Contents:
The ones who created Purple Fox malware have upgraded their malware arsenal, as currently, they are using a new FatalRAT version, a remote access trojan. Besides, its functionalities to avoid detection have been also upgraded.
New FatalRAT Version Wreaking Havoc on the Cyber Scene
Experts from TrendMicro have recently published a report on this topic emphasizing what’s the purpose of this new RAT version.
Users’ machines are targeted via trojanized software packages masquerading as legitimate application installers. The installers are actively distributed online to trick users and increase the overall botnet infrastructure.
The findings are based on previous Minerva Labs research that revealed a similar method of distributing the backdoor via phony Telegram applications. WhatsApp, Adobe Flash Player, and Google Chrome are among the other disguised software installs, as hackernews.com mentions.
How Does the Infection Chain Unfold?
According to the same report by TrendMicro, in the Purplefox infection chain, a single character is included in the installers, that matches a specific payload. The execution parent then adds the second stage payload as a single character to the first stage command and control (C&C) server’s request.
An illustration of the infection chain is shown below.
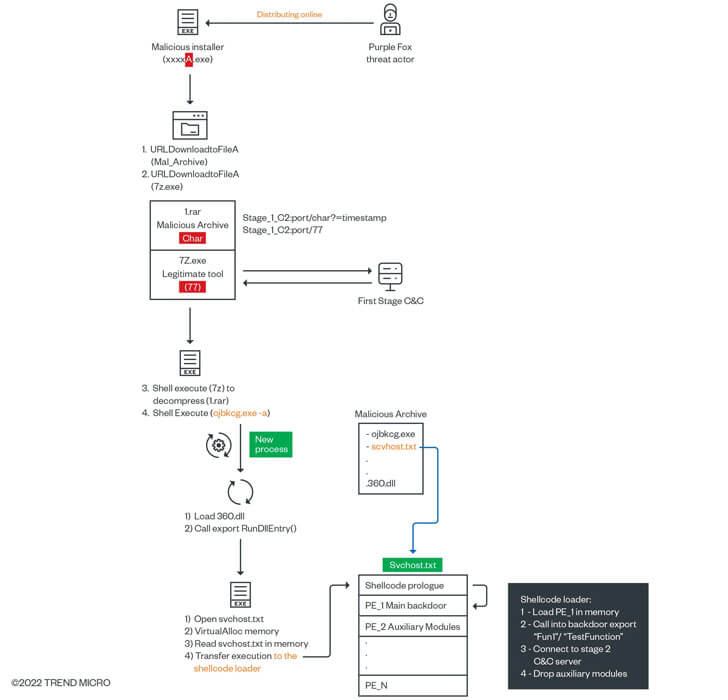
Which Tools Is Purple Fox Using
The report further talks about the tools employed by PurpleFox:
The svchost.txt Includes Masked Packages and Malware Components
The analysts discovered a compressed RAR package including the second stage loaders, as well as the file svchost.txt, which has all the components of the malicious portable executable (PE) module that will be further deployed in the second stage. This will be done on a server hosting the second stage payloads.
Malware Operators Use Shellcode User-mode Loader and Anti-forensics Techniques
A set of portable executable (PE) modules discovered in one of the malware’s most widely deployed clusters featured a wide variety of AV evasion capabilities.
FatalRAT Is Leveraged During the Process
After the shellcode loads and allocates memory for the PE modules inside svchost.txt, the execution flow will call into the first PE module found after the shellcode. This is a remote access trojan (RAT) that inherits its functionality from a malware known as FatalRAT, a sophisticated C++ RAT that implements a wide set of remote capabilities for the attackers.
What Is FatalRAT?
FatalRAT stands for a C++-based backdoor meant to conduct commands and exfiltrate sensitive data to a remote server, with the malware writers gradually adding new features to the backdoor.
The RAT is responsible for loading and executing the auxiliary modules based on checks performed on the victim systems. (…) Changes can happen if specific [antivirus] agents are running or if registry keys are found. The auxiliary modules are intended as support for the group’s specific objectives.
If you liked this article, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, Youtube, and Instagram for more cybersecurity news and topics.










 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management  Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security








