Contents:
One of the most recent finds exposed the Aurora Stealer malware imitating popular applications to infect as many users as possible.
Cyble researchers were able to determine that, in order to target a variety of well-known applications, the threat actors are actively changing and customizing their phishing websites. Aurora targets data from web browsers and crypto wallets, among others.
Aurora – the Shapeshifting Stealer
Since late August 2022, Aurora was marketed as a stealer on Telegram and darknet forums. The malware-as-a-service was priced at $250 per month or $1500 for a lifetime license.

On January 16th, 2023, Cyble Research and Intelligence Labs (CRIL) discovered a phishing website (hxxps[:]/messenger-download[.]top), pretending to be a website for a chat app. The following day, the same site was impersonating the official TeamViewer website.
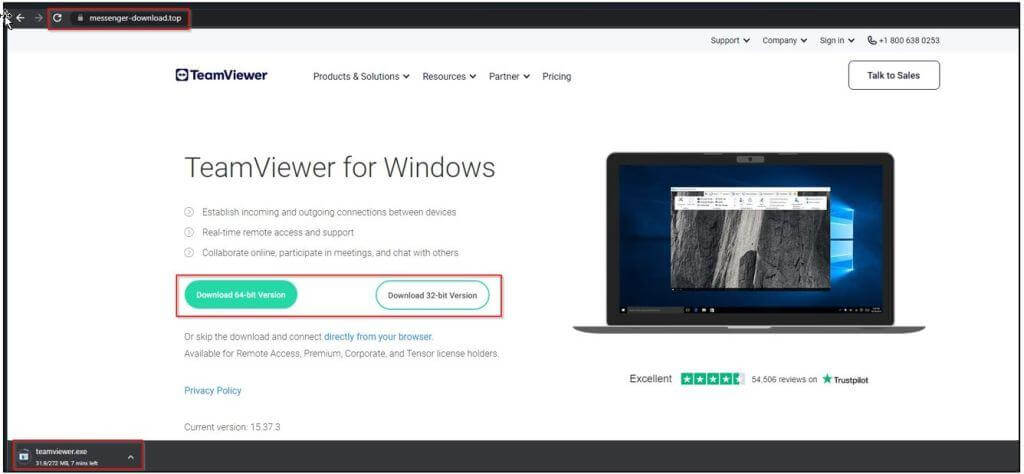
When a user clicks the Download button, malicious files with the names “messenger.exe” and “teamviewer.exe” are downloaded from the associated URLs.
The Process Step by Step
In their report, researchers mention that the malware file uses Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) commands to gather system information, including the operating system’s name, the graphics card’s name, and the processor’s name.
Additionally, the malware continues to gather information about the system including the username, Hardware Identification (HWID), Random-Access Memory (RAM) size, screen resolution, and IP address. Further, the malware also searches for specific browser-related files saved in SQLite, such as Cookies, History, Login Data, and Web Data, by querying the directories of installed browsers on the victim’s computer.
The stealer proceeds to extract information related to crypto wallets by querying and reading files from specific directories. It also steals data from crypto wallet browser extensions. Over 100 extensions have been specifically targeted and hard coded into the stealer binary, according to researchers.
The malware also grabs specific files from directories like the Desktop and Documents and takes screenshots of the victim’s system.
The Aurora stealer then prepares the stolen data for exfiltration by converting it to JSON format, putting it into a GZIP archive, and encoding the GZIP archive in Base64.
How to Stay Safe
As CSN points out, other stealers, including RedLine, Vidar, and RecordBreaker, are also found padding malware samples with unnecessary data in order to avoid detection.
You can greatly reduce the chances of becoming a victim by applying multi-factor authentication whenever possible, along with strong passwords. Additionally, activate the automatic software updates, and inform employees about how to defend themselves against dangers like phishing and unsafe URLs.
If you liked this article, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, Youtube, and Instagram for more cybersecurity news and topics.










 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management  Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security







