Picture this: You’re the head of IT at a medium-sized company, tasked with overhauling the cybersecurity approach.
First thing’s first: Installing patches. Should be fairly simple, right?
Then, you run a scan and realize the situation is a little more complex. There are hundreds of patches and updates on the list.
Some of these are feature updates for apps nobody uses anymore – barely even worth bothering with. Others are critical security patches that will protect sensitive IT assets and data. The best time to install these was yesterday and the second best time is right now.
The hard part is working out which are which.
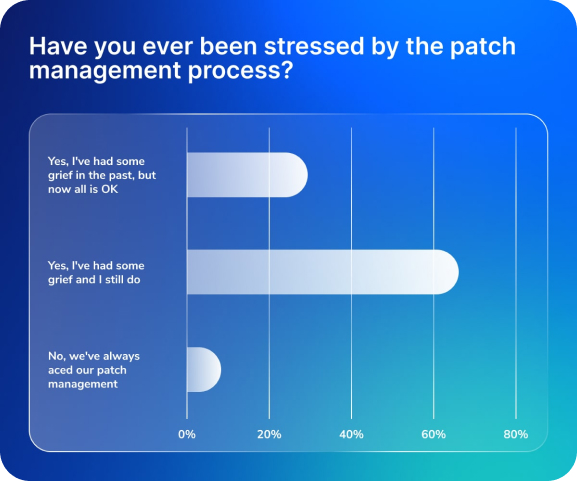
Here’s the issue: there are hundreds of patches and you don’t know how to prioritize them without going through one-by-one. Worse still, some will cause downtime when installed and others might have unforeseen consequences on other systems, apps, and workflows.
So where on earth do you start?
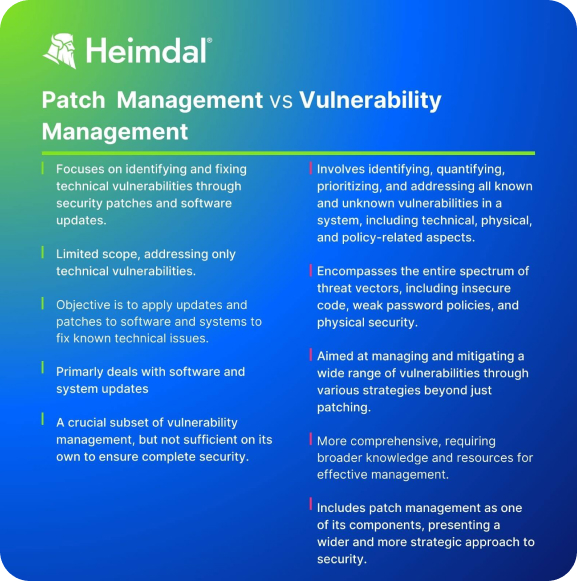
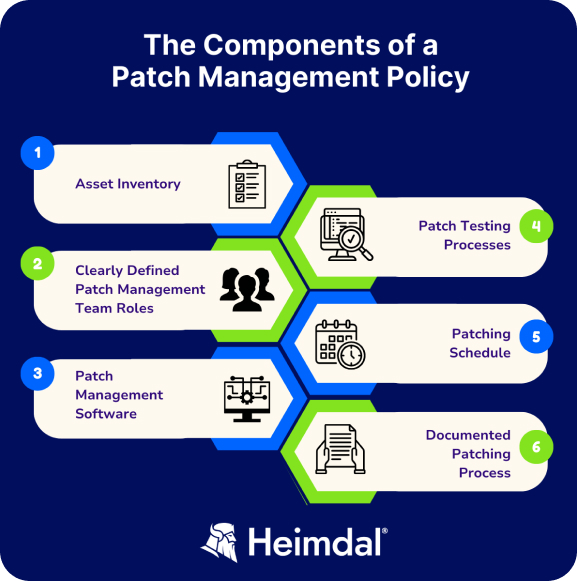
Here’s everything you need to know about patch management.










 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management  Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security



 “At the end of the day, the risk that many organizations face in their infrastructure and applications is ‘What if there’s a security vulnerability exploited before I have time to react?'”
“At the end of the day, the risk that many organizations face in their infrastructure and applications is ‘What if there’s a security vulnerability exploited before I have time to react?'”