Contents:
Following the cyberattacks that involved the Hive ransomware, the FBI (Federal Bureau of Investigation) has revealed some technical data and IoC (Indicators of Compromise) related to this topic.
Hive ransomware is a data encryption malware that has recently come to the public’s attention through its attacks targeting the Memorial Health System where employees had to use paper charts to go on working as their computers got encrypted. Another victim was also Altus Group, where hackers stole business info and files from the software provider that was later made public on HiveLeaks.
Hive Ransomware: How It Works
According to the document published by the FBI, Hive ransomware, which was initially noticed in June 2021, has the below characteristics:
- It can be distributed via compromised files through phishing emails and Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP).
- This way, hackers get initials access and then are able to perform the lateral movement on the network.
- As an attack pattern, the theft of the essential documents precedes the encryption routine in order to threaten the affected users with data leakage actions if the ransom is not paid.
- The cybercriminals behind it make the data encryption run smoothly by searching for processes that relate to the copying of information, backups, and security solutions (e.g. Windows Defender) in order to make them stop working.
- Then a hive.bat script is dropped: it erases the executable of the Hive ransomware and then deletes itself, thus engaging in a cleanup routine.
- Then the shadow.bat script has the role to remove backup files, shadow copies, and system snapshots. After doing this, it also erases itself.
- File-sharing services also make part of the cybercriminals’ arsenal: we can list here MEGA, Send.Exploit, SendSpace, Ufile or Anonfiles.
Hive Ransomware Attacks Related Files
According to BleepingComputer, among the files that hackers made use of in Hive ransomware attacks are Winlo.exe, useful in dropping 7zG.exe, the 19.0.0 of 7zG.exe, and also Winlo_dump_64_SCY.exe, remarked through the extension .KEY and the ransom note dubbed HOW_TO_DECRYPT.txt
An example of the ransom note can be seen below:
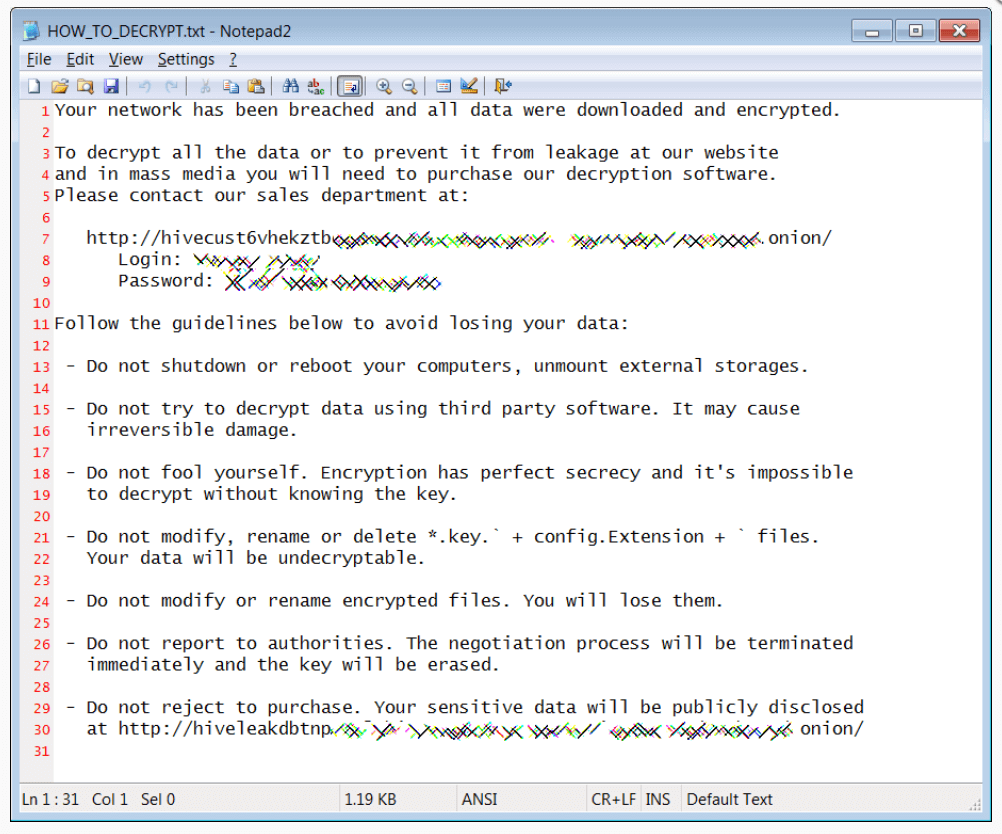
The FBI Note: Further Details
Even if it’s not a common practice when disclosing technical reports, the FBI also provided there the link to the website where data leakages are usually performed following Hive ransomware attacks. More exactly, cybercriminals reveal there the stolen info belonging to the organization that did not engage in paying the ransom.
In this regard, various victims were urged to pay the ransom:
The initial deadline for payment fluctuates between 2 to 6 days, but actors have prolonged the deadline in response to contact by the victim company.
Mitigation Measures Recommended
The overall advice from the Federal Bureau of Investigation mitigates for not paying the ransom, as cybercriminals are not trustworthy and there is no guarantee that the stolen info will not be further made use of.
Ransomware attacks should be reported by organizations to the local field office in a timely manner.
Other general mitigation measures include:
- The offline backup of the important data;
- The use of two-factor authentication;
- Make sure your systems and devices are up to date with the latest patches. This can be done through an efficient patch management process.


 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management
 Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security










