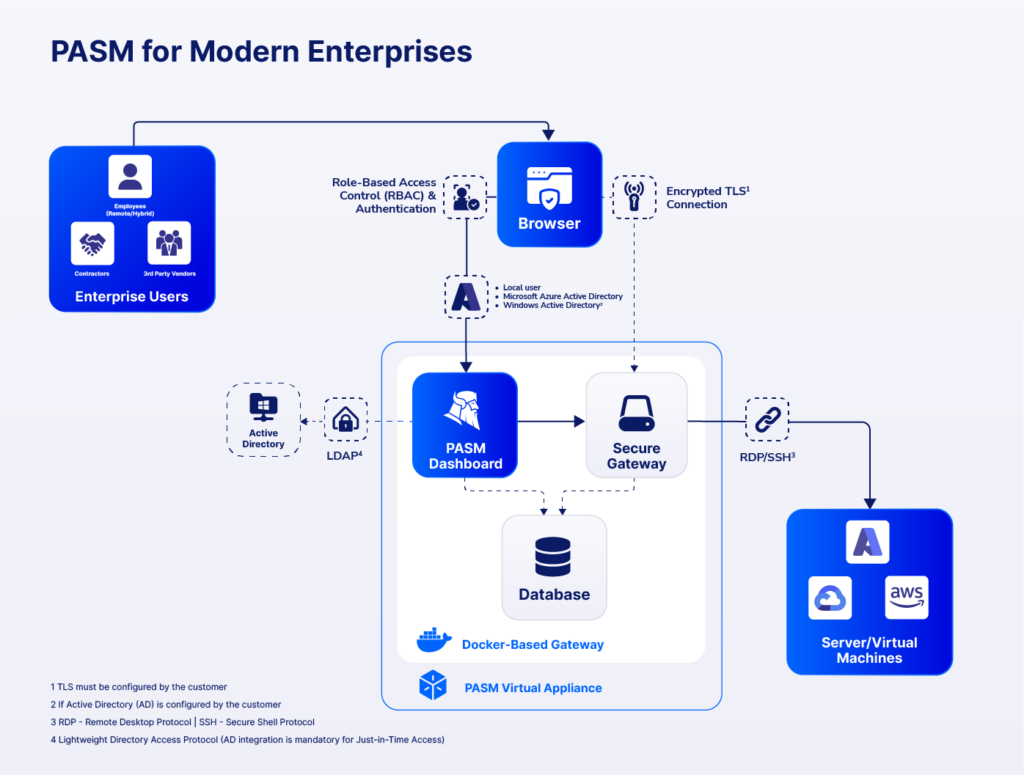
Contents:
A Privileged Access Workstation (PAW) is a secure computer built to safeguard sensitive tasks and privileged accounts.
IT admins and security teams use PAWs to manage critical systems like the Active Directory. They also use them to access cloud services, deploy software, or patch servers. They serve as a dedicated environment for performing sensitive operations.
Isolating these tasks from standard workstations reduces unauthorized access risk.
Key takeaways:
- privileged access workstations bolster security by separating access to sensitive tasks and data
- PAWs alone don’t cover session monitoring and logging
- best Privileged Access Management solutions include PAWs’ capabilities
- setting up a privileged access workstation requires more resources than using a complete PAM solution
Why do organizations need PAWs?
As businesses migrate to a highly digitalized, remote work environment, they need better access control. Also, healthcare, finance, and government organizations are increasingly targeted by cybercriminals. They collect large amounts of private data, so they must follow tighter security rules.
A hospital, for example, can use a PAW to manage access to patient data safely. It will help them comply with mandatory security protocols, like HIPAA.
A PAW might be used in finance to update software for the company’s financial management system. This is ideal for keeping transactions safe from tampering or spying.
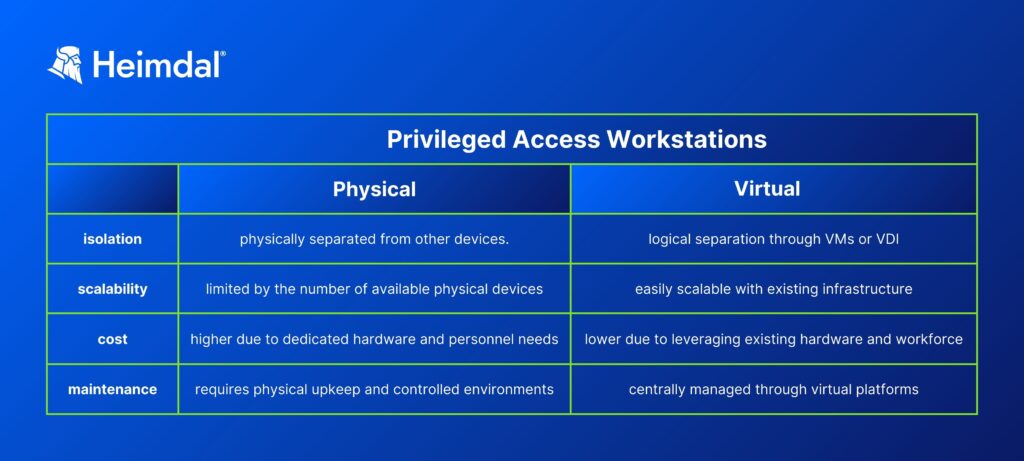
Privileged access workstation types
There are two main types of Privileged Access Workstations (PAWs). Each type offers different levels of isolation and security:
Physical privileged access workstations:
A physical PAW is a standalone device, separated from regular workstations. These machines are physically isolated and run on a dedicated network. This setup ensures that sensitive tasks are performed in a completely controlled environment.
Key features:
- Physical separation from non-privileged workstations ensures a higher level of security.
- No access to the internet or external applications reduces exposure to online threats.
- Controlled physical access: Often placed in secure areas to prevent unauthorized physical access.
- Strong access controls like multi-factor authentication (MFA) ensure only authorized users get access.
Use case
Physical PAWs work best for administrators who manage critical systems and sensitive data. For example, a government agency may use physical PAWs to access national security data. This ensures that if a regular workstation is hacked and the attackers succeed in a lateral movement, they won’t get privileged access. A highly secured PAW will prevent the attackers from intruding further. Here’s another instance. A bank might use a physical PAW to let administrators manage account databases.
Virtual privileged access workstations
Virtual PAWs are hosted on virtual machines (VMs) or virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI). This is another way to isolate privileged operations and sensitive data access from standard operations. Unlike physical PAWs, virtual PAWs provide a secure environment through software. Users can access this secure space from their regular computers.
Virtual PAWs can be set up to operate within a secure network location. This network location is carefully controlled to prevent unauthorized access, ensuring that only designated users can reach sensitive systems.
Key features
- Logical separation through virtualization keeps privileged tasks separate from other activities.
- Secure network segmentation keeps the virtual PAW environment isolated from the rest of the network. This limits the risk of infection spreading in case of attack.
- Scalability: Virtual PAWs can be set up quickly. They can grow to include more users without the need for new hardware. For example, a growing tech company could rapidly add virtual PAWs as more administrators join the team, making it easier to scale their secure environment.
- Strong authentication like MFA ensures that only approved users can access the virtual PAW.
Use case
Virtual PAWs are a good option when physical isolation isn’t practical or exceeds the budget. For instance, a tech company might use a virtual PAW to provide secure access for remote IT workers. This setup allows multiple users to access a secure space without needing separate physical devices.
A large retail chain might also use virtual PAWs to manage online payment systems across stores, ensuring secure transactions even when administrators work from different locations.
Pros and cons of using a privileged access workstation
A Privileged Access Workstation comes with benefits but also has limitations. While it can secure privileged tasks, it is not a cybersecurity tool. The PAW can be a part of a PAM solution, but it only solves one aspect of securing privileged tasks.
Pros
- Reduces the attack surface:
Isolating privileged sessions from the open internet lowers exposure to threats. When using a PAW, sensitive tasks happen in a separate, safer environment. This lowers the risk of cyberattacks.
- PAWs minimize the risk of insider threats:
Only a few approved users can access PAWs. This makes it less probable for a random disgruntled employee to cause damage by compromising or even exfiltrating company data.
For example, if an insider tries to access critical databases through a PAW, they will need to pass multiple layers of security checks. Also, as only a few people would be able to access such a workstation, the risk of being caught would be too high to take it.
- Helps meet regulatory requirements:
Many industries have strict data protection rules. Using PAWs can help meet these standards. Running a secure, isolated space for handling sensitive data is a common data protection requirement.
In healthcare, PAWs ensure that patient data remains protected according to HIPAA standards, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches. Thus, healthcare organizations avoid compromising customers’ data, getting fined, or being taken to court.
Cons
- Time and cost:
Setting up a PAW needs investment in hardware or virtual setups. It also requires skilled staff to configure and maintain the system.
Building a PAW setup for a large organization can take weeks and requires a significant budget for hardware and software.
- Maintaining separate systems:
Physical PAWs need their own devices. Virtual PAWs need extra network management. Both options can use up IT resources. This is especially challenging for smaller companies with limited IT staff.
- No built-in monitoring:
PAWs don’t automatically track user actions. Businesses will need extra tools to monitor and log privileged sessions.
On the other hand, a PAM solution like Heimdal’s PASM (Privileged Access Security Management) solves various privileged access security issues:
- Secures accounts by implementing multi-factor authentication and vaulting passwords.
- Automatically monitors privileged sessions to track who accessed sensitive accounts, when, and why.
- It creates reports that show access patterns, like which administrator logged in at a certain time.
Heimdal’s PASM reporting feature is useful for audits and meeting compliance needs.
6 Best Practices for Configuring a Privileged Access Workstation
Following best practices when configuring a privileged access workstation enhances overall security. Here are six key recommendations:
Isolate PAW on a separate network
Isolating the PAW on a dedicated network segment mitigates the risk of a potential infection spreading to the device. It’s like keeping important files in a locked cabinet.
No email access
Hackers often use phishing emails to spread malware and compromise credentials. Limiting email access on PAWs removes this risk. Phishing is still a leading cause of data breaches, according to Verizon’s Data Breach Investigation Report 2024:
Phishing and Pretexting via email continue to be the leading cause of incidents in this sector, accounting for 73% of breaches.
Use multi-factor authentication (MFA)
MFA requires users to confirm their identity by more than submitting a username and password. Those are credentials that hackers could easily steal. You should combine at least 2 means of authentication – something you know and something you own, like a token or mobile. Or ask for biometrics, like granting access after checking the fingerprint.
Setting multiple verification steps prevents breaches in case hackers compromise credentials.
Only use essential software
Install only the software you need for the jobs. This reduces the chances of software vulnerabilities. It’s like keeping only the tools you need in a tidy workspace. If you only use the PAW for server management, do not install web browsers or office tools. Thus, you minimize the attack surface.
Disable unnecessary ports and services
Open ports can become entry points for attackers. Turning them off makes the PAW more secure. Disabling ports that aren’t used for server updates reduces the number of ways hackers could break in. Regular updates and patches close off known security flaws. This is like fixing a broken lock to keep intruders out – it helps keep the PAW secure.

Privileged Access Workstations vs Jump Servers
Privileged Access Workstations (PAWs) and Jump Servers provide secure access methods but serve different purposes. Here’s a breakdown of their differences:
Security focus:
- PAWs provide a safe environment for sensitive tasks
- Jump servers control who can reach various systems and data
When to use each:
- PAWs provide a separate space for sensitive tasks. They support administrators in performing their duties in a locked-down environment. For instance, an HR database admin would use a PAW to ensure the data is safe.
- Jump servers enable or deny access to many systems from one place. They simplify access management without giving users a direct connection to sensitive servers. For example, a company might use a jump server to let IT staff access multiple databases without exposing each one directly.
Privileged Access Workstations vs Privileged Access Management (PAM) Solutions
Both solutions offer different types of security controls to improve your overall security posture. PAWs, for instance, provide a secure and isolated environment for performing high-privilege tasks.
Meanwhile, PAM solutions include controlling and monitoring access to sensitive accounts and systems across an organization. PAWs often fit into a PAM solution.
What PAM solutions do
Privileged Access Management solutions manage who, when, and how they can access sensitive accounts. They allow and monitor user access to privileged accounts and the actions they perform.
PAM monitors privileged sessions in real-time. It records activities and generates logs for audits.
Key features of PAM solutions:
Here are the key Privileged Access Management features you can expect from the best solutions.
- Automated session management: PAM tracks every action during a privileged session. It records this information for future audits or investigations.
- Granular access control: PAM allows you to set detailed rules for access. For example, access to certain servers might be allowed only during business hours.
- Credential management: PAM stores and encrypts passwords for sensitive accounts. It can also rotate these passwords automatically. This ensures that credentials are always secure.
When to use a PAW vs. a PAM Solution
- Use PAWs when you need to keep critical tasks separate from everyday activities. For example, an IT admin might use a PAW to manage a sensitive server and avoid exposure to internet threats.
- Use PAM solutions to also track and control access across various systems. For instance, if your company has many administrators, PAM can ensure that each admin only accesses the systems they need.
Combining PAWs with PAM for stronger security
Using both PAWs and PAM together enhances security posture. PAWs create a secure space for performing sensitive tasks. Meanwhile, Privileged Access Management solutions add another layer by controlling and monitoring access.
A bank could use a PAW to manage its core banking systems, keeping admin tasks isolated and secure. At the same time, it could use a PAM solution to monitor who accesses those systems, what changes they make, and when. This combination offers both isolation and detailed tracking, giving stronger protection overall.
Conclusion
Privileged Access Workstations (PAWs) are key in securing sensitive tasks. They reduce the attack surface and help meet compliance needs by isolating critical operations. But PAWs alone don’t cover all security needs.
Heimdal’s Privileged Access Security Management (PASM) adds extra layers for securing access. It tracks user activities and provides reports for audits.
It shows clearly who, when, and how someone accessed a sensitive database. Heimdal’s PASM helps organizations simplify security management while meeting compliance.
As cyber threats continue to grow, combining PAWs with comprehensive solutions like PAM ensures a more secure environment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How Do PAWs Improve Security?
PAWs offer an isolated, safe space for carrying out sensitive activities. You should only use these machines for sensitive data access and privileged tasks. Disabling browsing and email on privileged access workstations eliminates the risk of phishing attacks and malware deployment.
Can a virtual PAW be as secure as a physical PAW?
Yes, virtual PAWs can be secure if set up correctly. They need strong access controls and network isolation. But physical PAWs add extra safety through their physical separation.
What industries benefit most from using PAWs?
Industries like healthcare, finance, and government benefit from PAWs. They help protect sensitive data and meet strict security rules.
How do PAWs fit into a Privileged Access Management (PAM) strategy?
In a PAM strategy, PAWs help isolate sensitive tasks from other operations. Comprehensive solutions like Heimdal’s PASM not only protect sensitive tasks, but also automate privileged sessions tracking and reporting.
Are PAWs expensive to implement?
Setting up PAWs can be costly, as they require special hardware or virtual setups. However, their ability to prevent cyberattacks can make them worth the investment, especially in high-risk industries.
If you liked this article, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and Youtube, for more cybersecurity news and topics.










 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management  Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security