Contents:
Researchers discovered a new malware that fakes legitimate Google Drive extensions to inject malicious scripts and steal cryptocurrency. The new Rilide malware targets Chromium-based browsers like Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Brave, and Opera.
How Is Rilide Different
Just like other malware strains, Rilide also uses malicious browser extensions. But what makes it stand out from the crowd is the capability to simulate dialogs. Using forged dialogs, the malware lures unsuspicious users to disclose their two-factor authentication (2FA). The next step is to steal their cryptocurrencies.
Snatching cryptocurrency is not the only superpower the new malware has. Hackers can also use Rilide for spying activities, like monitoring browsing history and taking screenshots.
According to researchers, other similar browser extensions are advertised and ready to be used. Also, they found part of the new malware`s source code was leaked on underground forums. One of the interesting features implemented in the leaked source code is the malware`s ability to swap cryptocurrency wallet addresses by using an actor-controlled address hard-coded in the sample.
As the identity of the threat actor using Rilide is still unknown, a command-and-control server address that appears in the exposed code might bring some leads. According to TheHackerNews:
Furthermore, a command-and-control (C2) address specified in the Rilide code has made it possible to identify various GitHub repositories belonging to a user named gulantin that contain loaders for the extension. GitHub has taken down the account in question.
How Is the New Rilide Malware Installed
Until now, researchers discovered two malicious campaigns that aim to install the Rilide extension: Ekipa RAT and Aurora Stealer.
Both attack chains use the execution of a Rust-based loader. The loader changes the browsers’ LNK shortcut file and employs the “–load-extension” command line switch to launch the add-on.
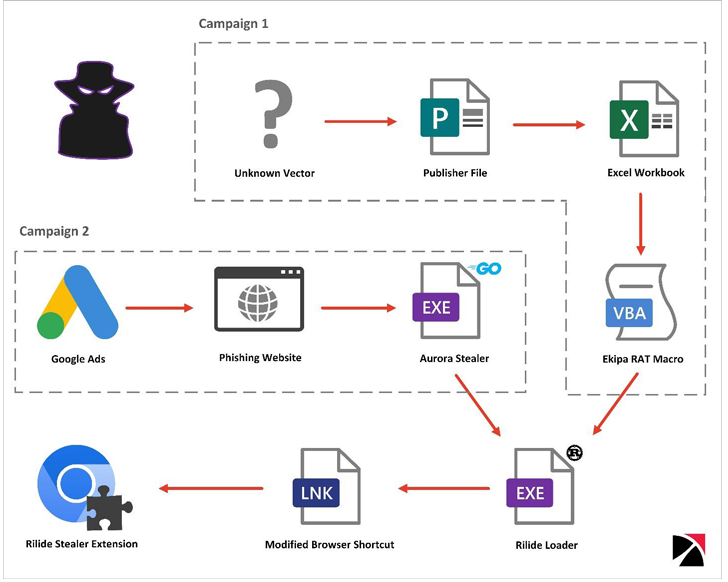
- Ekipa RAT Method
One of the Rilide samples is spread through a malicious Microsoft Publisher file. It is part of Ekipa RAT, a Remote Access Trojan (RAT).
- Aurora Stealer Method
In this case, malware is spread through forged Google Ads. This seems to be lately one of the hackers` favorite ways of working. Aurora Stealer was first discovered as a Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) on Russian-speaking underground forums, in April 2022.
And if you liked this article, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube for more cybersecurity news and topics.


 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management
 Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security









