Contents:
What is CryptoWall?
Cryptowall is a ransomware malware that encrypts files on an infected computer using and demands a ransom in exchange for a decryption key. Cryptowall is usually spread by spam and phishing emails, malicious ads, hacked websites, or other malware and uses a Trojan horse to deliver the malicious payload.
CryptoWall is an advanced piece of malware, a variant of the previous CryptoLocker, which has been taken down in 2015 by a number of security companies and state agencies across the world. Nevertheless, we all expected a comeback, which took place with CTB Locker followed by CryptoWall 3.0, which launched a massive attack on German users at the time.
How does it spread?
Like most data-stealing malware and ransomware, CryptoWall spreads mainly through phishing and spam campaigns that invite users to click a malicious link or access an e-mail attachment. At the same time, the cyber-criminals included CryptoWall code in websites ads in order to increase its online distribution.
You can find below an example of such an e-mail that is sent out to a number of users and which pretends to be an important invoice written in German.

When the user opens the e-mail, the targeted victim is asked to follow a link. If the victim clicks the link, the malicious payload from compromised domains will deliver the encryption tool to the system.
How does it work?
We will present shortly the main events that take place in the infection phase:
- The infection starts with an e-mail received by the victim, which contains a link that is connected to a number of compromised domains.
- When the potential victim follows the link, a downloader is placed on the system.
- The downloader connects to a number of domains controlled by hackers, from where it can download CryptoWall.
- One of the domains sends back and installs CryptoWall on the system.
- The ransomware encrypts the system data.
- A warning is presented on the screen with instructions on how to pay for the decryption key.
Differences between CryptoWall 3.0 and previous versions
Security analyst, Kafeine, presented in a blog post that one of the main differences between the CryptoWall 3.0 version and the previous ones is that communication with the C&C servers uses the RC4 encryption algorithm and it employs not just the TOR network, but also the I2P anonymity network, both of them being used mainly to conceal the identity of the user. Or cyber-criminals in our case. Apparently, CryptoWall 3.0 is the first version of this ransomware that used the I2P for communication purposes with the malicious servers. Another interesting difference is that CryptoWall presented localized messages towards the victim. In the example from Kafeine, we found that the ransomware could deliver the message in French or English.
CryptoWall 4.0
On a technical level, the code in this strain of CryptoLocker has been enhanced in several ways:
1. This new version possessed vastly improved communication capabilities. It included a modified protocol that enabled it to avoid being detected, even by 2nd generation enterprise firewall solutions. This lowered detection rates significantly compared to the already successful CryptoWall 3.0 attacks.
2. Malware creators have also made changes in the text message dropped on infected systems. The files were called:
HELP_YOUR_FILES.TXT
HELP_YOUR_FILES.HTML
HELP_YOUR_FILES.PNG
Here is an example of such a text:
C: \ Documents and Settings \ User \ Desktop \ HELP_YOUR_FILES.TXT
As you can see, the message used an obviously condescending tone. It also includes an FAQ with answers directed to the victim.
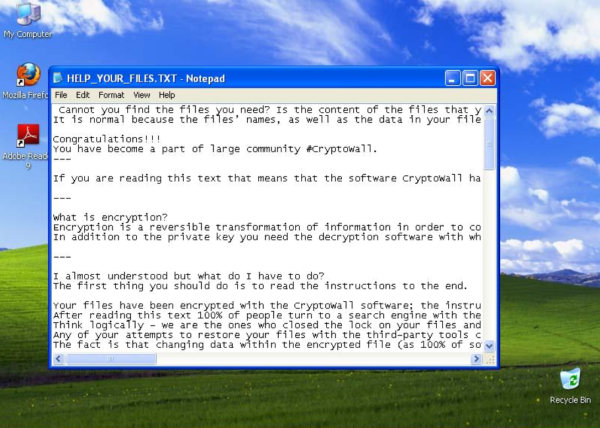
3. CryptoWall 4.0 now encrypts not only the data in your files, but the file names as well. This social engineering technique confuses the victims even more. It also enhances the pressure of wanting to retrieve their data as fast as possible. Consequently, this increases the “success” ratio of how many victims see the message versus how many pay the ransom. A clear business enhancement by cybercriminals.
How to stay protected from CryptoWall
Our security analysts recommend the following security measures to keep your computer safe from CryptoWall:
- Don’t access links in e-mails from people you don’t know. This is the main spreading method for CryptoWall.
- Don’t click links in e-mails you receive from unknown e-mail addresses.
- Create a Backup for your most important data. Keep the backup in a different location from your actual operating system. In case your system is infected with CryptoWall, you will not be able to access the backup.
- Make sure your security solution detects and blocks CryptoWall.
- Increase your online protection level by adjusting your web browser security settings.
- Keep your Windows operating system and your vulnerable software up-to-date with the latest security patches.
How does Heimdal Security keep you safe from Ransomware?
We, here at Heimdal Security, have developed an impressive suite of cybersecurity solutions to help you cover most of the possible ransomware attack vectors. From email security, antivirus and software patching to privileged access management, DNS security and a dedicated ransomware encryption protection solution. All integrated into a single agent and dashboard to deliver high visibility and protection against advanced cyberattacks.

Heimdal™ Ransomware Encryption Protection
- Blocks any unauthorized encryption attempts;
- Detects ransomware regardless of signature;
- Universal compatibility with any cybersecurity solution;
- Full audit trail with stunning graphics;
Conclusion
What we learned is that ransomware infections are feared by everybody, not only because you need to pay money for your data, but because you don’t know if you’ll be able to recover that information once you pay. And there is really little you can do when this happens. Therefore, we recommend that you pay attention to the received e-mails and the online locations you access because we are dealing with trained cyber-criminal minds that are only interested in economic and financial gains.










 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management  Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security








