Contents:
Unlike traditional security, threat hunting proactively detects and removes potential threats before they strike.
Modern tools use AI and behavior analytics for faster, smarter protection. Whether using commercial or free solutions, staying ahead is key to stronger security.
In this article, we’re going to take a closer look at the top 10 best threat hunting tools.
What Should You Look for in Threat Hunting Tools?
Threat hunters use various tools, including artificial intelligence, machine learning, advanced analytics, analytical statistics, information analytics, threat intelligence platforms, and security monitoring.
The threat of destructive malware keeps growing, and since hackers got access to AI tools, traditional threat detection solutions were outdated.
So, when looking for a threat-hunting tool, consider the following key features.

Best Threat Hunting Option – Heimdal® Threat-hunting & Action Center (TAC)
Free of charge, open-source threat hunting tools are useful and can help enhance an organization’s security posture. But what happens if you need technical support? Asking the online community for advice does not guarantee a fast enough, accurate, reliable response.
Also, free solutions often need manual setup and integration with other tools, like SIEMs (Security Information and Event Management), EDRs, cloud telemetry, etc.
Yes, open-source threat-hunting tools can be a budget saving solution for NGOs and start-ups, but will struggle in large, complex environments. A better option to enhance overall security is Heimdal®’s Threat-Hunting & Action Center (TAC).
This solution uses granular telemetry to enable swift decision-making and comes with a variety of pricing options to suit your specific needs.
It uses built-in hunting, remediation, and actioning capabilities, all managed from the Heimdal Unified Security Platform to provide security teams with a threat-centric view of their IT landscape.
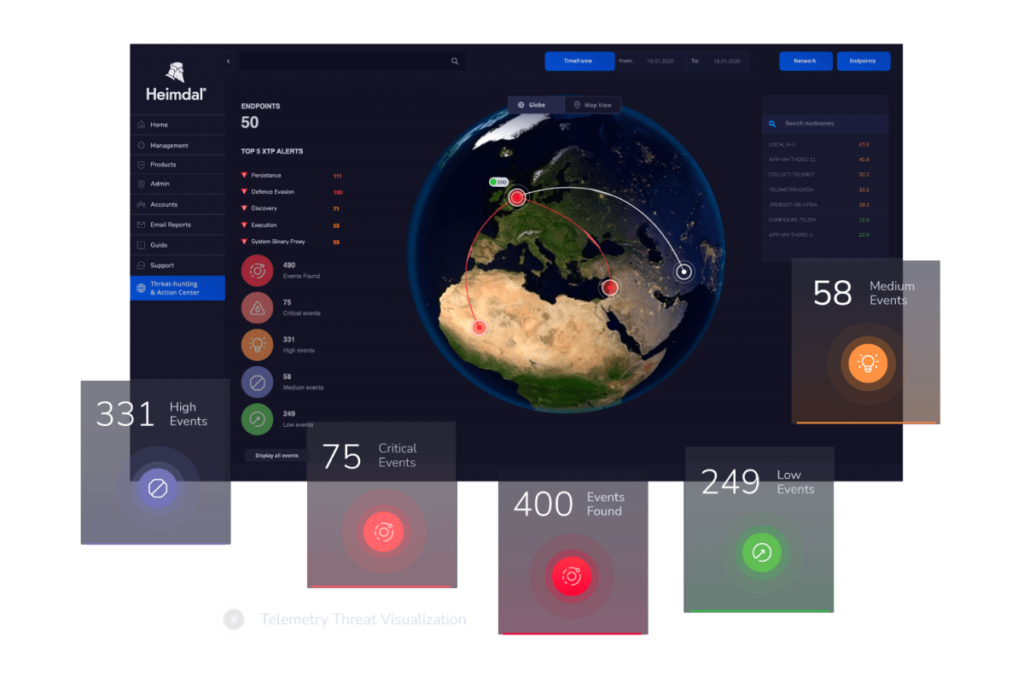
Key Features
- Unified Monitoring. Provides real-time visibility across endpoints, networks, cloud environments, and users, facilitating comprehensive oversight.
- Advanced Threat Detection. Employs User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) and Extended Threat Protection (XTP) to identify anomalies and potential threats proactively.
- Integrated Action Center. Enables swift responses with pre-built commands for actions like scanning, quarantine, and isolation, all accessible through a single interface.
- Microsoft 365 User Security. Integrates features such as Login Anomaly Detection, Email Security, and Ransomware Encryption Protection to safeguard user accounts and data.
Heimdal Threat-Hunting & Action Center Pros
- Comprehensive Visibility. Offers a holistic view of the IT landscape, enhancing the ability to detect and respond to potential security threats promptly.
- Proactive Threat Hunting. Uses advanced analytics to identify and mitigate threats before they can cause significant harm.
- Streamlined Incident Response. The integrated Action Center allows for quick decision-making and remediation, reducing potential downtime.
Heimdal Threat-Hunting & Action Center Cons
- Learning Curve: The extensive features and capabilities may require time for new users to get accustomed to.
Best Use Cases and Key Considerations
✅Best For:
- Ideal for organizations that need a comprehensive threat hunting service to monitor and protect their IT environment.
- Suitable for teams aiming to stay ahead of potential threats through advanced detection and swift response capabilities.
❌ Not Suitable For:
- Companies looking for basic security measures might find the extensive features unnecessary for their requirements.
10 Best Free and Open-Source Threat Hunting Tools
Here’s our list of free and open-source threat-hunting tools you can use to identify potential threats.
1. AI Engine
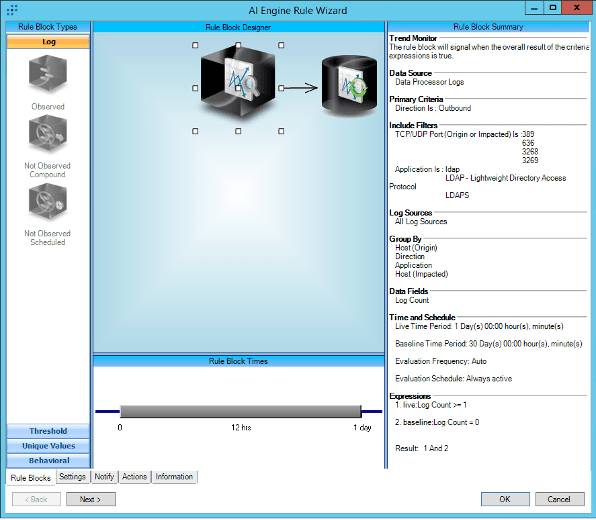
AI Engine is an interactive tool that can update the network’s IDS (intrusion detection system), detect spam and, collect networks without human interaction for learning and network forensics.
AI Engine Key Features
- Interactive network intrusion detection system (NIDS) with support for multiple scripting languages.
- Real-time packet inspection and customizable signature creation.
- Capabilities for DNS domain classification and network forensics.
AI Engine Pros
- Highly customizable and programmable for advanced users.
- Supports multiple scripting languages for flexibility.
- Effective in detecting and analyzing network anomalies.
AI Engine Cons
- Steeper learning curve for users without programming experience.
- Requires manual configuration and tuning for optimal performance.
Best Use Cases and Key Considerations
✅Best For:
- Organizations seeking a customizable NIDS with advanced scripting capabilities.
- Security teams with programming expertise looking for flexible threat detection.
❌Not Ideal For:
- Small businesses without dedicated security personnel.
- Users preferring out-of-the-box solutions with minimal configuration.
2. APT-Hunter
APT-Hunter is a threat-hunting tool for Windows event logs that can detect suspicious activity and track APT movements.
The default rules of this tool map Mitre ATT&CK tactics and techniques to Windows event log event IDs and detect the indicator of attack, which includes apt techniques.
APT-Hunter Key Features
- Analyzes Windows event logs to detect advanced persistent threats (APTs).
- Maps findings to MITRE ATT&CK framework for contextual understanding.
- Reduces large volumes of events to highlight hidden threats.
APT-Hunter Pros
- Automates detection of APT movements within Windows environments.
- Fast to identify anomalies
- Open-source and free to use.
APT-Hunter Cons
- Primarily focused on Windows event logs; limited applicability to other systems.
- May require tuning to reduce false positives.
Best Use Cases and Key Considerations
✅Best For
- Organizations using Windows systems seeking to detect APT activities.
- Security teams looking for tools aligned with the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
❌Not Ideal For
- Environments primarily using non-Windows operating systems.
- Organizations needing real time threat detection across diverse platforms.
3. Attacker KB

Attacker KB provides adversaries and their hunters with everything they need to comprehend exploits.
This includes information disclosure, technical evaluation, results, exploitability, usability, and more.
This information allows threat hunters to identify and rank both recent vulnerabilities as well as historical ones.
Attacker KB Key Features
- Provides insights into vulnerabilities with community-driven assessments.
- Offers technical evaluations, exploitability ratings, and potential impacts.
- Facilitates understanding of vulnerabilities’ relevance to specific environments.
Attacker KB Pros
- Aggregates expert opinions for informed vulnerability management.
- Helps prioritize patching efforts based on real-world exploitability.
- Free resource for security professionals.
Attacker KB Cons
- Relies on community contributions; coverage may vary.
- Not a standalone threat-hunting tool; complements other security measures.
Best Use Cases and Key Considerations
✅Best For:
- Security teams seeking contextual information on vulnerabilities.
- Organizations aiming to prioritize remediation efforts effectively.
❌ Not Ideal For:
- Businesses looking for automated threat detection tools.
- Environments requiring comprehensive vulnerability scanning solutions.
4. Automater

Automater analyzes URLs, hashes, and URLs to simplify intrusion analysis.
Using this tool, you can select a target and gather relevant information from well-known sources.
Automater Key Features
- Conducts OSINT searches on IP addresses, domain names, and MD5 hashes.
- Aggregates data from multiple reputable sources for analysis.
- Provides quick insights into potential threats associated with specific indicators.
Automater Pros
- Simplifies the process of gathering threat intelligence.
- User-friendly interface suitable for various skill levels.
- Open-source and easily accessible.
Automater Cons
- Limited to OSINT; may not detect hidden threats without external indicators.
- Dependent on the availability and accuracy of external data sources.
Best Use Cases and Key Considerations
✅ Best For:
- Security analysts performing initial threat investigations.
- Organizations seeking a lightweight tool for quick threat assessments.
❌ Not Ideal For:
- Comprehensive threat-hunting requiring internal network analysis.
- Environments needing real-time monitoring and alerting.
5. BotScout

BotScout is a that prevents automated web scripts by tracking bots’ names, IP addresses, and email addresses and storing them as unique signatures for future use.
BotScout Key Features
- Identifies and blocks automated bots from submitting forms and creating accounts.
- Maintains a database of known bot signatures for reference.
- Offers an API for real-time bot detection and prevention.
BotScout Pros
- Helps prevent spam and unauthorized automated activities.
- Easy integration with websites and applications.
- Free API access with generous usage limits.
BotScout Cons
- Primarily focused on web forms; limited applicability beyond that.
- May require customization to fit specific use cases.
Best Use Cases and Key Considerations
✅Best For:
- Website administrators aiming to reduce spam submissions.
- Organizations looking to prevent automated account creations.
❌Not Ideal For:
- Comprehensive threat-hunting across networks and endpoints.
- Environments without web form interactions.
6. CrowdFMS
Powered by CrowdStrike, CrowdFMS is an automated framework that collects and processes samples from a website that publishes information about phishing emails.
An alert is triggered if a phishing email reaches the network.
CrowdFMS Key Features
- Automates the collection and processing of phishing email samples.
- Integrates with VirusTotal for sample analysis.
- Provides alerts when phishing emails are detected within the network.
CrowdFMS Pros
- Enhances phishing detection through automation.
- Leverages VirusTotal integration for comprehensive analysis.
- Open-source and free to use.
CrowdFMS Cons
- Primarily focused on phishing threats; limited scope for other threat types.
- May require customization for specific organizational needs.
Best Use Cases and Key Considerations
✅Best For:
- Organizations aiming to strengthen defenses against phishing attacks.
- Security teams seeking automated tools for phishing email analysis.
❌Not Ideal For:
- Comprehensive threat-hunting across diverse threat vectors.
- Environments without significant phishing concerns.
7. Cuckoo Sandbox

This tool can analyze various malicious behavior and malicious files, including executables, office documents, pdfs, emails, scripts, and websites.
Given its open-source nature and modular design, you can customize the analysis environment, data processing, and reporting stages.
Cuckoo Sandbox Key Features
- Open-source malware analysis system.
- Supports analysis of various file types, including executables, documents, and scripts.
- Generates detailed reports on malware behavior and system impact.
Cuckoo Sandbox Pros
- Highly customizable and extensible.
- Provides in-depth insights into malware behavior.
- Strong community support and regular updates.
Cuckoo Sandbox Cons
- Complex setup process with multiple dependencies.
- Resource-intensive; requires robust hardware for optimal performance.
Best Use Cases and Key Considerations
✅Best For:
- Security researchers and analysts conducting in-depth malware analysis.
- Organizations with dedicated resources for threat research.
❌Not Ideal For:
- Small teams lacking specialized expertise.
- Environments needing quick, out-of-the-box solutions.
8. DeepBlue CLI
DeepBlueCLI is an open-source tool that analyzes Windows event logs automatically on Linux/Unix systems running ELK (Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana) or Windows (PowerShell version) (Python version).
DeepBlueCLI Key Features
- PowerShell script for analyzing Windows Event Logs.
- Detects suspicious command-line activity, lateral movement, and other anomalies.
- Provides summaries and visualizations of log data.
DeepBlueCLI Pros
- Simplifies the analysis of complex Windows Event Logs.
- Helps identify a wide range of malicious activities.
- Lightweight and easy to deploy
DeepBlueCLI Cons
- Limited to Windows environments.
- Requires familiarity with PowerShell for effective use.
Best Use Cases and Key Considerations
✅Best For:
- Organizations using Windows systems seeking efficient log analysis.
- Security teams aiming to detect anomalies in Windows Event Logs.
❌Not Ideal For:
- Non-Windows environments.
- Teams without PowerShell expertise.
9. CyberChef

CyberChef is a web-based app that can help you create binary and hex dumps, compress and decompress data, compute hashes and checksums, parse IPv6 and X.509, and more.
CyberChef Key Features
- Web-based tool for data analysis and manipulation.
- Offers a wide range of operations, including encoding/decoding, encryption/decryption, and data parsing.
- User-friendly interface with drag-and-drop functionality.
CyberChef Pros
- Versatile tool suitable for various data analysis tasks.
- No installation required. Accessible via web browser.
- Regularly updated with new features and operations.
CyberChef Cons
- Not specialized for threat-hunting; serves as a general-purpose tool.
- May require chaining multiple operations for complex tasks.
Best Use Cases and Key Considerations
✅Best For:
- Security analysts needing a flexible tool for data manipulation.
- Teams performing various encoding, decoding, and parsing tasks.
❌ Not Ideal For:
- Organizations seeking dedicated threat-hunting solutions.
- Users requiring automated threat detection capabilities.
10. Phishing Catcher

Phishing Catcher uses a YAML configuration file to assign a numeric score for strings that can be found in a TLS certificate’s common name or SAN field.
Phishing Catcher Key Features
- Monitors newly registered domains for phishing indicators.
- Analyzes SSL certificate data to identify suspicious patterns.
- Provides real-time alerts for potential phishing domains.
Phishing Catcher Pros
- Enhances proactive detection of phishing threats.
- Helps prevent phishing attacks before they impact users.
- Open-source and customizable.
Phishing Catcher Cons
- Focused solely on phishing; does not address other threat types.
- May generate false positives requiring manual verification.
Best Use Cases and Key Considerations
✅Best For:
- Organizations aiming to proactively monitor and block phishing domains.
- Security teams focused on preventing phishing attacks.
❌Not Ideal For:
- Comprehensive threat detection across multiple vectors.
- Environments without significant exposure to phishing risks.

- Granular telemetry across endpoints and networks.
- Equipped with built-in hunting and action capabilities.
- Pre-computed risk scores, indicators & detailed attack analysis.
- A single pane of glass for intelligence, hunting, and response.
Conclusion
These free, open-source tools can be combined for a robust, cost-effective defense against cyber threats.
Test them and decide if upgrading to a paid solution is necessary in your case.
Proactive threat hunting is a strategic battle – equipping yourself with the right tools ensures a stronger defense.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How does AI Engine help in threat hunting?
AI Engine analyzes network traffic in real-time, using deep packet inspection and customizable scripting to detect anomalies and potential threats before they escalate.
What makes APT-Hunter useful for threat detection?
APT-Hunter analyzes Windows event logs and maps suspicious activities to the MITRE ATT&CK framework, helping security teams detect and investigate Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs).
How does Attacker KB support security teams?
It provides community-driven intelligence on vulnerabilities, offering real-world exploitability insights that help security teams prioritize patches and defenses.
What type of threat intelligence does Automater provide?
Automater gathers OSINT (Open-Source Intelligence) on IP addresses, domains, and file hashes, helping analysts quickly assess potential threats.
How does BotScout prevent automated threats?
BotScout detects and blocks automated bots from creating fake accounts and submitting spam by comparing input data against a vast database of known bot signatures.
How does CrowdFMS help prevent phishing?
CrowdFMS automates the collection and analysis of phishing emails, helping organizations detect and respond to phishing threats more efficiently.
Why is Cuckoo Sandbox useful for malware analysis?
It provides a controlled environment where suspicious files can be executed and analyzed, revealing their behavior without risking a real system.
What is DeepBlue CLI’s primary function?
DeepBlue CLI is a PowerShell-based tool that analyzes Windows event logs to detect suspicious activities such as lateral movement and credential abuse.
How does CyberChef assist security analysts?
CyberChef is a versatile tool that simplifies data manipulation, allowing analysts to decode, decrypt, and analyze encoded data in an intuitive interface.
How does Phishing Catcher identify phishing threats?
It monitors newly registered domains and SSL certificate data to detect patterns commonly associated with phishing campaigns.
What sets Heimdal’s Threat-Hunting and Action Center apart?
It provides real-time threat monitoring, user behavior analytics, and faster incident response, all from a centralized dashboard.
If you liked this article, follow us on LinkedIn, Reddit, X, Facebook, and Youtube.










 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management  Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security











