible violations, where Client Address = ::1 and Account Name is not allowed to log on to any domain controller.
- All 4771 events with Client Port field value > 0 and < 1024 should be examined because a well-known port was used for the outbound connection.
Security monitoring recommendations for 4625(F): An account failed to log on.
- If you have a pre-defined “Process Name” for the process reported in this event, monitor all events with “Process Name” not equal to your defined value.
- You can monitor to see if “Process Name” is not in a standard folder (for example, not in System32or Program Files) or is in a restricted folder (for example, Temporary Internet Files).
- If you have a pre-defined list of restricted substrings or words in process names (for example, “mimikatz” or “exe”), check for these substrings in “Process Name.”
- If Subject\Account Nameis a name of service account or user account, it may be useful to investigate whether that account is allowed (or expected) to request logon for Account For Which Logon Failed\Security ID.
- To monitor for a mismatch between the logon type and the account that uses it (for example, if Logon Type4-Batch or 5-Service is used by a member of a domain administrative group), monitor Logon Type in this event.
- If you have a high-value domain or local account for which you need to monitor every lockout, monitor all 4625 events with the “Subject\Security ID” that corresponds to the account.
- It is recommended to monitor all 4625 events for local accounts because these accounts typically should not be locked out. Monitoring is especially relevant for critical servers, administrative workstations, and other high-value assets.
- It is recommended to monitor all 4625 events for service accounts because these accounts should not be locked out or prevented from functioning. Monitoring is especially relevant for critical servers, administrative workstations, and other high-value assets.
When it comes to audit failures it is important to know that they can approach silently and surprise any company and each one could qualify a report and lead to a less stable environment. It is important to stay rigorous, be informed of your environment, and monitor changes.
The latest version of Event Viewer can help you analyze the merged data from many logs in one view and you can take advantage of much more pliable filtering.
Contact us if you have any comments, questions, or suggestions regarding the topic of what is audit failure in Event Viewer. We look forward to hearing from you!


 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management
 Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security










