Contents:
MountLocker is a Ransomware as a Service operation, RaaS, that started operating in July 2020.
In the RaaS business model, the developers are in charge of programming the ransomware software and payment site, and in order to create revenue, affiliates are recruited to hack and encrypt devices belonging to businesses.
MountLocker core team receives a smaller cut of 20-30% of a ransom payment and the affiliate gets the rest, as part of this arrangement.
In March 2021, ‘Astro Locker’ ransomware group emerged and started using a customized version of the MountLocker ransomware with ransom notes pointing to their own payment and data leak sites.
“It’s not a rebranding, probably we can define it as an alliance,” Astro Locker declared for the news publication BleepingComputer when questioned about their connection to MountLocker.
But Astro Locker is not the only ransomware group that uses a customized MountLocker ransomware executable, as in May 2021, a third group called ‘XingLocker’ also appeared on the market.
MalwareHunterTeam had recently shared a sample of what is believed to be a new MountLocker executable containing a new worm feature that allows it to spread and encrypt to other devices on the network, which seems to have been created especially for the XingLocker team.
An analysis ran by BleepingComputer showed that you could enable the worm feature by running the malware sample with the /NETWORK command-line argument, therefore coming to the conclusion that MountLocker is now using the Windows Active Directory Service Interfaces API as part of its worm feature.
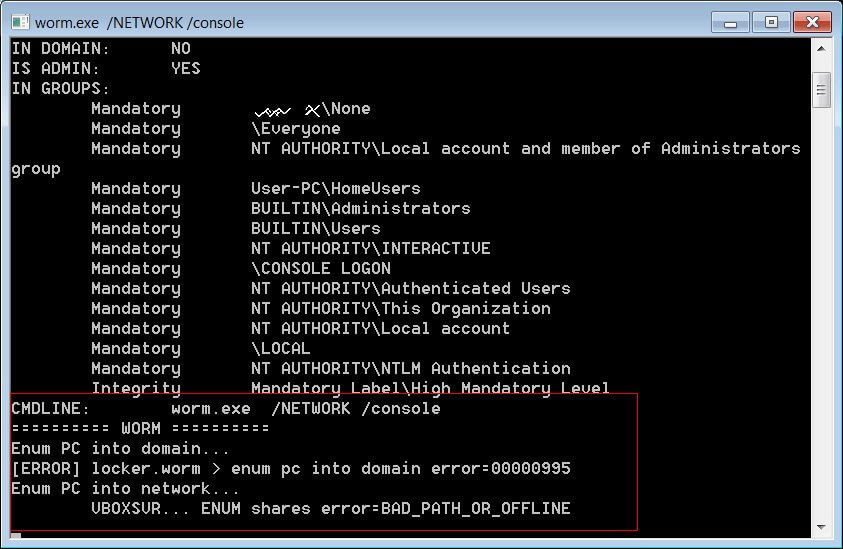
MountLocker ransomware first uses the NetGetDCName() function in order to retrieve the name of the domain controller, after this action is completed it performs LDAP queries against the domain controller’s ADS using the ADsOpenObject() function with credentials passed on the command line.
Once it managed to connect to the Active Directory services, it will iterate over the database for objects of ‘objectclass=computer’, and for each and every object it finds, it will attempt to copy the ransomware executable to the remote device’s ‘\C$\ProgramData’ folder, in order to then remotely create a Windows service able to load the executable so it can proceed to encrypt the device.
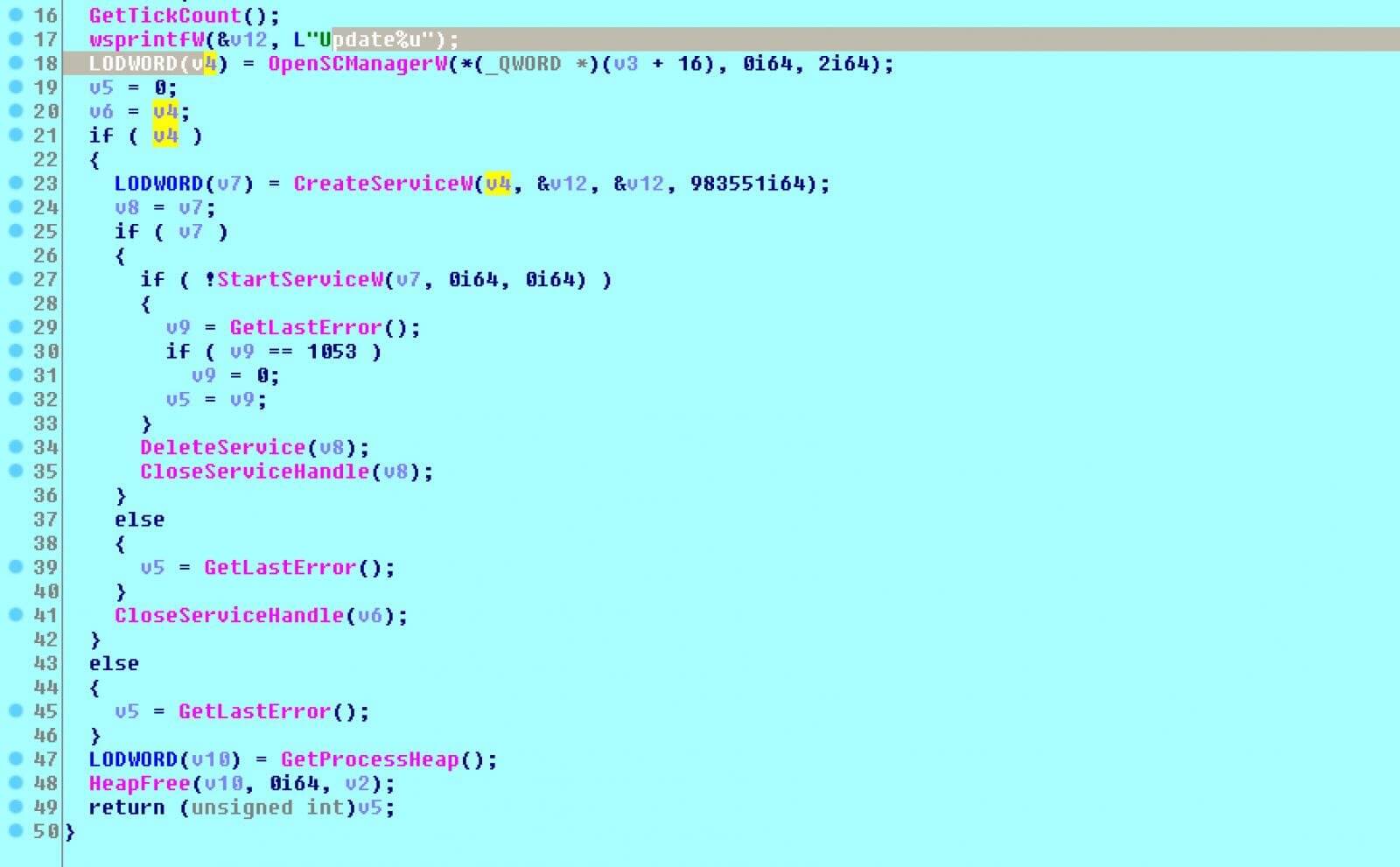
By making use of this API, the ransomware is able to locate all devices that are part of the compromised Windows domain and encrypt them by using the stolen domain credentials.
Many corporate environments rely on complex active directory forests and computers within them. Now MountLocker is the first known ransomware to leverage unique corporate architectural insight for the benefit of identifying additional targets for encryption operation outside of the normal network and share scan.
This is the quantum shift of professionalizing ransomware development for corporate network exploitation.
It’s interesting to note the fact that this API has been seen in other malware, such as TrickBot, but this may be the first corporate type ransomware for professionals that are using these APIs in order to perform built-in reconnaissance and spread to other devices.

Heimdal™ Ransomware Encryption Protection
- Blocks any unauthorized encryption attempts;
- Detects ransomware regardless of signature;
- Universal compatibility with any cybersecurity solution;
- Full audit trail with stunning graphics;










 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management  Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security








