Contents:
A privilege elevation flaw impacting the ImControllerService service in Lenovo laptops, including ThinkPad and Yoga models, enables cybercriminals to perform commands with admin rights.
According to BleepingComputer, the vulnerabilities are identified as CVE-2021-3922 and CVE-2021-3969 and impact the ImControllerService component of all Lenovo System Interface Foundation versions below 1.1.20.3. When visualizing the Windows services screen, this service has the display name “System Interface Foundation Service.”
Lenovo System Interface Foundation includes this particular service, which allows Lenovo laptops to connect with universal apps like Lenovo Companion, Lenovo Settings, and Lenovo ID.
The Lenovo System Interface Foundation Service provides interfaces for key features such as: system power management, system optimization, driver and application updates, and system settings to Lenovo applications including Lenovo Companion, Lenovo Settings and Lenovo ID.
If you disable this service, Lenovo applications will not work properly.
The vulnerabilities were spotted by NCC Group cybersecurity researchers, who communicated their discoveries to Lenovo laptops makers on October 29, 2021.
The security patches were released by the Chinese multinational technology company on November 17, 2021, and the relevant advisory was made public on December 14, 2021.
As explained by BleepingComputer, ImController runs with SYSTEM privileges because it needs to fetch and install files from Lenovo servers, perform child processes, and execute system setup and maintenance tasks.
SYSTEM privileges are the highest level of user rights in Windows, allowing you to run almost any command on the OS. In essence, gaining SYSTEM privileges in Windows gives a user full control over the system, allowing them to deploy malware, add users, and modify almost any system setting.
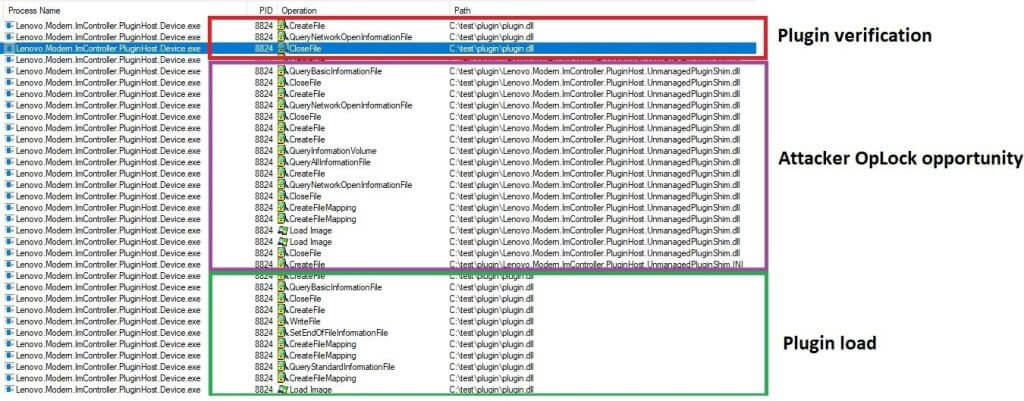
This Windows service will generate additional child processes, which will access named pipe servers used by the ImController service to connect with the child process. When ImController requires one of these services to carry out a command, it will communicate to the named pipe and issue XML serialized commands that should be performed.
Unfortunately, the service doesn’t handle the communications between privileged child processes securely and fails to validate the source of XML serialized commands. This means that any other process, even malicious ones, can connect to the child process to issue their own commands.
As a result, a threat actor exploiting this security gap can issue an instruction to load a ‘plugin’ from an arbitrary filesystem location.
The first vulnerability is a race condition between an attacker and the parent process connecting to the child process’ named pipe.
An attacker using high-performance filesystem synchronization routines can reliably win the race with the parent process to connect to the named pipe.
The second issue is a time-of-check to time-of-use (TOCTOU) flaw, which allows cybercriminals to block the loading of a verified ImControllerService plugin and change it with a DLL of their choice.
The DLL is run after the lock is removed and the loading process continues, resulting in privilege escalation.
What Can Be Done?
It is recommended that all Windows users with Lenovo laptops or desktops using ImController version 1.1.20.2 or older upgrade to the most recent version available (1.1.20.3).
Eliminating the ImController component, also known as the Lenovo System Interface Foundation, from your computer is not formally encouraged since it might impair certain of your device’s functions, even if it isn’t considered important.
Did you enjoy this article? Follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, Youtube, or Instagram to keep up to date with everything we post!










 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management  Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security








