Contents:
The latest version of the BRATA malware includes new and dangerous capabilities, such as GPS tracking, the ability to use various communication channels, and a function that wipes all evidence of malicious activity from the machine.
More on BRATA RAT
BRATA (Brazilian Remote Access Tool Android), discovered in 2019, is a malware that was developed to target Android operating systems. The malware quickly evolved into a banking Trojan, combining the capability of complete control over compromised machines with the ability to steal banking credentials.
Cybersecurity experts highlighted the trojan’s first campaign in Europe at the end of last year, where it was observed focusing on stealing login information from e-banking users. According to BleepingComputer, the attack included fraudsters who pretended to be bank customer support agents.
Cleafy’s security experts kept an eye on BRATA for new features, and a new report released yesterday shows how the malware is still evolving.
Attention to Detail
The Remote Access Trojan (RAT) has been updated, and it now targets e-banking users in the United Kingdom, Poland, Italy, Spain, China, and Latin America.
In order to target specific audiences, every version focuses on different financial institutions with customized overlay sets, languages, and even different apps.
The developers employ similar obfuscation methods in every variant, such as enclosing the APK file in an encrypted JAR or DEX package. As shown below, this obfuscation successfully avoids antivirus detections.
As explained by BleepingComputer, BRATA is now actively looking for signs of antivirus on the machine and tries to remove any identified security software before starting to exfiltrate data.
So, What’s New?
The keylogging feature, which enhances the existing screen capturing function, is one of the new additions discovered by Cleafy researchers in the latest BRATA variants. All upgraded versions also have GPS tracking, even though analysts aren’t sure what it’s for.
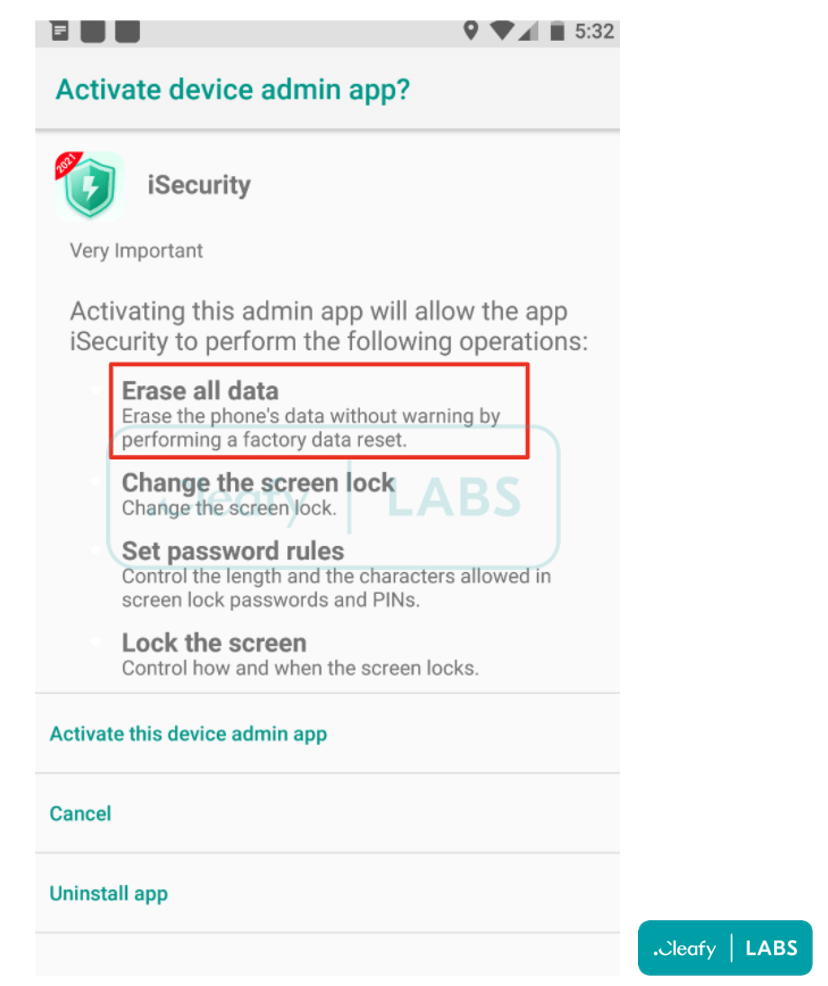
One terrifying new malicious function is the ability to execute factory resets, which the hackers employ when the compromise has been completed successfully, and the data has been stolen.
BRATA uses factory resets as a kill switch for self-protection, but since they wipe the device, they also introduce the possibility of sudden and irreversible loss of data for the victim.
How to Stay Safe
Installing mobile applications from the Google Play Store, avoiding APKs from dubious webpages, and scanning them with antivirus software prior to opening are some really smart first steps to prevent an Android malware infection.
Also, take notice of the permissions that are requested during installation and don’t allow any that don’t seem to be essential for the app’s core functionality.
Last but not least, keep an eye on battery usage and network traffic to spot any unusual spikes that could be caused by malicious operations carried out in the background.
If you liked this article, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, Youtube, and Instagram for more cybersecurity news and topics.










 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management  Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security








