Contents:
Netlogon is a Windows Server procedure allowing users and other domain services to get authenticated. Since it is a service rather than an application, Netlogon permanently runs in the background, and it can be terminated intentionally or as a result of a runtime fault.
What Does the Netlogon Service Do for Secure Communication Channel?
When responding to network login requests, the Netlogon service performs the following activities:
- chooses the target domain for logon authentication.
- identifies a domain controller in the target domain to perform authentication.
- establishes a secure channel of communication between Netlogon services on the originating and target systems.
- authenticates users by sending an authentication request to the appropriate domain controller.
- returns authentication results to Netlogon on the originating system.
- Netlogon is an important component of passthrough authentication and verifies a user’s identity to network services.
Passthrough authentication requires establishing a secure communication channel between Netlogon services on two systems:
- the originating/ local system
- a domain controller in the desired domain
Before passing login information between them, the Netlogon services on each system undertake a handshake known as Challenge and Challenge Response to confirm the source system’s legitimacy. The primary domain controller plays a crucial role in facilitating communication and synchronization between domain controllers.
How to Start the Netlogon Service?
Networks that use domain controllers and Active Directory rely on the Netlogon service for user’s authentication. Here’s how you start it:
Via Services Management Console
- press Win + R to open the Run dialog.
- type services.msc and press Enter. This will open the Services management console.
- scroll down to the Netlogon service
- right-click on the Netlogon service
- select Start
Via Command Prompt
- open Command Prompt as Administrator
- press Win + X
- select Command Prompt (admin) or Windows PowerShell (admin
- type the command net start netlogon and press Enter
Via PowerShell
- open PowerShell as Administrator
- right-click the Start button
- select Windows PowerShell (Admin)
- type the command Start-Service netlogon
- press Enter
What Is the NRPC Protocol in a Domain Controller?
The Microsoft Windows Netlogon Remote Protocol (MS-NRPC) is an Active Directory fundamental authentication component that supports user and machine account authentication. When authenticating computer accounts, MS-NRPC utilizes an initialization vector IV of zero-value in AES-CFB8 mode.
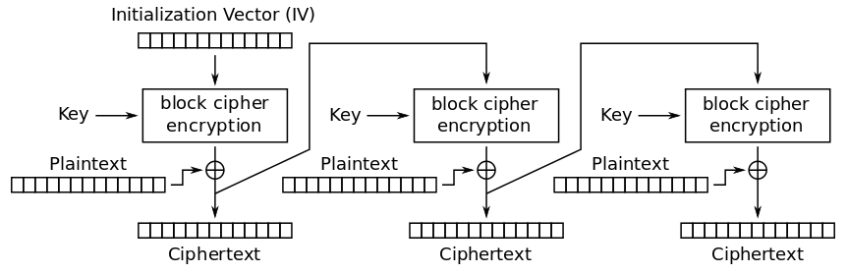
Specific registry keys are crucial in troubleshooting and configuring the Netlogon service to ensure it operates correctly, especially during server updates.
The Netlogon Remote Protocol is a remote procedure call interface that is used on domain-based networks for user and machine authentication purposes. The Computer Configuration section in the Group Policy Editor plays a vital role in managing security settings related to Netlogon, ensuring proper configuration for security policies in domain controllers.
The Zerologon Vulnerability. What Happened?
A vulnerability named CVE-2020-1472 was dubbed as Zerologon. The flaw was caused by a vulnerability in the logon process: the initialization vector (IV) is always set to all zeros when an IV should always be a random value.
The severity of this hazardous vulnerability is rated as 10 out of 10 (CVSS v3.1) by the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS), as the weakness made use of a cryptography bug in Microsoft’s Active Directory Netlogon Remote Protocol.
The main issue with this vulnerability is that MS-NRPC is also used to send account updates. The initial algorithm used to encrypt the logon process in Windows NT was 2DES, which has now been proven to be flawed. MS-NRPC now employs the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), which is widely regarded as the gold standard in encryption.
Aside from selecting an established, powerful algorithm, extra settings must be chosen to achieve suitable strength. MS-NRPC employs a cryptic option called Advanced Encryption Standard – Cipher FeedBack 8bit (AES-CFB8). AES-CFB8 is mysterious since it is not widely recognized or tested.
Unfortunately, the usage of AES-CFB8 within MS-NRPC has a problem with the IV, where this should be a random number but is set at 16 bytes of zeros.
A hacker could’ve exploited this vulnerability to gain control of a domain controller, even the root DC by changing or deleting the password for a controller service account. The malicious actor can then either cause a denial of service or seize control of the entire network. Microsoft issued a fix for the Zerologon vulnerability (CVE-2020-1472) in August 2020.
Wrapping Up
Our Heimdal™ Patch & Asset Management will handle all software updates and patches within 4 hours since their launch, silently, in the background, with no interruptions.
You can set it and forget it, as we like to say, or set a few preferences (like the right to exclude updates from one app or category, or to be asked before applying a patch on all endpoints within your organization, or the possibility to deploy and patch your own custom software through the platform). Make sure you request a demo and give it a try!
Did you enjoy this article? Follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, Youtube, or Instagram to keep up to date with everything we post!
FAQs on Netlogon
What do I do if Netlogon services don’t start?
If Netlogon doesn’t start, check for any dependencies that might not be running. Check the Event Viewer for specific error messages that could guide further troubleshooting.
Where is the Netlogon folder?
The NetLogon folder is located in the %systemroot%\Sysvol\Sysvol\Domain Name\Scripts path. It contains logon scripts and group policies that can be used by computers deployed within a domain.
What are 5 common Netlogon error codes?
- Incorrect network password – 0XC000006A
- User is not allowed to sign in to this computer – 0XC0000070
- Logon was attempted but the network logon service was not active – 0XC0000192
- User must change password before signing in – 0XC0000224
- The computer is protected by an authentication firewall. The account is not allowed to authenticate to the computer – 0XC0000413










 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management  Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security








