Contents:
A new online threat actor has emerged: the Money Message ransomware gang. These cybercriminals are attacking companies all over the world, demanding millions of dollars in ransom for the decryption key and not leaking the stolen data.
When Did Money Message Appear?
Victims signaled the new ransomware gang on March 28, 2023. Soon after, ThreatLabz reported its double extortion techniques on Twitter.
?ThreatLabz has discovered a new #ransomware group named Money Message performing double extortion attacks.
Sample hash: bbdac308d2b15a4724de7919bf8e9ffa713dea60ae3a482417c44c60012a654b
Data leak site: blogvl7tjyjvsfthobttze52w36wwiz34hrfcmorgvdzb6hikucb7aqd[.]onion pic.twitter.com/P7xYnHy6wL
— Zscaler ThreatLabz (@Threatlabz) March 29, 2023
The hackers already listed two victims on their data leak site. One of the victims is an Asian airline with a $1 billion yearly income. Threat actors announced that they have exfiltrated information from this company, posting a screenshot of the files as proof.
How Money Message Ransomware Works?
The ransomware gang uses the C++ language for the encryptor, with an embedded JSON file deciding on an encryption method for a gadget.
The JSON file determines what folders will not be encrypted, the added extensions, the services and the processes that will be stopped, if logging is on, and what domain login names and passwords will be used.
The only files that Money Message does not encrypt by default are: desktop.ini, ntuser.dat, thumbs.db, iconcache.db, ntuser.ini, ntldr, bootfont.bin, ntuser.dat.log, bootsect.bak, boot.ini, autorun.inf.
After encrypting the data, the gang will send the victim a ransom note. The message is called money_message.log, includes a link to a TOR negotiation site, and warns that if a ransom is not paid, the cybercriminals will publish the stolen data.
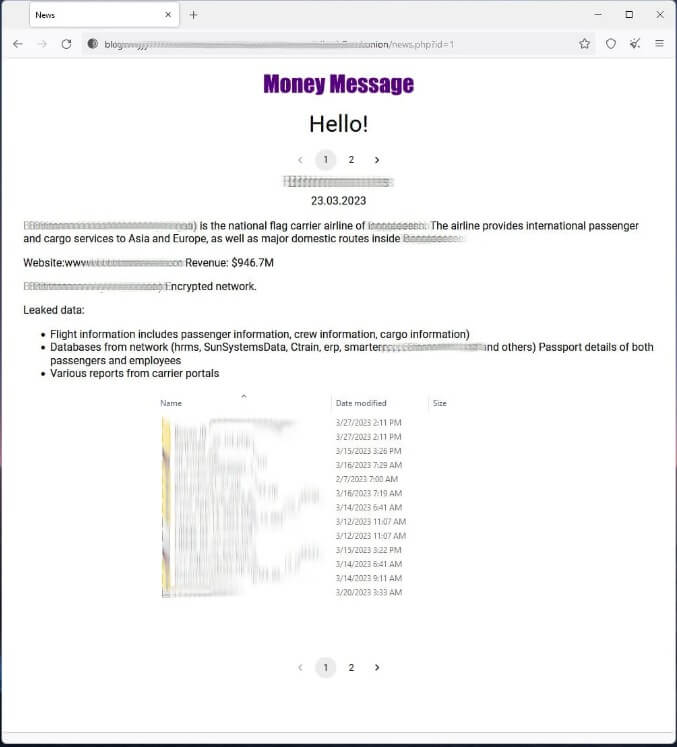
Although the Money Message’s encryption is rather slow and not sophisticated, this is an additional online threat to organizations, successfully stealing data and encrypting devices.
If you liked this article, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube for more cybersecurity news and topics.










 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management  Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security







