Contents:
Cybersecurity firm Kaspersky discovered a malicious variant of the FMWhatsApp mod that spreads malware to users’ devices.
What Is a WhatsApp Mod?
A WhatsApp mod is an altered version of the WhatsApp app, or better said, a user-created version of the application that is not officially authorized by the company. This version, created by third-party developers, usually offers features and functions that are not found in the original WhatsApp version.
FMWhatsApp, a well-known WhatsApp MOD developed by Fouad Mokdad offers:
- The possibility to hide the last connection time, the blue checks for reading messages, or the fact that you’ve seen your contacts’ statuses;
- Additional protection options to restrict access to the app and to conversations using a PIN, password, or the touch ID;
- Possibility to use two WhatsApp accounts at the same time on the same device;
- Custom chat themes;
- Images sent at the highest quality;
- New emoji packs from other social networks;
Most of the time, organizations advise users to not download such apps as they sometimes can be riddled with malware.
What Malware Was Discovered in the FMWhatsApp Mod?
Cybersecurity experts at Kaspersky found the Trojan Triada malware in a malicious version of the FMWhatsApp mod along with the advertising software development kit (SDK).
This app was available on some popular WhatsApp mods distributing sites. We cannot share the links to them though.
As for [FMWhatsApp clones] on Google Play — these applications usually only contain various ads and instruct users on how to download and install mods, while not actually containing the malicious mods themselves.
How Does It Work?
Experts said that following the installation, Trojan Triada starts executing ads, usually in the form of various different banners showed in the app, on the user’s mobile. Most of the times, users have no idea that these ads are running in the background.
It also gathers important device information that can be used to compromise user’s data.
The collected data is sent to a remote server to register the device. The command-and-control server (C2) responds by sending a link to a payload which the malware will download and run on the infected Android mobile.
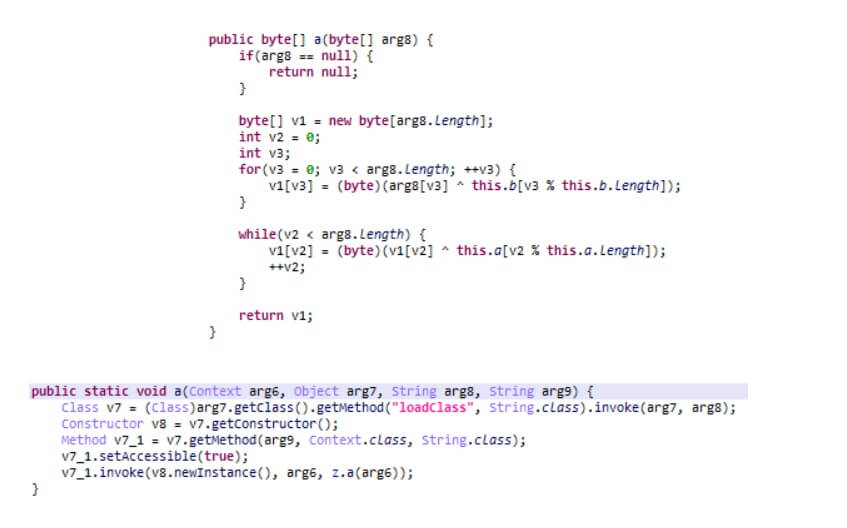
Here are the different types of malware that can be run by Trojan Triada identified by the Kaspersky security experts:
- Trojan-Downloader.AndroidOS.Agent.ic – downloads and launches other malicious modules.
- Trojan-Downloader.AndroidOS.Gapac.e – also downloads and launches other malicious modules but also shows full-screen ads when users least expect.
- Trojan-Downloader.AndroidOS.Helper.a – downloads and launches the xHelper Trojan installer module and also runs invisible ads in the background.
- AndroidOS.MobOk.i – sign the device user up for paid subscriptions.
- AndroidOS.Subscriber.l – also serves to sign victims up for premium subscriptions.
- AndroidOS.Whatreg.b – signs in WhatsApp accounts on the victim’s phone and collects data about the user’s device and mobile contractor, then sends it to the C&C server. The server responds with an address to request a confirmation code and other information it needs in order to sign in.
The researchers call attention to the fact that FMWhatsapp users enable the app to access their messages meaning that the Trojan Triada will also have access to them.
This way, the hackers behind the malware can easily sign the target up for premium subscriptions even if in order to finish the process they need a confirmation code.
With this app, it is hard for users to recognize the potential threat because the mod application actually does what is proposed – it adds additional features.
However, we have observed how cybercriminals have started to spread malicious files through the ad blocks in such apps. That is why we recommend you only use messenger software downloaded from official app stores.
They may lack some additional functions, but they will not install a bunch of malware on your smartphone.
Kaspersky researchers concluded by saying that they don’t agree with unauthorized app modifications, especially WhatsApp mods. By using it, individuals risk getting premium subscriptions, or worse, have their account taken over by attackers and used to deliver malware.










 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management  Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security








