Contents:
The newly discovered unpatched vulnerability in Linux Pling is affecting Pling-based free and open-source software (FOSS) marketplaces for the Linux platform and has the potential to be abused in order to stage supply-chain attacks and achieve remote code execution (RCE).
Linux marketplaces that are based on the Pling platform are vulnerable to a wormable [cross-site scripting] with the potential for a supply-chain attack. The native PlingStore application is affected by an RCE vulnerability, which can be triggered from any website while the app is running.
Some of the Pling-based app stores impacted by the flaw are appimagehub.com, store.kde.org, gnome-look.org, xfce-look.org, and pling.com.
What Is PlingStore?
PlingStore is an Installer and Content Management App for OCS-compatible websites like pling.com, gnome-look.org, appimagehub.com, that allows users to download, install and apply desktop themes, icon themes, wallpapers, or mouse cursors directly under various desktop environments using the “Install”-button.
This specific unpatched vulnerability in Linux Pling is stemming from the manner in which the store’s product listings page parses HTML or embedded media fields, therefore potentially allowing an attacker to inject malicious JavaScript code that could result in arbitrary code execution.
The concerning fact is that this unpatched vulnerability in Linux Pling can allow for a supply-chain attack XSS worm in which a JavaScript payload could be exploited by an adversary to upload versions of software that are containing trojans and also to be able to tweak the metadata of a victim’s listing in order to include and propagate the attack code.
As the application can install other applications, it has another built-in mechanism to execute code on the [operating system] level. As it turns out, that mechanism can be exploited by any website to run arbitrary native code while the PlingStore app is open in the background.
How Does the Vulnerability Work?
It all starts with a user that visits a malicious website using the browser. The XSS gets triggered inside the Pling app while it’s running in the background allowing the JavaScript code to establish a connection to the local WebSocket server that’s used to listen to messages from the app, and also to send messages in order to execute arbitrary native code by downloading and executing an .AppImage package file.
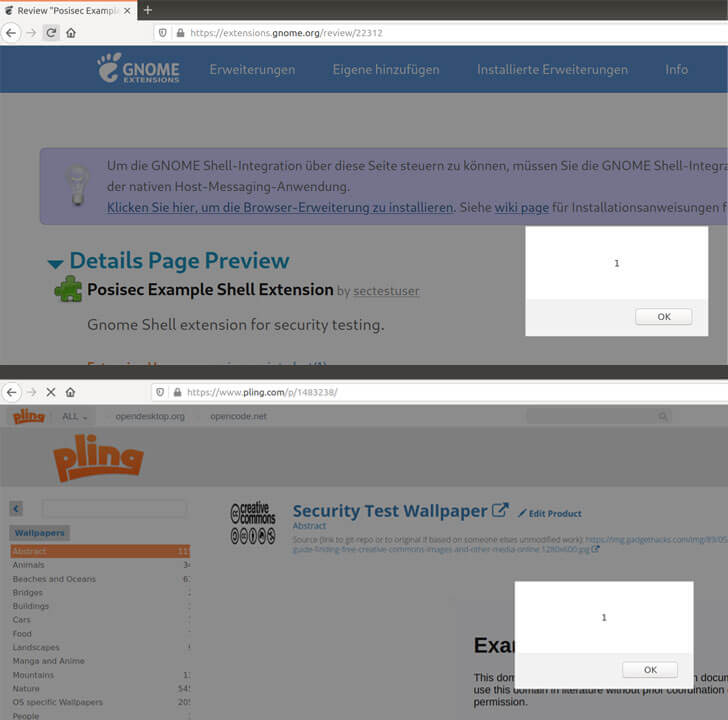
Unfortunately, this is not the only situation in which an unpatched vulnerability in Linux Pling can become dangerous as a similar XSS flaw was uncovered in the GNOME Shell Extensions marketplace.
[The flaws] demonstrate the additional risk associated with such marketplaces. In this environment, even relatively small vulnerabilities (e.g. a missing origin check) can lead to severe consequences (drive-by RCE from any browser with the vulnerable application running in the background). Developers of such applications must put in a high level of scrutiny to ensure their security.


 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management
 Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security










