Contents:
VPNs and proxy servers are both technologies that allow you to keep your online activities private while browsing, sending emails, reading online messages, streaming video, or downloading files. However, each of these instruments operates in a unique manner.
What Is a Proxy Server?
Proxy servers function as a bridge between the website you’re accessing and your device. Your traffic is routed through a middleman, which is a remote machine that connects you to the host server. The web proxy server masks your actual IP address, which makes the website you want to access only see the proxy’s IP address (the endpoints of other proxy users may sometimes be used for this). Proxy servers only operate at the application level, rerouting traffic from a particular app that you configure your proxy with, and they do not encrypt your data.
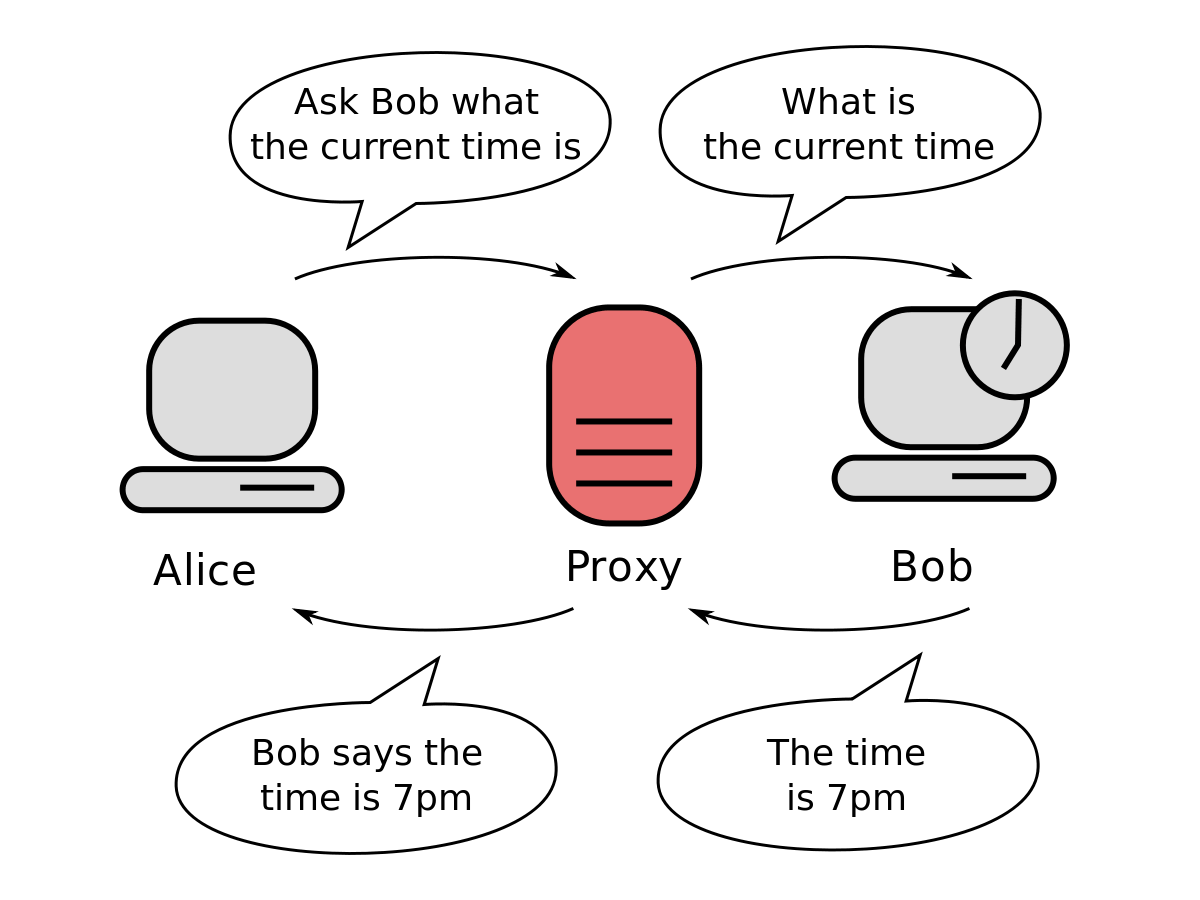
Proxy servers are classified into three main types:
HTTP Proxies
HTTPS proxies are often used to enable access to websites, as well as geo-restricted information. If you configure your browser to use an HTTP proxy server, all browser traffic will be redirected through it.
SOCKS5 Proxies
SOCKS5proxies are typically used to gain access to video streaming services, file-sharing platforms, or online games. They also operate at the application level and can accommodate all traffic flows; however, they are generally slower than HTTP proxies due to their popularity and heavy load.
Transparent Proxies
Employers or parents who want to monitor users’ online activities and prohibit access to specific websites can use these proxies to do so. Hotels and cafes are using them to authenticate customers on public Wi-Fi, and businesses and home users may enable them to conserve bandwidth.
What Is a VPN (Virtual Private Network)?
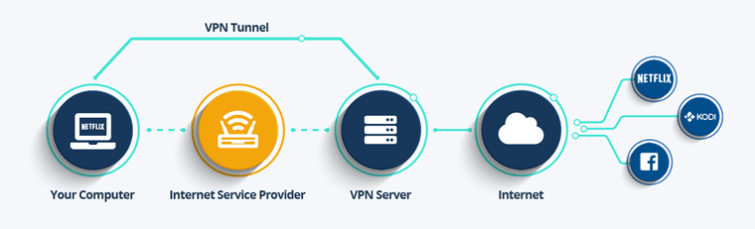
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) are excellent tools for ensuring online privacy and security. They redirect internet traffic through a remote server and mask IP addresses, preventing websites from seeing your original IP address or location. They function at the operating system level, redirecting all traffic, whether from a browser or a background app.
A VPN client encrypts internet communication between a device and the internet. The result? Internet Service Providers (ISP) that track internet activity and gather data become unable to see what users are doing online – they can only see that they are connected to a VPN server. Encryption also protects users from government monitoring, web tracking, and hackers that might attempt to infiltrate into their systems.
VPNs function by establishing a data passageway between a local network and an exit terminal in another area, which might be miles and miles away, giving the illusion that the person using them is in another location. This perk provides online flexibility as well as easy, mobile access to apps and websites. VPNs employ encryption to obscure data transferred over a Wi-Fi network, rendering it unintelligible.
Proxy vs VPN – Main Differences
As you may have already guessed, there is more than one difference between proxy and VPN. I’ll list them below:
- This one is obvious: virtual private networks encrypt your browsing activity as well as any data you send or receive, so nobody will be able to see what you’re doing when you’re online.
- VPNs operate at the operating system level, rerouting all traffic through a VPN server, whereas proxies operate at the application level, rerouting only traffic from a certain app or browser.
- A free proxy might track connections and distribute information to third parties, whereas a VPN provider with a no-log policy can commit not to track and maintain a record of your activities while you connect to the Internet using their service.
- VPNs are mainly priced services (you should avoid free VPN services because they have restrictions and tend to collect your data), whereas many proxy servers are available for free.
Proxy vs VPN – Which One Is Better?
If you must choose between a proxy and a VPN, you should think about what you need them for.
A proxy server will:
- conceal your IP address (from a particular website or application);
- allow quick browsing;
- connect to specific free sites, apps, or file-sharing services;
A VPN can:
- maintain your browser history invisible to prying eyes;
- allow you to visit different websites in a secure manner, especially when interacting with bank accounts or credit card websites.
VPNs deliver higher security since they encrypt traffic. A VPN is the appropriate choice for enterprises that handle sensitive information and need to keep their internet activity anonymous.
A proxy server might help organizations who merely want their employees to browse the internet secretly. This also allows them to see which websites their employees are viewing and ensures that staff can access websites that are normally restricted in their region.
How Can Heimdal Help?
VPNs and proxies allow you to hide your browsing activity, while VPNs also ensure privacy thanks to the encryption feature that they add. As you can probably tell, however, online privacy is not enough in a world where the cyber threatscape changes every day, and cybercrime is already organized – you also need prevention.
As Heimdal’s CEO, Morten Kjaersgaard says,
[…] threat prevention solutions are a more innovative ally in the fight against cybercriminals, laying a bet on proactivity and the obstruction of cyber incidents in the first place.
Heimdal’s Threat Prevention solution protects both endpoints and networks by employing AI and machine learning to identify and prevent future threats. It inspects and stops harmful URLs and processes in DNS, HTTP, and HTTPS traffic.
By screening all network packages based on the origin and destination of DNS requests and preventing malicious packages from connecting over the network, our software stops man-in-the-browser attacks, discovers zero-hour exploits, fights against data leakage, and prevents security breaches or network infections. It works in conjunction with any existing antivirus product to prevent malicious domains and communications to or from command and control centers and other malicious servers.
Heimdal® DNS Security Solution
Final Thoughts
Proxies and VPNs are simple methods for obscuring your internet activity and encrypting communication (in the case of VPNs). However, if you are looking for prevention, neither a proxy nor a VPN will defend you from the cybersecurity risks that an organization may face: they will not prevent an insider from stealing sensitive information, a ransomware attack, or a coordinated infiltration operation.
P.S. Did you enjoy this article? Follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, Youtube, or Instagram to keep up to date with everything we post!










 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management  Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security









