Contents:
Apache HTTP Server users have been advised to patch as soon as possible as a zero-day bug in the open-source cross-platform web server software is actively being exploited in the wild. At this time, it seems that over 100.000 servers have been vulnerable to attacks.
A few days after the Apache HTTP Server developers were notified about the vulnerability, Apache Software Foundation released version 2.4.50 in order to address it.
Cybersecurity specialist Ash Daulton was the one who found and reported the flaw to Apache HTTP Server on September 29, 2021.
The vulnerability exploited in the wild is tracked as CVE-2021-41773 and, according to researchers, is a path traversal and file disclosure flaw in the previous version (2.4.49).
What Is Apache HTTP Server?
The Apache HTTP Server is a free and open-source cross-platform web server software, developed and maintained by an open community of developers under the guidance of the Apache Software Foundation.
Most of the open-source HTTP Server instances run on a Linux distribution but current versions also run on Microsoft Windows, OpenVMS, and a wide variety of Unix-like systems.
An attacker could use a path traversal attack to map URLs to files outside the expected document root. If files outside of the document root are not protected by ‘require all denied’ these requests can succeed. Additionally, this flaw could leak the source of interpreted files like CGI scripts.
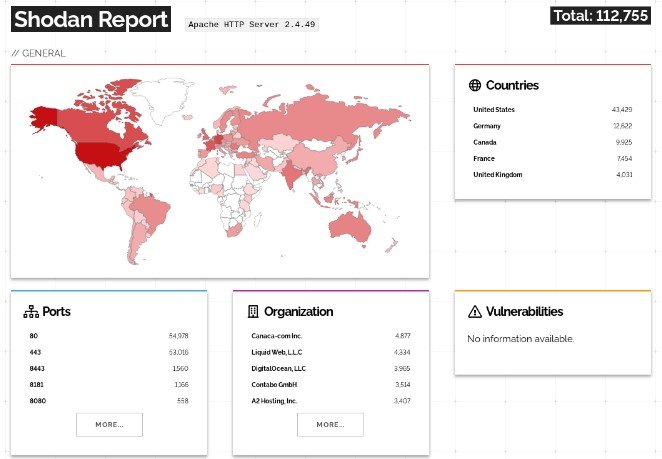
As we already mentioned, there are approximately 112,000 potentially exposed servers all over the world:
- United States (43,000)
- Germany (12,000)
- Canada (10,000)
- France (7,000)
- the United Kingdom (4,000)
This weakness does not affect previous Apache Server versions or those with a different access configuration.
Since its disclosure, security experts have been able to replicate the flaw and have advised administrators to update as soon as possible.
? We have reproduced the fresh CVE-2021-41773 Path Traversal vulnerability in Apache 2.4.49.
If files outside of the document root are not protected by “require all denied” these requests can succeed.
Patch ASAP! https://t.co/6JrbayDbqG pic.twitter.com/AnsaJszPTE
— PT SWARM (@ptswarm) October 5, 2021
It is still unknown how the vulnerability is being exploited in attacks. When asked about the incident, Apache said to BleepingComputer:
As Apache HTTP Server 2.4.49 was only released a few weeks ago it’s likely many users will not have upgraded yet. If and how this issue can be exploited is highly dependent on how users will have configured the server. If you are using 2.4.49, it is recommended that you upgrade to the latest version instead of using access control configuration as mitigation.
On a default installation, an attacker could still use the flaw to obtain the source code of interpreted files like CGI scripts.
The new Apache HTTP Server Version 2.4.50 also includes a patch for a null pointer dereference vulnerability that can be exploited for denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, CVE-2021-41524. The issue was discovered and fixed a few weeks ago, and there is no evidence that it had been used in malicious activities.










 Network Security
Network Security
 Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability Management
 Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management  Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security
 Threat Hunting
Threat Hunting
 Unified Endpoint Management
Unified Endpoint Management
 Email & Collaboration Security
Email & Collaboration Security








