Contents:
The Exploit Prediction Scoring System (EPSS) is a data-driven tool highlighting what vulnerabilities hackers will likely exploit. EPSS was created by a group of experts at the Forum of Incident Response and Security Teams (FIRST).
Its purpose is to make it easier for security teams to prioritize vulnerability remediation better. Making a better choice of which vulnerabilities to close first is a key factor for effective patch management.
Key takeaways:
- How EPSS works
- Where do you get EPSS scores from
- EPSS vs CVSS
- The 5 steps of the EPSS process
- How can EPSS scores help prioritise vulnerabilities
How does the EPSS score calculator work?
The EPSS calculator is a machine-learning model that correlates and analyzes data from other systems.
To make it even clearer, EPSS also uses percentile rankings. The model compares each score to all the others, showing where it stands in the big picture.
This mix of probability and ranking helps you better prioritize what CVE to fix first.
When calculating a vulnerability`s score, the Exploit Prediction Scoring System uses the following data and sources:
- Vendor name
- Disclosure date, according to the MITRE CVE list
- Category labels that define it on the MITRE and NVD List
- Details in the description of the vulnerability on the MITRE CVE List
- Data about the weakness in the vulnerability, extracted from CWE, via NVD
- CVSS metrics from CVSS 3.x, via NVD
- Discussions about the CVE on websites like CISA KEV, Google Project Zero, and others
- Publicly available exploit code from databases like Exploit-DB, GitHub, MetaSploit
- Various security scanners.
The EPSS score ranges between 0 and 1 (0 to 100% exploitation chances) and refers to the following next 30 days.
The EPSS model – A five steps process
To analyze a vulnerability, the EPSS model goes through five steps:
Data gathering
The EPSS model collects information about the vulnerability from all the sources I mentioned above.
Close up look on exploitation
The model focuses on gathering evidence of daily exploitation activity from honeypots, IDS/IPS sensors and host-based detection measures.
Training the AI model
On this phase the machine analyzes the connection between the vulnerability features and its exploitation. EPSS uses machine learning to spot patterns in the collected data.
Optimization
The researchers measure how accurate the model is. After obtaining the results (predictions), they go back to training and optimizing the model. The four types of results they focus on are:
- True positives (TP)
- False positives (FP)
- False negatives (FN)
- True Negatives (TN)
Refresh
Now it`s time to do it all over. On a daily basis, researchers look for updates about the vulnerability. So, they basically repeat step 1.
Then they have to repeat the training (step 3), based on the new-found information. The result is a daily estimate of the probability that the analyzed CVE will be exploited in the next 30 days.
Why use the EPSS score in Risk analysis?
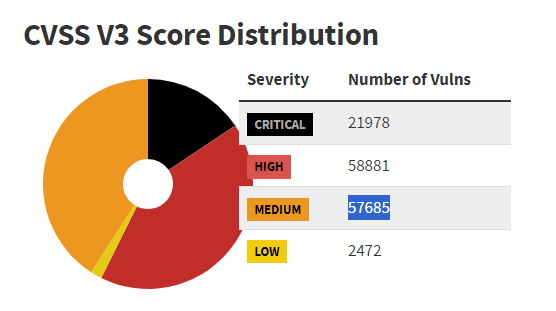
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) estimates most vulnerabilities as Medium to Critical severity level. A look on the National Vulnerability Database dashboard will show why Security Officers can`t use this scoring system alone to prioritize vulnerabilities.
Source – National Vulnerability Database
Out of the 141,016 CVEs assessed with CVSS V3, only 2,472 have a Low severity score. Another 57685 reported CVEs rank Medium, so the vast majority is of either High or Critical severity.
The CVSS data is not something you should ignore. However, it won`t help you get a manageable list of what flaws to patch first.
There are too many high and critical vulnerabilities to patch them all. So, how do you make a choice?
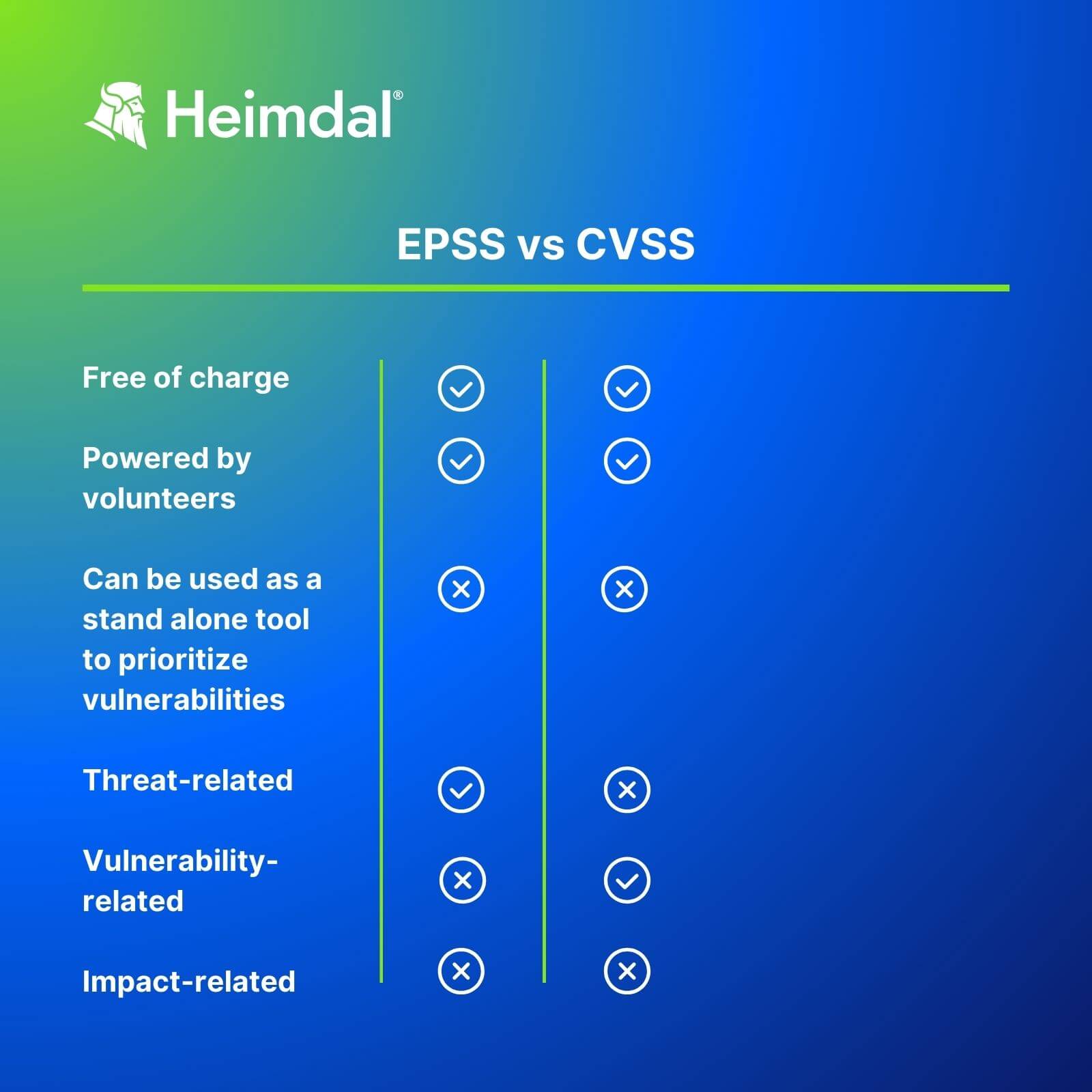
EPSS vs CVSS
Risk-Based Prioritization is high on the patch management best practices checklist. Use both EPSS and CVSS scores to better asses risk. EPSS is not meant to replace CVSS, but to work along it and improve the way you prioritize applying updates.
First, let’s focus on the differences of those vulnerability scoring systems.
Usually, for risk analysis, Security Officers use this formula Risk= Threat x Vulnerability x Impact. In this frame, the EPSS probability score deals with the Threat factor, while the CVSS evaluates the severity of the Vulnerability.
To indicate how serious is a flaw, CVSS scores use three sets of metrics: Base, Terminal, and Environmental. The scores are:
- Low – going from 0.1 to 3.9
- Medium – going from 4 to 6.9
- High – going from 7 to 8.9
- Critical – going from 9 to 10
EPSS scores, on the other hand, predict whether a vulnerability will be exploited in the next 30 days. To achieve that, the system uses a variety of data sources, including the CVSS. Its scores go from 0 to 1.
There are also some features that bring these scoring systems under the same umbrella.
Both are free to use and are powered by volunteer groups. Also, none of them reflects the impact of a vulnerability.
What else do EPSS and CVSS have in common? Both EPSS and CVSS scores aim to help Security Administrators in their vulnerability assessment and vulnerability management tasks. Use both to do a better job when deciding which flaw to address first in your network.
How can you use EPSS scores
You can use the EPSS scores as an initial vulnerability prioritization tool for the CVEs you detected in your environment. The values will show you what chances are that those specific CVEs will be exploited in the wild.
There are two ways to get EPSS scores:
- Download the daily CSV with all the CVEs from the data and statistics section on first.org. There’ also available a Top-rated CVEs display for the last 2, 30 and 90 days.
- Use the API that FIRST team members documented here.
I recommend you use this tool along with the CVSS scores and your regular vulnerability management solution.
Conclusions
Although the EPSS score adds valuable information, it doesn’t replace CVSS or a vulnerability assessment tool. Put it on your intelligence sources checklist, but make sure you use it along with other instruments to prioritize vulnerabilities.
Additionally, nothing can replace a well-done system inventory. At the end of the day, no matter how high the EPSS or CVSS scores are, you need to put things into context.
Ask yourself how exploitation of a CVE would impact businesses that activate in your sector. Is the potentially vulnerable asset in your system exposed online? What would be the attacker’s next step in case they succeed exploiting a certain vulnerability?
So, use available tools with an open mind, and don’t forget that, as always, context is key.

Heimdal® Patch & Asset Management Software
- Schedule updates at your convenience;
- See any software assets in inventory;
- Global deployment and LAN P2P;
- And much more than we can fit in here...
EPSS model FAQs
What is EPSS used for?
Security Officers use the Exploit Prediction Scoring System (EPSS) to better prioritize vulnerabilities and patching. EPSS predicts the probability of a CVE being exploited and thus helps detect high risk vulnerabilities.
How much does using EPSS cost?
Using EPSS scores is free. The EPSS model is built by security experts volunteers. It is a FIRST project.
What is EPSS percentile?
The EPSS percentile is a percentage score that shows how likely a vulnerability is to be exploited compared to others. For example, an 85% EPSS percentile suggests the vulnerability is more likely to be exploited than 85% of other analyzed CVEs.
Are EPSS enough for vulnerability prioritization?
EPSS scores predict whether hackers will exploit a vulnerability. They do not assess the severity of the vulnerability. You should use it along with CVSS scores or vulnerability management tools that integrate CVSS data.
What are the downsides of EPSS?
- EPSS only focuses on the probability of a flaw’s exploitation. It doesn’t consider other factors, like the system’s online accessibility. This is why you should use it along other scoring systems.
- Like any other machine-learning model, EPSS too can be biased.
The EPSS probability score can change daily, due to information updating. So, you need to keep an eye on how it evolves.
If you liked this article, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and Youtube, for more cybersecurity news and topics.


 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management
 Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security