Contents:
DNS MX records are a key element in delivering an email successfully to its rightful recipient.
But have you ever wondered what it takes to deliver an email?
When sending an email, a lot happens within fractions of seconds to direct the email to the correct address in the vast internet space.
Just like your postal service would need a postman and postal address to deliver mail to the correct post office and then to the right recipient, DNS MX records work like that postman.
Without DNS MX records, the mail server will have no direction to send the email to.
The article will help you understand DNS MX records and their importance in email delivery and security.
Key Takeaways
- A DNS MX record directs an email to the mail server responsible for receiving emails for a specific domain.
- The components of a DNS MX record are – Domain name, record type, priority, mail server, and time-to-live (TTL).
- DNS MX records route emails properly to ensure they reach the intended mail server.
- There are priority levels assigned to MX records, enabling various mail servers to be listed under a domain. Even if the primary server fails, the back server will step in to ensure emails are delivered.
- To check your DNS MX record, you can use tools like Google Admin Toolbox and MXToolbox, as well as command-line utilities like nslookup and dig.
- Misconfigured, incorrect, or outdated MX records can result in email attacks like phishing, spam, and spoofing.
- Monitor, maintain, and update your DNS MX records regularly and use security protocols like DMARC, DKIM, and SPF to ensure email security.
What Are DNS MX Records?
Domain Name System (DNS) is like the internet’s naming service that assigns domain names to web resources like computers and online services. It translates easy-to-read domain names into IP addresses for computers to communicate with one another.
DNS has several records to manage, like MX records, DMARC, DKIM records, and SPF records containing crucial domain data in the DNS database. These records control email delivery and protect against security risks like spoofing fraud, and phishing attacks.
Among DNS records, Mail Exchange (MX) records are vital for email delivery. A DNS MX record directs an email to the mail server tasked to receive emails for a given domain. This way, it ensures emails sent to your domain are correctly routed to your email servers under a protocol like Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP).
Let’s understand this with a scenario. Suppose you want to email the support team of a website like “heimdalsecurity.com”. The DNS will look for the MX record corresponding to the site to determine the mail server responsible for handling the email. This ensures the email reaches successfully to the desired recipient.
Examples of a DNS MX Record
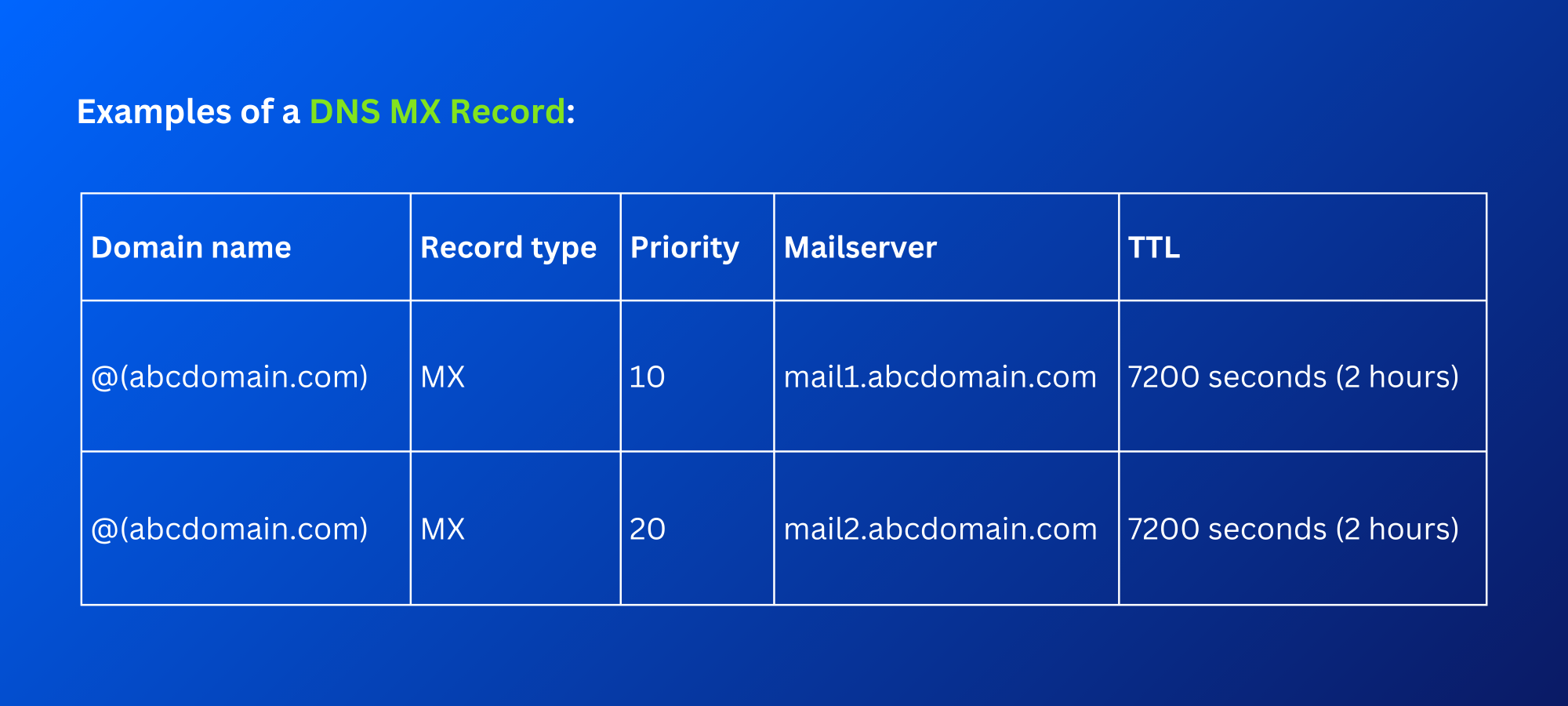
Components of MX Records
In the above DNS MX record example, you can see various components – domain name, record type, mail server, TTL, and priority. Let’s understand what each component means.
- Domain name: It’s a website’s domain name like “heimdalsecurity.com”. In the example, the domain name is “abcdomain.com” and the MX record will be configured for this domain.
You can also see the symbol “@”, indicating the zone origin or root domain name for DNS records. “@” applies directly to the domain (here, abcdomain.com).
- Record type: For DNS MX records, the record type will be “MX”. It routes emails to the correct mail server for successful email delivery.
- Priority: It’s a number that indicates which email server is given how much priority. This number ranges from 0-65535, with 0 being the highest priority while 65535 is the lowest.
In the above example, the mail server with priority 10 will connect first with the domain for sending the email to the intended recipient.
- Mail server: It’s the host server that will handle incoming mail for a given domain. In the example, “mail1.abcdomain.com” is the host server or mail server for the domain “abcdomain.com”. One domain can have multiple host servers to handle more incoming emails and help in delivering emails faster than a single mail server.
- TTL: Time-to-Live (TTL) is a number that indicates the duration for which a DNS resolver caches an MX record in DNS. In the above example, TTL is 7200 seconds which equals 2 hours. This means a DNS server will cache the MX record for 2 hours. If a TTL expires, the DNS resolver will query the relevant DNS servers to refresh the data.
How Do DNS MX Records Work in Directing Email Traffic?
Similar to the postal service directed to a post office to ensure it reaches the right recipient, MX records instruct a mail server (out of many) to route an email based on SMTP.
Here’s a detailed overview of how this process works:
In a successful email delivery, DNS servers and message transfer agents (MTAs) play an important role. DNS servers host MX records. When you send a mail, your MTA (or sender’s mail server) will send a query to the DNS server for the required MX records to identify the receiver’s mail servers and route emails.
Next, the DNS server will provide the requested MX records like priority values, TTL, IP addresses, etc. Using the IP address, your MTA or mail server will set up an SMTP connection with the receiver’s mail servers, starting with the highest-priority server to send the email and moving down to lower-priority servers, delivering the email successfully.
Finally, your mail server will send the email message to the recipient’s mail server with the help of commands for smooth data transfer. This way, the email reaches the designated receiver’s inbox.
Role of Multiple MX Records and Priority for Email Delivery
One domain can have multiple MX records with different priority numbers. When a mail server sends an email, it first picks the MX record with the lowest priority number.
With multiple MX records in place, your email deliverability improves. If the main mail server is unavailable, the sender’s mail server will route the email to the available mail server which has the next highest priority in the DNS MX records. This way, the email deliverability will not be affected even when one server goes down.
How to Check Your MX Record?
Here are some methods and online tools to perform DNS MX record lookup:
- Online tools: Some of the best tools for checking MX records include Google Admin Toolbox, MXToolbox, and DNSstuff.
Just enter a domain name and let the tool provide you with associated MX records. This information will enable you to determine if your mail servers have the correct priorities and configurations for higher email deliverability.
- nslookup: It’s a command-line utility that you can use in many operating systems, including Windows and Unix. It retrieves MX records along with other DNS records.
On Windows, search and open “cmd” or the Command Prompt. Enter the below command to look for MX records:
nslookup -type=MX abcdomain.com #Use your domain name in abcdomain.com
Press “Enter” to retrieve your domain’s MX records.
- dig: For macOS and Linux users, you can use the “dig” command-line tool to query DNS servers for detailed DNS MX records.
On your system, open “Terminal”. Enter the below command:
dig abcdomain.com MX
Press “Enter” to see MX records data in the terminal.
MX Records and Email Security
DNS MX records not only ensure all your emails are sent successfully to their designated recipients but also are associated with email security.
Being publicly available, anyone, including cyber attackers, can check for MX records of a domain they are targeting. They can exploit this information to launch an attack like a phishing attack, record hijacking, man-in-the-middle attacks, etc.
Attackers can also spoof or modify MX records to generate fake emails and make them look genuine to fool users. Once spoofed, they can redirect emails to their server to intercept confidential data transmitted over email.
In addition, if your MX records are misconfigured or have some common issues like below, attackers can exploit them for attacks:
- Incorrect/outdated data like IP addresses or domain names
- Missing/inconsistent records
- Incorrect priority
- Unavailable mail servers
- Alignment issues with DMARC, DKIM, or SPF
This is why you must regularly keep a tab on your domain’s MX records, keep them accurate and updated, and invest in securing them.
Best Practices to Secure Your MX Records
Follow the below DNS MX record best practices to secure your emails and prevent email fraud:
Regularly Update and Monitor MX Records
Keep monitoring your DNS MX records to check for any errors, mistakes, misconfigurations, modifications, or irregularities. This is especially necessary when you’ve changed your company’s email system or migrated to a new email server.
If anything looks unusual, discuss it with your security team immediately and correlate it to your records. Correct and update your MX records periodically before any attacker can exploit them to conduct a cyberattack.
Implement DNSSEC
Implement DNS Security Extensions (DNSSEC) to protect your company’s DNS infrastructure. against cybersecurity threats. DNSSEC can address DNS vulnerabilities that make associated systems susceptible to attacks like DNS spoofing and cache poisoning, unauthorized DNS modifications, etc.
This way, DNSSEC safeguards your MX record from tampering and ensures its integrity. Thus, your email receives the right recipient, keeping email deliverability high.
Use DNSBLs to Manage Reputation
DNS-based blocklists (DNSBLs) are a kind of database you can create on your DNS and list malicious domains and IP addresses. This spam prevention method tracks and monitors IP addresses sending spam and keeps them in the blocklist.
You can configure your mail servers to flag or reject emails coming from these addresses. This helps protect your targeted recipients and maintain your domain’s reputation in the market.
Use Email Authentication Protocols
Email authentication is done to verify an email’s authenticity.
Use email authentication protocols like domain-based message authentication, reporting, and conformance (DMARC), domain keys identified mail (DKIM), and sender policy framework (SPF) that use DNS MX records for email verification.
These protocols verify if an email is tampered with or comes from a legitimate mail server. It will protect your emails from cybersecurity attacks.
You can use Mailtrap SMTP API to send emails which also comes with automatic email authentication functionality. This solution validates emails for all important DNS records.
Backup MX Server
Set up a backup MX server that can create a queue for your incoming emails when your main mail server is unavailable. Once it becomes available, the backup server will start delivering those emails, ensuring emails are delivered uninterrupted.
In addition, monitor the mail server’s performance to spot issues and remediate them so that email delivery is not affected.

Conclusion: Secure Your DNS MX Records to Strengthen Email Security
DNS MX records ensure all your emails are delivered successfully by pointing emails to the right mail servers and prioritizing which one to deliver first. Apart from enabling smooth email delivery and reducing delays and email bouncing, MX records are crucial in cybersecurity.
Thus, secure your DNS MX records by updating records regularly, using advanced methods like email authentication, DNSSEC, DNSBL, and backup MX servers. This will protect your MX records from cyberattacks, keep recipients safe, and maintain your reputation in the market.
With Heimdal Email Security’s advanced protection against spam, phishing, and ransomware, security teams, CIOs, and CISOs can safeguard their emails. It automatically scans every inbound and outbound email in real-time for threats and blocks them to offer all-around email protection.
Get a demo to explore Heimdal Email Security

Heimdal® Email Security
- Completely secure your infrastructure against email-delivered threats;
- Deep content scanning for malicious attachments and links;
- Block Phishing and man-in-the-email attacks;
- Complete email-based reporting for compliance & auditing requirements;
FAQs
What if there is no MX record?
If a domain has no MX records, the mail server will have no clue where to send an email to.
What is the highest priority MX record?
Higher priority in MX is given to the lowest number. Typically, 0 will be the highest priority.
Is high TTL good?
A high time-to-live (TTL) means less traffic but more latency after making changes. However, if the TTL is low, the changes you’ve made will propagate faster. However, this will increase traffic or queries.
About the author

Veljko Ristić, Content Manager @ Mailtrap
Linguist by trade, digital marketer at heart, I’m a Content Manager who’s been in the online space for 10+ years. From ads to e-books, I’ve covered it all as a writer, editor, project manager, and everything in between.
Now, my passion is with email infrastructure with a strong focus on technical content and the cutting-edge in programming logic and flows. But I still like spreading my gospels while blogging purely about marketing.
If you liked this piece, you can find more on the blog. Follow us on LinkedIn, X, Facebook, and YouTube for more cybersecurity news and topics.










 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management  Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security







