Contents:
Notorious North Korean hacking group Lazarus was caught installing a Windows rootkit that abuses a Dell hardware driver in a new attack. The spear-phishing campaign, which reportedly had the purpose of espionage and data theft, has been unfolded in the autumn of 2021.
The victims of the spear-phishing campaign include an aerospace expert from the Netherlands and a political journalist from Belgium. The EU-based targets were emailed fake job offers from Amazon. According to BleepingComputer, the emails contained documents that if downloaded would trigger a remote template from a hardcoded address, after which the victims’ systems would be infected with malware loaders, droppers, custom backdoors, and more.
BYOVD Tactics Were Used for the Attack
However, the most interesting tool deployed in the campaign is a new FudModule rootkit which abuses a BYOVD (Bring Your Own Vulnerable Driver) technique to exploit a vulnerability in a Dell hardware driver. This is the first ever recorded abuse of this vulnerability.
A BYOVD attack occurs when threat actors load legitimate, signed drivers in Windows which contain vulnerabilities. Windows will permit the driver to be installed in the operating system since kernel drivers are signed.
Through the vulnerability, the attackers were able to obtain access to read and write the drivers’ kernel memory, and through it disable mechanisms such as registry, process creation, event tracing, and others, to blind the machine’s security system.
Lazarus was using the CVE-2021-21551 vulnerability, which relates to a series of five weaknesses that were exploitable for 12 years until the computer manufacturer eventually released security updates for them, to gain access to a Dell hardware driver (dbutil 2 3.sys).
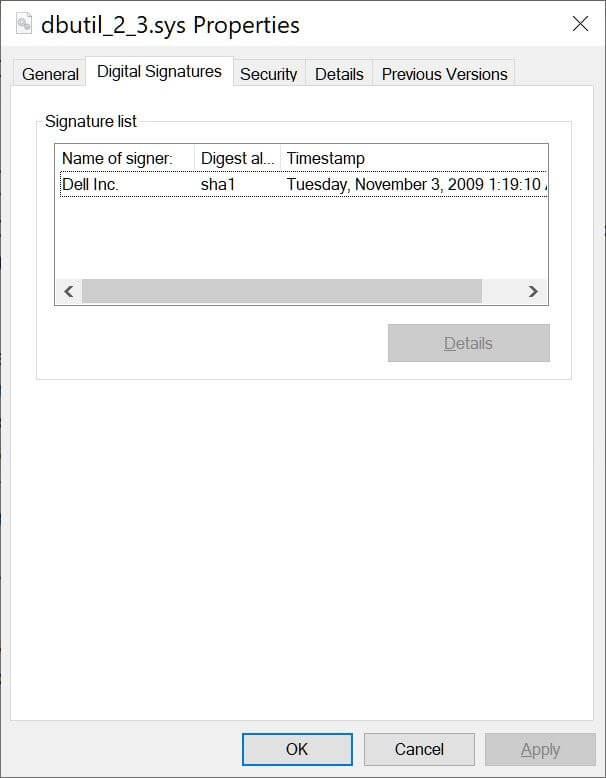
Dell’s signed dbutil_2_3.sys driver used in the attack (Source)
The IT company has been warned about the vulnerability of the driver since December last year. It appears that the threat actor was already well aware of the vulnerability and exploited the Dell driver before security analysts issued public warnings.
Other Tools Used by the Threat Actor
The group also deployed its trademark custom HTTP(S) backdoor “BLINDINGCAN”, a remote access trojan (RAT) that supports an extensive set of 25 commands, covering file actions, command execution, C2 communication configuration, screenshot taking, process creation, and termination, and system info exfiltration.
The previously mentioned FudModule Rootkit, an HTTP(S) uploader for secure data exfiltration, and numerous trojanized open-source programs like wolfSSL and FingerText are additional tools employed in the presented effort.
Lazarus continues to trojanize open-source products, applying this tactic to PuTTY, KiTTY, TightVNC, Sumatra PDF Reader, and the muPDF/Subliminal Recording software installer.
If you liked this article, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, Youtube, and Instagram for more cybersecurity news and topics.










 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management  Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security








